Test4LearningObjectives
advertisement

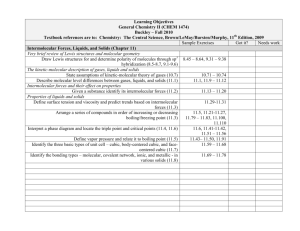
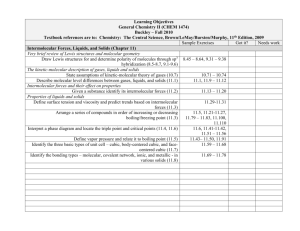
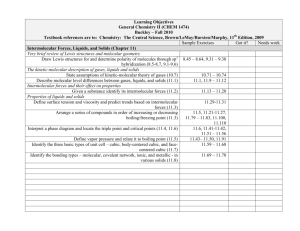
Learning Objectives General Chemistry II (CHEM 1474) Buckley – Fall 2010 Textbook references are to: Chemistry: The Central Science, Brown/LeMay/Bursten/Murphy, 11th Edition, 2009 Sample Exercises Got it? Needs work Other Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria (Chapter 17) The Common Ion Effect Identify “common ions” in a given solution (17.1) Calculate the pH and associated quantities in systems made with compounds containing common ions (17.1) Buffered solutions Define and identify buffer systems (17.2) Calculate the pH and associated quantities in buffer systems (17.2) Calculate changes in pH when acids and bases are added to buffer solutions (17.2) Acid-base titrations Generate titration curves for strong acid-strong base, weak acid-strong base, polyprotic acid titrations (17.3) 17.13-17.14 17.15-17.18 17.19-17.20 17.21-17.26 17.27-17.28 17.29-17.32 ↓↓↓↓TEST 4 Objectives↓↓↓↓ Solubility equilibria Given any chemical equation expressing the dissolution of a solid, write the mathematical expression for the Ksp (17.4) Given sufficient information, calculate missing information related to a solubility situation (17.4-17..5) Predict solubility based on the introduction of common ions (17.5) 17.33-17.38 17.39-17.46 17.49-17.50, 17.5317.56, 17.59-17.62 17.57-17.58 Learning Objectives General Chemistry II (CHEM 1474) Buckley – Fall 2010 Textbook references are to: Chemistry: The Central Science, Brown/LeMay/Bursten/Murphy, 11th Edition, 2009 Sample Exercises Got it? Needs work Electrochemistry (Chapter 20) Oxidation States and Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Use oxidation number to identify the species oxidized, reduced, the oxidizing 20.11-20.16 agent and reducing agent in a redox reaction (20.1) Balancing Oxidation-Reduction Equations Use the half-reaction method to balance redox reactions in neutral, acidic, and 20.17-20.22 basic solution (20.2) Voltaic Cells Identify the anode and cathode in a voltaic cell (20.3) 20.25-20.26 Find the standard cell potential of a voltaic cell (20.4) 20.27-20.40 Identify the relative strengths of oxidizing agents and reducing agents from 20.41-20.48 standard reduction half-cell potentials (20.4) Determine the cell potential of a cell under nonstandard conditions using the 20.37-20.68 Nernst equation (20.6) Electrolysis Manipulate equations relating current, time, moles of electrons, and mass to 20.87-20.89, 20.91determine missing information (20.9) 20.92 Learning Objectives General Chemistry II (CHEM 1474) Buckley – Fall 2010 Textbook references are to: Chemistry: The Central Science, Brown/LeMay/Bursten/Murphy, 11th Edition, 2009 Sample Exercises Got it? Needs work Chemical Thermodynamics (Chapter 19) Spontaneous Processes Distinguish between the terms spontaneous process and nonspontaneous process (19.1) Distinguish between reversible and irreversible processes (19.1) Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Describe the role of entropy in determining the spontaneity of a process (19.2) State and apply the Second Law of Thermodynamics (19.2) Given sufficient information, determine the entropy change in a chemical or physical process (19.2, 19.4) Gibbs Free Energy Given sufficient information, calculate the Gibbs Free Energy change for a reaction (19.5) Determine temperature ranges of spontaneity based on enthalpy and entropy changes (19.6) Free Energy and the Equilibrium Constant Manipulate the relationships between ΔG and K and E° (19.7) 19.9-19.20 19.25-19.26 19.21-19.24, 19.2719.28, 19.43-19.50 19.53-19.60, 19.6919.72 19.61-19.68 19.73-19.82 ↑↑↑↑TEST 4 Objectives↑↑↑↑