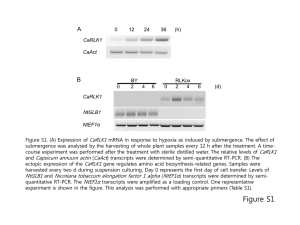
Supplementary Table S1 Literature data on QTLs detected on
advertisement

Supplementary Table S1 Literature data on QTLs detected on pepper chromosome P5 for resistance to P. capsici Reference Lefebvre and Palloix (1996) (a) Thabuis et al. (2003) Thabuis et al. (2004a) Thabuis et al. (2004b) Ogundiwin et al. (2005) Sugita et al. (2006) Bonnet et al. (2007) Minamiyama et al. (2007) Kim et al. (2008) Truong et al. (2012) Resistant parent Perennial Mapping progeny (d) 114 DH (PY) P. capsici isolate Name Origin Pc101 (e) France QTL name Linked markers LOD score Vania (b) Perennial 101 DH (HV) 114 DH (PY) Pc101 (e) Pc101 (e) France France CM334 151 F2 (F2YC) Pc197 (e) France CM334 450 BC (Morelos) Pc101 (e) Perennial 620 BC (BC1S1(DH285)) PI201234 94 RIL F7 (PSP-11xPI201234) CM334 AC2258 (b) CM334 94 F2 (JoeE.ParkerxCM334) 176 DH (K9-11xAC2258) 297 RIL F5 (F5YC) CM334 96 DH (ManganjixCM334) CM334 YCM334 (c) NA Confidence interval NA NA TG483 France Pc5.1 Pc5.1 Pc5.2 Pc5.1 Pc5.2 Phyto.5.2 Pc101 (e) France PC17E GPS1-1 M Keihoku Pc197 (e) Taiwan California New Mexico Japan France P-5 Japan 100 F2 (CM334xChilsungcho) Pa23 South Korea 126 RIL F8 (YCM334 x Tean) 09-051 South Korea 07-127 South Korea R² 41 to 55% 6.9 to 26.0 2.3 to 24.9 3.4 to 6.4 4.4 to 35.7 15.3 NA NA NA NA NA NA NA 17 to 54% 10 to 74% 6 to 26% 21 to 70% 42% 16% Pc5.1 E38M61-139 E43M53-159 E33M53-Cp E43M53-159 E36M47-183 E38M61-249/E38M61220 E43M53-159/ASC037 NA NA 71% Phyto-P Phyto-P Phyto-U Phyt-1 Pc5.1 Pc5.2 NA H03b909/Hpms2-23 H03b909/Hpms2-23 J12b1480/E33M49-434 M10E3-6 Mfvt_M02 E41M61-348 CAMS420 2.5 4.3 6.2 67.0 14.3 to 33.9 11.5 10.6 to 16.1 7.0 cM 7.0 cM 42.3 cM 85.0 cM 10.0 cM 5.0 cM NA 16% 22% 35% 83% 20 to 53% 24% 40 to 58% NA NA Ph051-5.1 Ph051-5.2 Ph051-5.3 Ph051-5.4 Ph0127-5.5 Ph0127-5.6 Ph0127-5.7 HpmsE015/pR5_93 CDI78/CDI25 a015_7/a133_4 a133_4/a170_1 a015_7/a133_4 a133_4/a170_1 a057-6/a133_4 a133_4/a170_1 a057_6/a119_7 2.2 to 2.4 4.6 to 10.5 7.1 13.4 8.3 15.4 16.6 21.6 20.6 30.0 cM 9.3 cM 8.6 cM 8.4 cM 8.1 cM 8.3 cM 4.1 cM 6.2 cM 4.7 cM 8 to 9% 19 to 42% 20% 34% 22% 37% 40% 47% 48% NA: Not available (a) While this QTL was not linked to any chromosome by Lefebvre and Palloix (1996), the linked RFLP marker TG483 was later mapped to chromosome P5 (Lefebvre et al. 2002). (b) Thabuis et al. (2003) indicated that Vania was issued from a recurrent selection including in its genealogy PM217 that is derived from PI201234. Sugita et al. (2006) indicated that AC2258 was derived from PI201234. (c) YCM334 is an F6 RIL derived from the cross Yolo Wonder x CM334 developed at INRA Montfavet France (Bonnet et al. 2007). (d) Progeny size, population type (DH: doubled haploids, RIL: recombinant inbred lines, F2: second generation progeny, BC: backcross progeny), name of the cross in brackets. (e) Names of INRA strains were formerly S101 and S197. 