Unit 6: Revolution - Curriculum Standards
advertisement

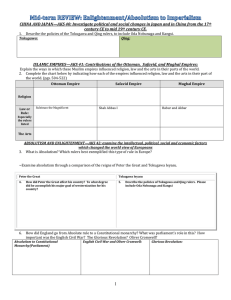
Unit 6: Revolution Standards SSWH11 Students will investigate political and social changes in Japan and in China from the seventeenth century CE to mid-nineteenth century CE. a. Describe the policies of the Tokugawa and Qing rulers; include Oda Nobunaga and Kangxi. b. Analyze the impact of population growth and its impact on the social structure of Japan and China. SSWH13 The student will examine the intellectual, political, social, and economic factors that changed the world view of Europeans. b. Identify the major ideas of the Enlightenment from the writings of Locke, Voltaire, and Rousseau and their relationship to politics and society. SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. b. Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in England (1689), United States (1776), France (1789), Haiti (1791), and Latin America (1808-1825). c. Explain Napoleon’s rise to power, the role of geography in his defeat, and the consequences of France’s defeat for Europe. d. Examine the interaction of China and Japan with westerners; include the Opium War, the Taiping Rebellion, and Commodore Perry. SSWH15 The student will be able to describe the impact of industrialization, the rise of nationalism, and the major characteristics of worldwide imperialism. a. Analyze the process and impact of industrialization in England, Germany, and Japan, movements for political reform, the writings of Adam Smith and Karl Marx, and urbanization and its affect on women. b. Compare and contrast the rise of the nation state in Germany under Otto von Bismarck and Japan under Emperor Meiji. c. Describe the reaction to foreign domination; include the Russo-Japanese War and Young Turks, and the Boxer Rebellion. d. Describe imperialism in Africa and Asia by comparing British policies in Africa, French policies in Indochina, and Japanese policies in Asia; include the influence of geography and natural resources. Enduring Understandings and Essential Questions The student will understand that when there is conflict between or within societies, change is the result. How did the introduction of new ideas, concepts, beliefs led to political, economic, and social changes? How did conflict within and/or between societies bring about change/s? The student will understand that as a society increases in complexity and interacts with other societies, the complexity of the government also increases. How did imperialism change the relationship/s that countries had previously experienced? How did the rise of nationalism have global impact? The student will understand that the actions of individuals, groups, and/or institutions affect society through intended and unintended consequences. What were some consequences of the Enlightenment writings? How did the actions of various rulers bring about change? The student will understand that the movement or migration of people and ideas affects all societies involved. What was the impact of population growth of various regions of Europe, China, Japan, and the Western World? How can human movement, initiated by needs and wants, create patterns and centers of activity? The student will understand that technological innovations have consequences, both intended and unintended, for a society. How did technological changes in societies have worldwide impacts on subsequent generations? How did industrialization bring about social, political, and economic changes? Unit 6 Vocabulary 1. Absolutism 2. Adam Smith 3. American Revolution (1776) 4. Boxer Rebellion 5. Commodore Perry 6. Emperor Meiji 7. Enlightenment 8. French Revolution (1789) 9. Imperialism 10. Indochina 11. Industrialization 12. Kangxi 13. Karl Marx 14. Latin American Revolutions (1808-1825) 15. Locke 16. Louis XIV 17. Napoleon Bonaparte 18. Nationalism 19. Oda Nobunaga 20. Opium War 21. Otto von Bismarck 22. Qing Empire 23. Revolution in England (1689) 24.Revolution in Haiti (1791) 25. Rousseau 26.Russo-Japanese War 27. Tokugawa Empire 28.Tokugawa Ieyasu 29.Tsar Peter the Great 30. Urbanization 31. Voltaire 32. Young Turks