California`s Mineral, Energy, and Soil Resources
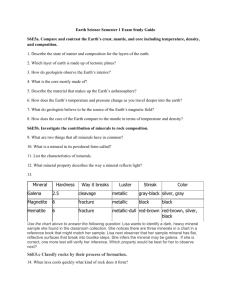
advertisement

California’s Mineral, Energy, and Soil Resources Chapter 13A, Section 1 Geology of California • Some of the features of the California landscape formed as the result of tectonic processes that took place deep beneath the surface • Wind, water, ice, and other agents of erosion at the surface carved other features of the landscape • Millions of years ago, the subduction of an oceanic plate beneath the North American plate forming large pools of magma and later crystallizing • Uplift and erosion eventually exposed these batholiths to form the Sierra Nevada Mountains • Surface processes formed places like the Central Valley (used to be an inland sea) California’s Mineral Resources • California’s major mineral resources include sand, gravel, crushed stone, building stone, gold, silver, iron, evaporite minerals, and clay • Sand and gravel are California’s most valuable industrial minerals, used in road-building and construction • Gold, silver, and iron are the major metallic minerals mined in California • The most productive gold mines include the Sierra Nevada, the Klamath Mountains, and the Mojave Desert • Silver is mined in the Sierra Nevada • Iron is from the Mojave desert region • We also have an abundance of non-metallic minerals, including: borates, gypsum, and clay • Small quantities of gemstones, such as tourmaline, garnet, agate, and jade California’s Mineral Resources Concept Check • What does the term mineral resources mean? • Natural resources that include minerals, rocks, and sediment California’s Energy Resources • California’s major energy resources—oil, natural gas, and geothermal energy—are the result of geologic processes that occur deep beneath the surface • Source Rocks – rocks in which oil forms • Reservoir Rocks – porous rocks in which oil collects and becomes trapped • Geothermal Field – an area of land where magma lies relatively close to the surface and heats the groundwater Geothermal Energy Concept Check • What is a geothermal field? • An area where magma that is close to the surface heats the groundwater. California’s Soil Resources • The soils of California include soils of the Sierras, soils of the Coast Ranges and Cascades, valley soils (including the Central Valley), and desert soils • CA’s fertile valley soils are its most important soil resource • In northern CA, heavy rains wash away the nutrients from the soil • In southern CA, the soils contain more nutrients, due to the small amount of rainfall • Every year, many acres of farmland are lost or damaged because of soil erosion or the spread of urban areas • It can take over 500 years to build up 2.5 cm of soil California’s Soil Resources Assignment • Read Chapter 13A (pg. CA 4 – CA 26) • Ch 13 Assessment – # 1 – 33 (pg. CA 31 – CA 32) – # 1 – 6 (pg. CA 33)