1 Supplementary Table S2 Resistance/susceptibility allele configuration at QTL Pc5.1 for resistance against P. capsici in the 19 progeny lines and parental lines assessed for the resistance spectrum Plant Genotype CM334 YW F6YC-009 F6YC-017 F6YC-034 F6YC-038 F6YC-055 F6YC-125 F6YC-247 F6YC-277 Vania H3 HV-021 HV-023 HV-038 HV-040 HV-057 HV-122 Perennial YW PY-238 PY-253 PY-255 PY-260 PY-279 Pc5.1 R S R R S R S R R R R S S R R S R S R S S S R R S R: alleles of the markers within the QTL CI are associated with resistance in the progeny. S: alleles of the markers within the QTL CI are associated with susceptibility in the progeny. 2 Supplementary Table S3 List of pepper maps included in the chromosome P5 consensus map (a) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Map identifier AC99-1 PY HV F5YC CC TH-1 TH-2 KA MC AC99-2 FA03-1 YCT JC FA03-2 Parental cross C. annuum cv. “NuMex RNaky” x C. chinense PI 159234 C. annuum Perennial x C. annuum CM334 C. annuum H3 x C. annuum Vania C. annuum cv. "Yolo Wonder" x C. annuum CM334 C. annuum CM334 x C. annuum Chilsungcho C. annuum cv. "TF68" x C. chinense cv. "Habanero" C. annuum cv. "TF68" x C. chinense cv. "Habanero" C. annuum K9-11 x C. annuum cv. "AC2258" C. annuum cv. "Manganji" x C. annuum CM334 C. annuum cv. "NuMex RNaky" x C. chinense PI 159234 C. annuum cv. "NuMex Rnaky" x C. frutescens BG 2814-6 C.annuum YCM334 RIL F6 x C.annuum cv. "Tean" C. annuum cv. "JEP" x C. annuum CM334 C. annuum cv. "NuMex Rnaky" x C. frutescens BG 2814-6 Cross type (b) Progeny size Number of markers from chromosome P5 F2 DH DH RIL F5 F2 F2 F2 DH DH F2 F2 RIL F8 F2 F2 75 114 101 297 100 107 107 176 96 100 100 126 94 94 11 21 20 43 10 14 13 24 8 16 (c) 27 (c) 16 5 25 (c) Reference (Livingstone et al. 1999; Quirin et al. 2005) (Lefebvre and Palloix 1996; Thabuis et al. 2003); this paper (Thabuis et al. 2003); this paper (Barchi et al. 2007); this paper (Kim et al. 2008) (Yi et al. 2006) (Lee et al. 2004) (Sugita et al. 2006) (Minamiyama et al. 2007) Sol Genomic Network Sol Genomic Network; (Rao et al. 2003) (Truong et al. 2012) (Ogundiwin et al. 2005; Quirin et al. 2005) (Wu et al. 2009) (a) Order of projection: the markers on individual maps of chromosome P5 were iteratively projected onto the reference P5 map of Livingstone et al. (1999) in the order presented in this table. (b) F2: second generation progeny, DH: doubled haploids, RIL: recombinant inbred lines. (c) We used only markers that were regularly distributed and improved the anchorage between maps of chromosome P5 containing resistance QTLs to P. capsici. 3 4 Supplementary Figure S1 UWNJ phenetic tree reflecting genomic similarities between the four P. capsici isolates, Pc101, Pc107, Pc197 and Pc204, based on the Jaccard coefficient using 97 AFLP markers and 28 SSR markers Root branching of the outgroup is indicated by the point on the main branch. Bootstrap values are shown. 5