Year 3 Autumn term Changes in Britain from the Stone Age to the
advertisement

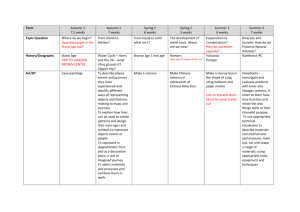
Year 3 Autumn term Changes in Britain from the Stone Spring term What is the attraction Summer term - Ancient Egypt Age to the Iron Age History Changes in Britain from the Stone Age to the Iron Age –trip to Dartmoor – link Bronze age Skills taught within the topics Chronological understanding •Can they describe events and periods using the words: BC, ADand decade? •Can they describe events from the past using dates when things happened? •Can they describe events and periods using the words: ancientandcentury? •Can they use a timeline within a specific time in history to set out the order things may have happened? •Can they use their mathematical knowledge to work out how long ago events would have happened? Science Rocks – link geography volcanoes/ Dartmoor Compare and group together different kinds of rocks on the basis of their appearance and simple physical properties. Describe in simple terms how fossils are formed when things that have lived are trapped within rock. Recognise that soils are made from rocks and organic matter. Link with work in Geography, explore different kinds of rocks and soils, including those in the local environment. Investigate the work of Mary Anning (fossil hunter) – Stone Girl, Bone Girl by Laurence Anholt Compare materials – stone vs bronze vs iron. • Investigate rocks and soils • Find out about the formation of fossils • Use caves as a starting point for exploring light and shadows Plan and create stone circle outside. How are the Shadows formed and how and why do they change during the day Ancient Egypt trip to Plymouth Museum Skills taught within the topics Knowledge and interpretation Do they appreciate that theearly Brits would not have communicated as we do or have eaten as we do? •Can they begin to picture what life would have been like for the early settlers? •Can they recognise that Britain has been invaded by several different groups over time? •Do they realise that invaders in the past would have fought fiercely, using hand to hand combat? •Can they suggest why certain events happened as they did in history? •Can they suggest why certain people acted as they did in history? Forces and Magnets:- Geography magnetic pole Compare how things move on different surfaces. Notice that some forces need contact between two objects, but magnetic forces can act at a distance. Explore the behaviour and everyday uses of different magnets (for example, bar, ring, button and horseshoe) Observe how magnets attract or repel each other and attract some materials and not others. Compare and group together a variety of everyday materials on the basis of whether they are attracted to a magnet, and identify some magnetic materials. Describe magnets as having two poles. Predict whether two magnets will attract or repel each other depending on which poles are facing. Light – linked to Literacy text Leon and Leap Year .Recognise that they need light in order to see things and that dark is the absence of light. Notice that light is reflected from reflective surfaces such as mirrors, play mirror games to help them answer questions about how light behaves. Recognise that light from the sun can be dangerous and there are ways to protect their eyes. Skills taught within the topics Historical enquiry Do they recognise the part that archaeologists have had in helping us understand more about what happened in the past? •Can they use various sources of evidence to answer questions? •Can they use various sources to piece together information about a period in history? •Can they research a specific event from the past? •Can they use their ‘information finding’ skills in writing to help them write about historical information? •Can they, through research, identify similarities and differences between given periods in history? Plants linked to ancient Egyptian farmers Identify and describe the function of different parts of flowering plants: roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers. Explore the relationship between structure and function: the idea that every part has a job to do. Explore questions that focus on the role of the roots and stem in nutrition and support, leaves for nutrition and flowers for reproduction. Explore the requirements of plants for life and growth (air, light, water, nutrients from soil and room to grow) and how they vary from plant to plant. Investigate the way in which water is transported within plants. Explore the part that flowers play in the life cycle of flowering plants, including pollination, seed formation and seed dispersal. Animals including humans – linked to gods in Egypt Identify that animals, including humans, need the right types and amount of nutrition, and that they cannot make their own food; they get nutrition from what they eat. Identify that humans and some other animals have skeletons and muscles for support, protection and movement. Geography Geography based on /Dartmoor trip 5/10/15 volcanoes, map work Linked to science Can they describe how volcanoes are created? Can they describe how volcanoes have an impact on people’s lives? Can they locate and name some of the world’s most famous volcanoes? Do they use correct geographical words to describe a place and the events that happen there? Can they identify key features of a locality by using a map? Can they begin to use 4 figure grid references? Can they accurately plotNSEW on a map? Maths link Can they use some basic OS map symbols? Can they make accurate measurement of distances within 100Km? Can they confidently describe physical features in a locality? Can they recognise the 8 points of the compass (N,NW, W, S, SW, SE, E, NE)?Maths link Can they confidently describe human features in a locality? Can they explain why a locality has certain human features? • Where was the best place to build an Iron Age settlement? Why? Recognise that shadows are formed when light from a light source is blocked by a solid object. Find patterns in the way that they size of shadows change. Introduce the main body parts associated with the skeleton and muscles, finding out how different parts of the body have special functions. Where are we in the world ? CC Magnetic Pole Fair trade linked to plants Locate and name the continents on a World Map. Locate the main countries of Europe inc. Russia. Identify capital cities of Europe. Locate and name the countries making up the British Isles, with