Final Review Questions
advertisement

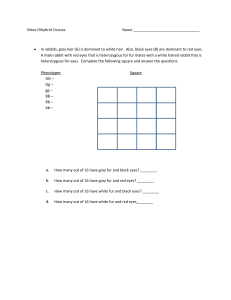
AP Bio Final Part 2 Practice Questions 1. According to the competitive exclusion principle no two species can occupy the same niche. Define an ecological niche. Provide two ways in which two similar species of woodpecker may still live and thrive in the same region of a habitat. Scientists are sure that these are two separate species. According to the biological species concept describe two barriers that might exist to prevent hybridization of these species. 2. Water is often cited as the most important molecule of life. Describe the bonds that hold single water molecule together and the type of bonding that occurs between water molecules. Define and describe two properties of water molecules that make it an excellent source of temperature control and/or a medium to support life. 3. We describe 4 major classifications of biochemical molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Pick one of these 4 categories and describe the most simple functional unit (monomer), identify how there can be variation in these basic subunits, define and describe the chemical reaction that takes place in order to link monomers of your chosen category together. Justify the important biological functions of the chosen category in order, citing examples. 4. Compare eukaryotes and prokaryotes, citing at least 2 distinctions. Describe the endosymbiont theory. Compare and contrast the organelles: mitochondria and chloroplasts. 5. The cell membrane is one of the most important regulators of a cell. Describe the structure of a eukaryotic cell membrane including the types of proteins that would be associated. 6. Compare and contrast diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport across a cell membrane. 7. Enzymes are said to be substrate-specific. Explain enzyme specificity. Define and compare the methods of enzyme regulation, competitive inhibition and allosteric inhibition. 8. In eukaryotic cell respiration that various “steps” involved in the breakdown of glucose are often compartmentalized. Explain what takes place and the specific location of the “event” for glycolysis, Kreb’s Cycle, the Electron Transport Chain, and ATP synthesis. 9. What are the reactants and products of the “Light” and “Dark” reactions of photosynthesis? Explain where in the chloroplast these reactions take place. 10. Oxidative phosphorylation couples the electron transport chain with the function of ATP synthase. This process occurs in both cell respiration and photosynthesis. Compare and contrast the location of these processes in the mitochondria and chloroplast. 11. Communication between cells is vital for survival. This is often carrier out by receptors on the surface of cell membranes. Choose one type of cellular receptor and explain how this receptor is activated, its response to activation, and the result of its activation. 12. Cellular replication is a process with multiple phases. Name the phases of the cell cycle and describe the events that take place during each phase of the cell cycle. Explain the role of cyclins and cyclin-dependant kinases in regulating the cell cycle. 13. Compare and contrast meiosis. Describe two ways that can produce variation thanks to the events of meiosis. 14. Mendelian genetics assumes traits for a character exhibit dominance. Describe the difference between a phenotype and genotype. Exceptions to Mendelian genetics are codominance and incomplete dominance. Compare codominance and incomplete dominance with regard to genotype and phenotype. 15. In dogs floppy ears (F) are dominant to perky ears (f). Draw a punnett square or show the math required to determine the ratio of phenotypes produced from a cross between a dog heterozygous for ears with a dog homozygous recessive for the trait. 16. Cat fur color is sex-linked. Black fur (B) is dominant to orange fur (b). What percentage of the male offspring would show orange fur color from a cross between a female heterozygous for fur color with an orange male? Draw the Punnett Square to provide evidence for your decision. 17. DNA is the molecule of inheritance. Briefly explain the structure of DNA. Outline the semiconservative model of DNA replication and name the enzymes involved in the process and their function. 18. Genes code for specific peptides. The process of gene expression is generally similar among prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Outline the major steps in gene expression. Identify and explain three modifications made to eukaryotic mRNA that must take place before proper expression. 19. Microevolution is defined as a change in the gene frequencies of alleles in a population. Microevolution can occur as a result of a number of events. Define and compare 3 methods in which microevolution can take place. 20. In a population of crested ibis, blue feather color (B) is dominant to green (b). If the frequencies of individuals in the population with green feathers is 16% what is the frequency of heterozygous individuals in this population? 21. In mammals, specific immunity is divided into humoral and cell-mediated immunity. If a person is exposed to the chickenpox for the first time explain how this individual’s specific immunity would respond on both the humoral and cell-mediated fronts. Be sure to include the cells responsible, and how they recognize the pathogen, and their cellular response to the pathogen. How does specific immunity help a person from suffering from a repeat infection?