Study Guide-Unit A Earth*s Layers
advertisement

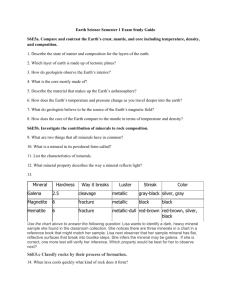
Study Guide-Formative Test 1 2011 My Test is on ____________________ 6.E.2.1 Layers and Density (most dense and least dense) A. On the drawing of the Earth below, label the 4 layers of the Earth B. Number the layers 1-4 from MOST to LEAST dense. (1 is most dense, 4 is least) d. 1. What is layer D? 2. How does density relate to the layers of Earth? 6.E.2.1 Convection Currents (Hot material and cold material) 3. Describe a convection current. 4. What causes convection currents? 5. What do convection currents cause? 6.E.2.2 Tectonic Plate Movement: Label the 3 types of boundaries →← _____________________________ ↑↓ _____________________________ ←→ 6. At which plate boundary does new crust form? _____________________________ 7. If tectonic plates stopped moving, what would happen to volcanoes and earthquakes? 6.E.2.2 Geologic Formations (earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountains) 8. Which geologic formations can occur at a convergent plate boundary? Ocean + Continental Crust: ____________________________ Continental + Continental Crust: ____________________________ 9. Where do earthquakes occur (what type of boundaries)? 6.E.2.2 Maps 10. The boundary at point A is the same as the B boundary at point C. What type of boundary is at A and C? _______________________ -Explain what geologic formations will happen at A? C A -What geologic formations will happen at C? -Why will these A and C have different geologic activity even though they are the same type of boundary? 11. Where are earthquakes and volcanoes most often located? 12. Why do you think there are so few earthquakes in North Carolina? 13. What will happen when all the inner core heat energy is lost? (Think about convection currents) 14. Based on this map, where would you expect to find a plate boundary (Area A, B, C or D) and WHY? 15. Where are earthquakes and volcanoes most often located? a. center of crustal plates b. edges of crustal plates c. center of continents d. edges of continents 6.E.2.3 Weathering and Soil Formation The picture below shows how a type of rock forms at the bottom of the ocean. What type of rock is this? a) b) c) d) Soil is a mixture of what? a. water and minerals b. water, minerals, and organic matter c. water and organic matter d. water, minerals, air, and organic matter Soil is useful for a. absorbing water and nutrients b. supporting buildings c. supporting all life d. all of the above Which of the following is a type of soil? a. Topsoil b. Sand c. Clay d. All of the above are types of soil What is the difference between soil and dirt? Which of the following is NOT a type of soil? a. Topsoil b. Sand c. Clay d. Dirt What is the soil horizon? a. Layers of soil on top of each other b. Different types of soil in different parts of the country c. Properties of soil d. How much water different types of soil absorb Lava Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock Which type of soil absorbs the LEAST water? a. Topsoil b. Sand c. Clay d. Dirt 6.E.2.3 Rocks and Minerals A property of a mineral, the color of the powder a mineral leaves when it is scratched on a surface. a. Luster b. Hardness c. Cleavage d. Streak A measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched a. Luster b. Hardness c. Cleavage d. Streak The way a mineral shines, or reflects light a. Luster b. Hardness c. Cleavage d. Streak When a mineral breaks with jagged edges a. Cleavage b. Fracture c. Texture d. Breakage Which mineral is the hardest? a. Talc b. fingernail c. topaz d. diamond Which mineral will apatite scratch? a. calcite b. quartz c. corundum d. feldspar A solid, non-living material that is made up of one or more minerals a. mineral b. soil c. rock d. crust What is the difference between rocks and minerals? a. b. c. d. Minerals were never living and rocks used to be living Rocks are mixtures of minerals Rocks have a crystal structure and minerals do not have crystals All of the above are correct The rock cycle is: a. How rocks are formed b. How rocks multiply c. How rocks change over time d. The properties of rocks What are sand, bits of rock, soil, and remains of plants and animals? a. Sediment b. Soil c. Minerals d. Rocks What type of rock forms from the cooling and hardening of magma? a. igneous b. metamorphic c. sedimentary d. all of the above What type of rock forms when rocks exposed to heat and pressure? a. igneous b. metamorphic c. sedimentary d. all of the above Use the diagram below to answer the next two questions: IGNEOUS SEDIMENTARY Which part of the rock cycle is happening at number 1? a. Melting, Cooling, Hardening b. Weathering, Erosion, Compacting c. Heat and Pressure Which part of the rock cycle is happening at number 2? a. Melting, Cooling, Hardening b. Weathering, Erosion, Compacting c. Heat and Pressure METAMORPHIC 6.L.2.1 Energy flow and Natural Cycles 1. List 3 Abiotic Factors 2. List 3 Biotic Factors 3. Name the four substances that are cycled between the living and non-living environments 6.L.1.2 Photosynthesis 1. What is photosynthesis? 2. What are 3 things chlorophyll in a plant NEEDS to perform photosynthesis (ingredients)? 3. What are 3 things chlorophyll MAKES when it performs photosynthesis (product or output)? 4. Can photosynthesis occur without sunlight? EXPLAIN YOUR ANSWER!