AP English Language
advertisement
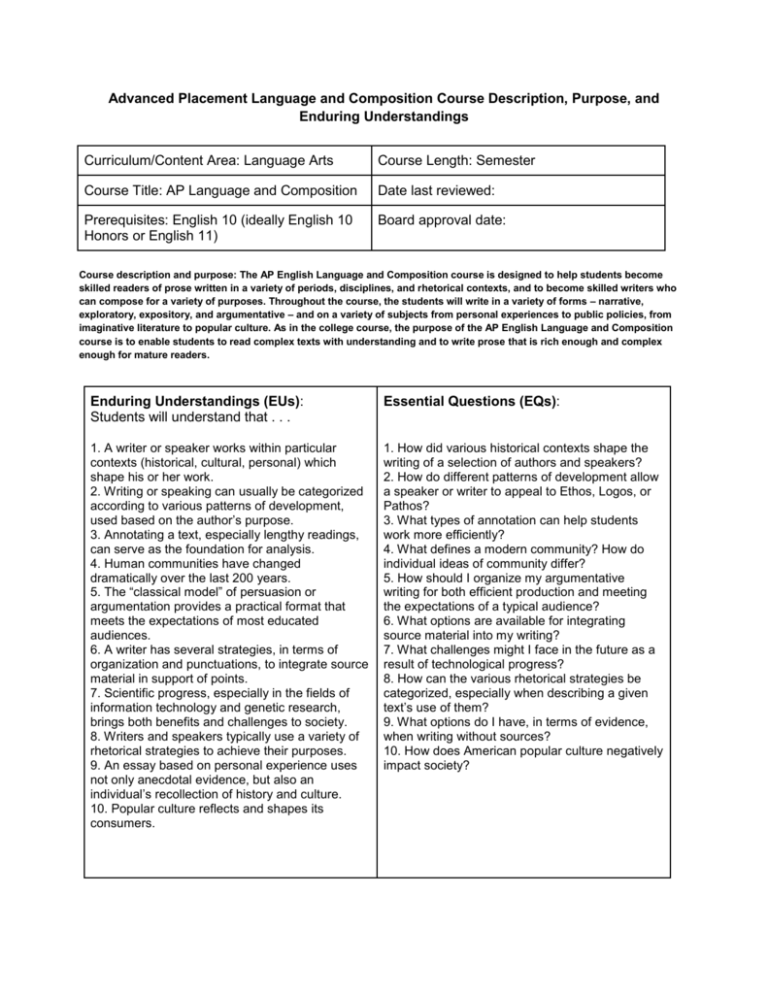
Advanced Placement Language and Composition Course Description, Purpose, and Enduring Understandings Curriculum/Content Area: Language Arts Course Length: Semester Course Title: AP Language and Composition Date last reviewed: Prerequisites: English 10 (ideally English 10 Honors or English 11) Board approval date: Course description and purpose: The AP English Language and Composition course is designed to help students become skilled readers of prose written in a variety of periods, disciplines, and rhetorical contexts, and to become skilled writers who can compose for a variety of purposes. Throughout the course, the students will write in a variety of forms – narrative, exploratory, expository, and argumentative – and on a variety of subjects from personal experiences to public policies, from imaginative literature to popular culture. As in the college course, the purpose of the AP English Language and Composition course is to enable students to read complex texts with understanding and to write prose that is rich enough and complex enough for mature readers. Enduring Understandings (EUs): Students will understand that . . . Essential Questions (EQs): 1. A writer or speaker works within particular contexts (historical, cultural, personal) which shape his or her work. 2. Writing or speaking can usually be categorized according to various patterns of development, used based on the author’s purpose. 3. Annotating a text, especially lengthy readings, can serve as the foundation for analysis. 4. Human communities have changed dramatically over the last 200 years. 5. The “classical model” of persuasion or argumentation provides a practical format that meets the expectations of most educated audiences. 6. A writer has several strategies, in terms of organization and punctuations, to integrate source material in support of points. 7. Scientific progress, especially in the fields of information technology and genetic research, brings both benefits and challenges to society. 8. Writers and speakers typically use a variety of rhetorical strategies to achieve their purposes. 9. An essay based on personal experience uses not only anecdotal evidence, but also an individual’s recollection of history and culture. 10. Popular culture reflects and shapes its consumers. 1. How did various historical contexts shape the writing of a selection of authors and speakers? 2. How do different patterns of development allow a speaker or writer to appeal to Ethos, Logos, or Pathos? 3. What types of annotation can help students work more efficiently? 4. What defines a modern community? How do individual ideas of community differ? 5. How should I organize my argumentative writing for both efficient production and meeting the expectations of a typical audience? 6. What options are available for integrating source material into my writing? 7. What challenges might I face in the future as a result of technological progress? 8. How can the various rhetorical strategies be categorized, especially when describing a given text’s use of them? 9. What options do I have, in terms of evidence, when writing without sources? 10. How does American popular culture negatively impact society?