1/20/00
advertisement

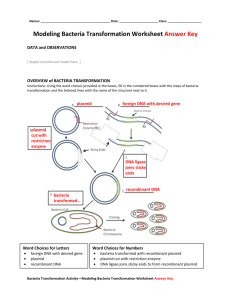
DNA Structure Today: 1) Set up PCR (p. 164) – do first - Quiz on this lab (RPP, PCR) will be Wednesday after Spring Break. 2) Recombinant paper plasmids (p. 189) For Monday: - Turn in page 190 (maps, showing ALL restriction sites) and tell what enzyme you chose. - Turn in completed recombinant plasmid (with chromosomal DNA inserted). - For each part of the lab, understand what we did (methods) and why. Background: Bacteria have a single, circular chromosome. Some bacteria also have plasmids: a small circular piece of DNA carrying only a few genes. - They aren't essential for survival, but they often help. - Ex. some give the bacteria resistance to antibiotics. As we saw before with the bacteriophages, some viruses can inject their genes into bacteria, turning them into virus-producing factories. Over time, bacteria have developed weapons against such DNA invasions. These are called restriction enzymes: enzymes that recognize and cut up foreign DNA. - They always cut at specific (& symmetric) base sequences. - Discovered in the late 1960s: a big advance (now > 3000 have been identified). - Researchers have learned to use these enzymes to produce DNA fragments. - These can be used to make a DNA “fingerprint.” - They can also be used to make recombinant DNA. Part 1: PCR (See lab manual page 163) Part 2: Recombinant Paper Plasmids (page 189): Our goal is to cut out a piece of chromosomal DNA that codes for the production of a protein and then insert it into a bacterial plasmid. Cut plasmid DNA strips (p. 191) and tape them together in any order, then make a circle. Cut chromosomal DNA strips (p. 193) and tape together in the order in which they are given so that the protein gene is intact (rows 2-4). There are several possible restriction enzymes to choose from (p. 195) and you need to pick the most appropriate one for your particular plasmid and chromosomal DNA. - Locate all the restriction sites on both of your DNA pieces and mark them on the map provided (page 190). Remember they cut at ALL available restriction sites. - Determine which enzyme to use. We must not cut the origin of replication or the protein-coding region, and we want to cut one of the antibiotic resistance sites. - Cut at all the sites and make your recombinant plasmid. Turn this in on Monday.