M_8thGr_1st_6wks_GPS_1112 - Curriculum
advertisement
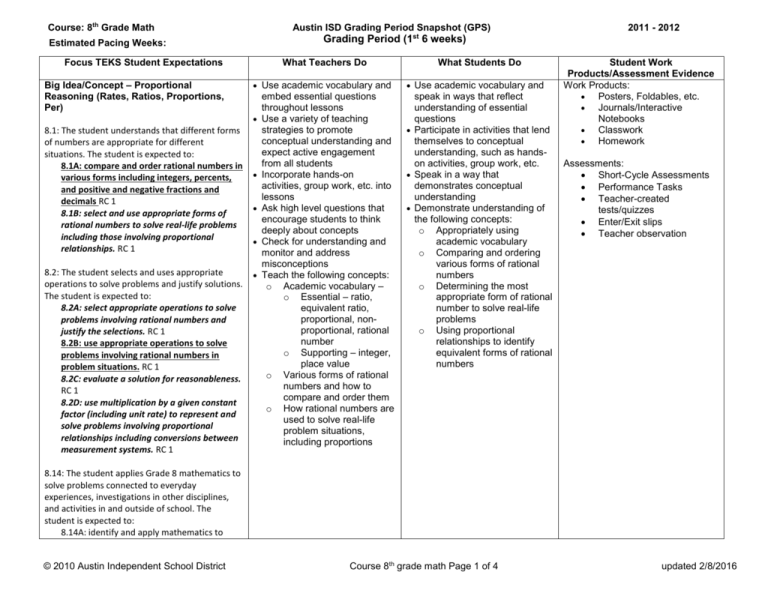
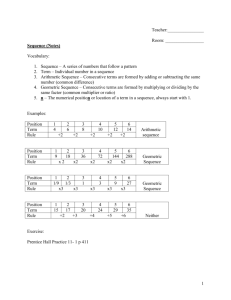
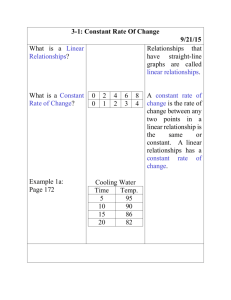
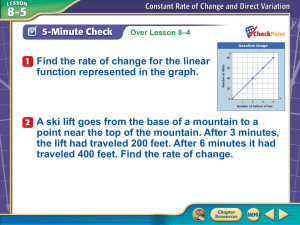
Course: 8th Grade Math Austin ISD Grading Period Snapshot (GPS) Grading Period (1 6 weeks) Estimated Pacing Weeks: Focus TEKS Student Expectations Big Idea/Concept – Proportional Reasoning (Rates, Ratios, Proportions, Per) What Teachers Do Use academic vocabulary and 8.1: The student understands that different forms of numbers are appropriate for different situations. The student is expected to: 8.1A: compare and order rational numbers in various forms including integers, percents, and positive and negative fractions and decimals RC 1 8.1B: select and use appropriate forms of rational numbers to solve real-life problems including those involving proportional relationships. RC 1 8.2: The student selects and uses appropriate operations to solve problems and justify solutions. The student is expected to: 8.2A: select appropriate operations to solve problems involving rational numbers and justify the selections. RC 1 8.2B: use appropriate operations to solve problems involving rational numbers in problem situations. RC 1 8.2C: evaluate a solution for reasonableness. RC 1 8.2D: use multiplication by a given constant factor (including unit rate) to represent and solve problems involving proportional relationships including conversions between measurement systems. RC 1 2011 - 2012 st embed essential questions throughout lessons Use a variety of teaching strategies to promote conceptual understanding and expect active engagement from all students Incorporate hands-on activities, group work, etc. into lessons Ask high level questions that encourage students to think deeply about concepts Check for understanding and monitor and address misconceptions Teach the following concepts: o Academic vocabulary – o Essential – ratio, equivalent ratio, proportional, nonproportional, rational number o Supporting – integer, place value o Various forms of rational numbers and how to compare and order them o How rational numbers are used to solve real-life problem situations, including proportions What Students Do Use academic vocabulary and speak in ways that reflect understanding of essential questions Participate in activities that lend themselves to conceptual understanding, such as handson activities, group work, etc. Speak in a way that demonstrates conceptual understanding Demonstrate understanding of the following concepts: o Appropriately using academic vocabulary o Comparing and ordering various forms of rational numbers o Determining the most appropriate form of rational number to solve real-life problems o Using proportional relationships to identify equivalent forms of rational numbers Student Work Products/Assessment Evidence Work Products: Posters, Foldables, etc. Journals/Interactive Notebooks Classwork Homework Assessments: Short-Cycle Assessments Performance Tasks Teacher-created tests/quizzes Enter/Exit slips Teacher observation 8.14: The student applies Grade 8 mathematics to solve problems connected to everyday experiences, investigations in other disciplines, and activities in and outside of school. The student is expected to: 8.14A: identify and apply mathematics to © 2010 Austin Independent School District Course 8th grade math Page 1 of 4 updated 2/8/2016 Course: 8th Grade Math Estimated Pacing Weeks: Focus TEKS Student Expectations Austin ISD Grading Period Snapshot (GPS) 2011 - 2012 st Grading Period (1 6 weeks) What Teachers Do What Students Do Student Work Products/Assessment Evidence everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics. DC 8.15: The student communicates about Grade 8 mathematics through informal and mathematical language, representations, and models. The student is expected to: 8.15A: communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models. DC © 2010 Austin Independent School District Course 8th grade math Page 2 of 4 updated 2/8/2016 Course: 8th Grade Math Austin ISD Grading Period Snapshot (GPS) 2011 - 2012 st Grading Period (1 6 weeks) Estimated Pacing Weeks: Note: Numbers do not equate priority Focus TEKS Student Expectations Big Idea/Concept – Proportional Reasoning (Rates, Ratios, Proportions, and Percents Multiple Representations of Linear Relationships) 8.3: The student identifies proportional or nonproportional linear relationships in problem situations and solves problems. The student is expected to: 8.3A: compare and contrast proportional and non-proportional linear relationships. RC 2 8.3B: estimate and find solutions to application problems involving percents and other proportional relationships such as similarity and rates. RC 2 8.4: The student makes connections among various representations of a numerical relationship. The student is expected to: 8.4A: generate a different representation of data given another representation of data (such as a table, graph, equation, or verbal description). RC 2 8.5: The student uses graphs, tables, and algebraic representations to make predictions and solve problems. The student is expected to: 8.5A: predict, find, and justify solutions to application problems using appropriate tables, graphs, and algebraic equations. RC 2 8.5B: find and evaluate an algebraic expression to determine any term in an arithmetic sequence (with a constant rate of change). RC 2 © 2010 Austin Independent School District What Teachers Do Use academic vocabulary and embed essential questions throughout lessons Use a variety of teaching strategies to promote conceptual understanding and expect active engagement from all students Incorporate hands-on activities, group work, etc. into lessons Ask high level questions that encourage students to think deeply about concepts Check for understanding and monitor and address misconceptions Teach the following concepts: o Academic vocabulary – o Essential –linear relationship, independent variable, dependent variable, rate of change, constant rate of change, proportional relationship, nonproportional relationship, arithmetic sequence, term, position, nth term o Supporting – table of values, coordinate graph, coordinate pair o Similarities and differences between proportional and nonproportional linear relationships What Students Do Use academic vocabulary and speak in ways that reflect understanding of essential questions Participate in activities that lend themselves to conceptual understanding, such as handson activities, group work, etc. Speak in a way that demonstrates conceptual understanding Demonstrate understanding of the following concepts: o Appropriately using academic vocabulary o Use graphs, tables, equations, verbal descriptions to determine if a relationship is proportional or nonproportional o Solving real-world application problems involving rate and percents o Create representations of data using tables, graphs, equations, verbal descriptions o Write and use algebraic sequences Course 8th grade math Page 3 of 4 Student Work Products/Assessment Evidence Work Products: Posters, Foldables, etc. Journals/Interactive Notebooks Classwork Homework Assessments: Short-Cycle Assessments Performance Tasks Teacher-created tests/quizzes Enter/Exit slips Teacher observation updated 2/8/2016 Course: 8th Grade Math Austin ISD Grading Period Snapshot (GPS) 2011 - 2012 st Grading Period (1 6 weeks) Estimated Pacing Weeks: Focus TEKS Student Expectations What Teachers Do o o o What Students Do Student Work Products/Assessment Evidence Rates, unit rates, percents How to represent the same set of data in tables, graphs, equations, verbal descriptions Arithmetic sequences and constants rates of change Note: Numbers do not equate priority © 2010 Austin Independent School District Course 8th grade math Page 4 of 4 updated 2/8/2016