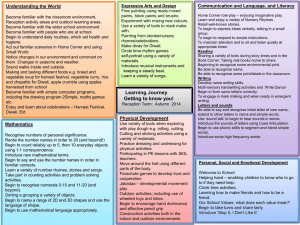
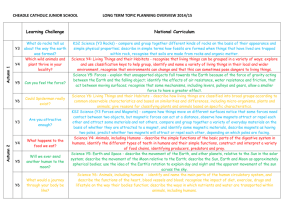
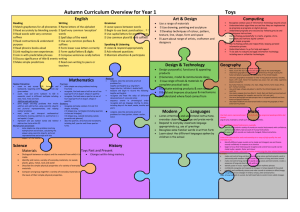
Term Autumn 1 7.5 weeks Autumn 2 7 weeks Spring 1 6 weeks
advertisement

Term Autumn 1 7.5 weeks Autumn 2 7 weeks Spring 1 6 weeks Spring 2 5 weeks Topic Question Where do we begin? How did people in the Stone Age live? From Stone to Shelter? From liquid to solid what am I? The development of metal tools, where are we now? History/Geography Stone Age TRIP TO GORDON BROWN CENTRE Water Cycle – rivers and the UK – what cities go past it? Clipper trip? To describe places events and journeys they have experienced and identify different ways of representing objects and features relating to maps and journeys To explore how lines can be used to create patterns and design their own signs and symbols to represent objects events or people To represent in diagrammatic form and as a decorative piece, a real or imagined journey To select materials and processes and combine them in work Bronze age / iron age Romans Art/DT Cave paintings What did the romans do for us? Make a volcano Make Chinese lanterns in celebration of Chinese New Year. Summer 1 6 weeks Summer 2 7 weeks Evaporation to Condensation? Why do volcanoes explode? Volcanos Pompei Diversity and Growth: How do we Preserve Natural Habitats? Rainforest IPC Make a money box in the shape of a pig using balloons and paper mache Storybooks investigate and evaluate products with lever and linkages systems, in order to learn how they function and relate the way things work to their intended purpose To use appropriate technical vocabulary to describe materials and mechanisms and measure, mark out, cut and shape a range of materials, using appropriate tools, equipment and techniques Link to Volcano short film from pixar inside out ICT Fact file on a cave man 4.1 Google sketch We are Toy Designers 4.2 In this unit, the children work together to design a simple toy that incorporates sensors and outputs and then create an on-screen prototype of their toy in Scratch. Finally, they pitch their toy idea to a Dragons’ Den-style panel. Science All living things – Recognise that living things can be grouped in a variety of ways Explore and use classification keys to help group and identify and name a variety of living things in their local and wider environment Recognise that environments can change. Electricity identify common appliances that run on electricity series electrical circuit, identifying and naming its basic parts, including cells, wires, bulbs, switches and buzzers not a lamp will light in a simple series circuit, based on whether or not the lamp is part of a complete loop Data – Excel 4.2 Planning a children’s party introducing children to excel spread sheets and formula to calculate total amounts. Presentation State of Matter Study of the particle makeup of solids liquids and gases, looking at reversible and irreversible changes. Experiments involving separating mixtures. Animals, including Humans describe the simple functions of the basic parts of the digestive system in humans identify the different types of teeth in humans and their simple functions construct and interpret a variety of food chains, identifying producers, predators and prey. describe the simple functions of the basic We are meteorologists 4.6 This unit brings together data measurement, analysis and presentation, as the children take on the role of meteorologists and weather presenters. We are HTML editors 4.4 In this unit the children learn about the history of the web, before studying HTML (hypertext mark-up language), the language in which web pages are written. They learn to edit and write HTML, and then use this knowledge to create a web page. Sound identify how sounds are made, associating some of them with something vibrating vibrations from sounds travel through a medium to the ear between the pitch of a sound and features of the object that produced it between the volume of a sound and the iPad Garageband We are Musicians 4.3 How many children in your class play an instrument? How many of them like singing, or simply enjoy listening to music? In this unit, the children produce music suitable for any purpose they choose. Resources:2 simple toolkit: music toolkit Animals including humans: habitats and food chains Recognise that living things can be grouped in a variety of ways Explore and use classification keys to help group and identify and name a variety of living things in their local and wider environment Recognise that environments can with a battery parts of the digestive system in humans switch opens and closes a circuit and associate this with whether or not a lamp lights in a simple series circuit different types of teeth in humans and their simple functions common Literacy texts Christophe’s Story Iron Man Creating Images A Huge First Step PSHE Year A- We’re all stars Year B- It’s our world Year A: Dear Diary Year B: People around us Year A: Be Friendly, Be wise Year B: Say no Dance / Gymnastics / PE Music Invasion games Dance – Stone Age Exploring Rhythmic Patterns VULNERABILITY Natural History museum Gordon Brown Centre Invasion Games and Dance Gymnastics RE Trips/visitors interpret a variety of food chains, identifying producers, predators and prey. Animals and the Outdoors The Spiderwick Chronicles Year A:Living long, living strong Year B: Money Matters Ball Sports and Skills, Swimming strength of the vibrations that produced it change. sounds get fainter as the distance from the sound source increases. The Shang Dynasty of Ancient China Sounds Spooky Year A:Daring to be different Year B: Who likes chocolate Swimming and Ball Sports and Skills Year A: Joining in and Joining up Year B: Growing up Museum of LondonThe Bronze to Iron Age Trip – London Zoo Athletics and Gymnastics Exploring Melodies and Scales VULNERABILITY