their capital cities. Compare with UK. Identify the position and significance of Equator, N. and S. Hemisphere, Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. Compare a region of the UK with a region in Europe, eg. local hilly area with a flat one or under sea level. Link with Science, rocks. Can they use maps and atlases appropriately by using contents and indexes? Can they locate the Mediterranean and explain why it is a popular holiday destination? Can they explain how the lives of people living in the Mediterranean would be different from their own? Can they name a number of countries in the Northern Hemisphere? Can they name and locate some well-known European countries? Can they name and locate the capital cities of neighbouring European countries? Are they aware of different weather in different parts of the world, especially Europe? Sailors using magnets for sailing locate the world • Map UK monuments located in different counties and cities • What happened to settlements like Skara Brae over time? • Why has Stone Henge been preserved? • Make a giant hill fort map for your programmable robot. Art Drawing Lines and Marks Make marks and lines with a wide range of drawing implements e.g. charcoal, pencil, crayon, chalk pastels, pens etc. Experiment with different grades of pencil and other implements to create lines and marks. Shape & Form Experiment with different grades of pencil and other implements to draw different forms and shapes. Begin to show an awareness of objects having a third dimension Paint Experiment with tools and techniques Experiment with and combine different tools, media and effects Lines and Marks Use a variety of tools and techniques including different brush sizes and types Printing Create printing blocks using a relief or impressed method. Textile linked to Stone Age Use a variety of techniques, e.g. printing, dyeing, weaving and stitching to create different textural effects Ideas Iron Age Celtic patterns in shields and Jewellery Representations of Stone Henge in art and Models • Look at cave paintings - subjects, materials and colours used •Make own paint colours from natural resources. For example onion skins •Create cave paintings using natural materials - charcoal, chalk, natural paint colours Drawing Colour & Tone Experiment with different grades of pencil and other implements to achieve variations in tone. 3d models and clay Plan, design and make models from observation or imagination Apply tone in a drawing in a simple way. Join clay adequately and construct a simple base for extending and modelling other shapes Paint Shape & Form Experiment with different effects in paint to represent different forms and shapes. Drawing Colour & Tone Experiment with different grades of pencil and other implements to achieve variations in tone. Begin to show an awareness of objects having a third dimension. Apply tone in a drawing in a simple way. Textiles – Linked to magnets for Mothering Sunday Use a variety of techniques, e.g. printing, dyeing, weaving and stitching to create different textural effects Collage Experiment with a range of collage techniques such as tearing, overlapping and layering to create images and represent textures Use collage as a means of collecting ideas and information and building a visual vocabulary ICT shape collage Digital media Record and collect visual information using digital cameras and video recorders Use a graphics package to create images and effects with; Lines by controlling the brush tool with increased precision Changing the type of brush to an appropriate style e.g. charcoal Create shapes by making selections to cut, duplicate and repeat Paint Colour & Tone Colour Mix colours and know which primary colours make secondary colours Use more specific colour language Mix and use tints and shades Texture & Pattern Create different effects and textures with paint according to what they need for the task. DT Food In this unit children should be more aware of personal Mouldable clay Ceramic Project preference and do some research to find out what people like or dislike. That should make a product that meets someone’s preferences eg Design a yoghurt according to their preferences – Use of Milk in the Stone, Bronze, Iron Age Textiles- making fridge magnet Mothering Sunday 6th March Link this unit with Art and Design and make something with Clay or Modroc. It should have a design brief and set criteria to cover aspects of Design Technology Mechanical components ideas Linked to Author Study The key idea for this unit is that children make a product that uses a mechanism to create movement. This may be a slider, lever or gear. Computing We are researchers We are communicators Computing • Build a multimedia presentation about the Stone Age including video, image and text. • Write a series of programming instructions to navigate a programmable robot around your Hill Fort map We are comic writers We are opinion Pollsters We are animators We are presenters RE Worship, Pilgrimage and Sacred Places Prayer Teachings Music Autumn 1 Unit: Three Little Birds Style: Reggae Spring 1 Unit: Glockenspiel Stage 2 Style: Learning basic instrumental skills by playing tunes in varying styles Summer 1 Unit: Let Your Spirit Fly Style: R&B, Michael Jackson, Western Classical, Musicals, Motown, Soul Autumn 2 Unit: Ho, Ho, Ho! Style: Christmas, Big Band, Motown, Elvis, Freedom Songs Spring 2 Unit: Benjamin Britten - There was a Monkey style: Britten (Western Classical Music), Reggae, R&B PE Games Gym Dance Games Gym Dance Literacy Text Stone child Poetry linked to World Poetry Day and Poet coming in Mimi and the Mountain Dragon linked to Volcano work Text: Until I met Dudley by Roger McGough and Chris Reddell -explanations Text – Leon Poetry Year 3 objectives Summer 2 Unit: Reflect, Rewind and Replay Style: Western Classical Music and your choice from Year 3 Games Gym Dance Rio Olympics Text: Grow your own Lettuce- instructions Text: Paint me a poem by Grace Nicholls Text: Ask Dr K Fisher About… letter Dinosaurs/Animals/Weather /Reptiles/Minibeasts How to Invent Theatre Alib- November Fair Brown and Trembling Maths . Year 3 objectives Number Sense Additive reasoning Multiplicative reasoning Geometric reasoning Firebird by Saviour Pirotta- quest traditional tale Year 3 objectives Number Sense Additive reasoning Multiplicative reasoning Geometric reasoning Year 3 objectives Year 3 objectives Number Sense Additive reasoning Multiplicative reasoning Geometric reasoning