Unit Plans - Penasco ISD
advertisement

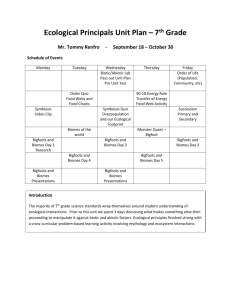
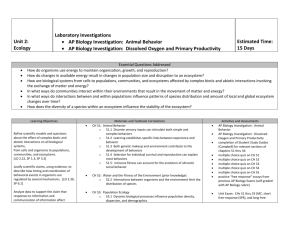
Unit Plans TEACHER: Jessica Esquibel Class: Biology Grade: 10-12 Time Frame: 14 weeks Unit Number: 1 Unit Title: The Study of Life/ Ecology Purpose Statement/Overview: . Biology is the study of life. All living things share the characteristics of life All living things require energy to perform all life processes. All living things have structures and functions s that help them maintain homeostasis. Essential Questions: What is biology? What is the difference between abiotic factors and biotic factors? What are the interactions between the levels of biological communities? What are the producers and consumers in an ecosystem? How does energy flow through an ecosystem? How do nutrients move through the biotic and abiotic parts of an ecosystem? Why are nutrients important to living organisms? How do unfavorable abiotic and biotic factors affect species? How is latitude related to the three major climate zones? What the major abiotic factors that determine the aquatic ecosystem? What are the characteristics of populations and how they are distributed? What aspects affect human population growth? Measurable Learning Objectives: Recognize some possible benefits from studying biology. Summarize the characteristics of living things. Compare different scientific methods. Differentiate among hypothesis, theory, and principle. Compare and contrast quantitative and qualitative information. Explain why science and technology cannot solve all problems. Distinguish between the biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. Compare the different levels of biological organization and living relationships important in ecology. Explain the difference between a niche and a habitat. Compare how organisms satisfy their nutritional needs. Trace the path of energy and matter in an ecosystem. Analyze how matter is cycled in the abiotic and biotic parts of the biosphere. Identify some common limiting factors. Explain how limiting factors and ranges of tolerance affect distribution of organisms. Sequence the stages of ecological succession. Describe the conditions under which primary and secondary succession take place. Compare and contrast the photic and aphotic zones of marine biomes. Identify the major limiting factors affecting distribution of terrestrial biomes. Distinguish among biomes. Compare and contrast exponential and linear population growth. Relate the reproductive patterns of different populations of organisms to models of population growth. Predict effects of environmental factors on population growth. Identify how the birth rate and death rate affect the rate at which a population changes. Compare the age structure of rapidly growing, slow growing, and no-growth countries. Explain the relationship between a population and the environment. Prerequisite Skills (Prior Knowledge): Standards: Quality Core, Common Core State Standards, State Standards: Strand II: The Content of Science Standard II (Life Science): Understand the properties, structures, and processes of living things and the interdependence of living things and their environments. 9-12 Benchmark I: Understand how the survival of species depends on biodiversity and on complex interactions, including the cycling of matter and the flow of energy. Ecosystems 1. Know that an ecosystem is complex and may exhibit fluctuations around a steady state or may evolve over time. 2. Describe how organisms cooperate and compete in ecosystems (e.g., producers, decomposers, herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, predator-prey, symbiosis, and mutualism). 3. Understand and describe how available resources limit the amount of life an ecosystem can support (e.g., energy, water, oxygen, nutrients). 4. Critically analyze how humans modify and change ecosystems (e.g., harvesting, pollution, population growth, technology). Energy Flow in the Environment 5. Explain how matter and energy flow through biological systems (e.g., organisms, communities, ecosystems), and how the total amount of matter and energy is conserved but some energy is always released as heat to the environment. 6. Describe how energy flows from the sun through plants to herbivores to carnivores and decomposers. 7. Understand and explain the principles of photosynthesis (i.e., chloroplasts in plants convert light energy, carbon dioxide, and water into chemical energy). Biodiversity 8. Understand and explain the hierarchical classification scheme (i.e., domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species), including: • classification of an organism into a category • similarity inferred from molecular structure (DNA) closely matching classification based on anatomical similarities • similarities of organisms reflecting evolutionary relationships. 9. Understand variation within and among species, including: • mutations and genetic drift • factors affecting the survival of an organism • natural selection. Materials: Resources: Biology New Mexico Textbook Student Sheets Internet sources Science Spot Classroom Lesson Planet The Biology Corner Research Based Strategies: Marzano, Bloom’s Taxonomy, Depth of knowledge Academic Vocabulary: Content (Assessment) Vocabulary: Level 1: List, identify, label, illustrate measure, draw, define, calculate, arrange, draw, explain, label, & recognize. Level 2: Infer, categorize, organize, construct, predict, interpret, make observations, graph, classify, separate, graph, classify, distinguish, modify, relate, summarize, & estimate. Level 3:Construct, compare, investigate, differentiate, formulate, critique, describe, formulate, hypothesize, investigate, & revise) Level 4: Design, connect, apply, critique, analyze, create, prove, & synthesize) Biology, organism, organization, growth, development, reproduction, species, stimulus, response, homeostasis, adaptation, science, theory, law, observation, inference, scientific method, hypothesis, experiment, control, independent variable, dependent variable, ecology, biosphere, biotic factor, abiotic factor, population, biological community, ecosystem, biome, habitat, niche, predation, symbiosis, mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, autotroph, heterotroph, herbivore, carnivore, omnivore, detritvore, trophic level, food chain, food web, biomass, matter nutrient, biogeochemical cycle, nitrogen fixation, denitrification, community, limiting factor, tolerance, ecological succession, primary succession, climax community, secondary succession, weather, latitude, climate, tundra, boreal forest, temperate forest, woodland, grassland, desert, tropical savanna, tropical seasonal forest, tropical rain forest, limnetic zone, litoral zone, plankton, profundal zone, wetlands, estuary, intertidal zone, photic zone, aphotic zone, benthic zone, abyssal zone Differentiated Instruction Strategies: Flex Grouping. Portfolios, Independent study Modifications: Assigned seating. Modified assignments, extended time to complete assignment, and other modifications as called for by IEP’s. Proper seating arrangements. Provide positive feedback. Avoid confrontation, allow for “time out” from classroom when needed. Follow BIP. Unit Topic/Outline (Sequence): Chapter 1 The Study of Life (section 1 Introduction to Biology, Section 2 The Nature of Science, Section 3 The Methods of Science ) Chapter 2 The Principles of Ecology (Section 1 Organisms & Their Relationships, Section 2 Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem, Section 3 Cycling of Matter) Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems (Section 1 Community Ecology, Section 2 Terrestrial Biomes, Section 3 Aquatic Ecosystems) Chapter 4 Population Ecology (Section 1 Population Dynamics, Section 2 Human Population) Depth of Knowledge: Learning Strategies: Level 1 (Recall-involves recall and student response is automatic) Level 2 (Skill/concept-increases in complexity and requires students to engage in mental processing beyond recall or rote response) Level 3 (Strategic thinking-requires higher cognitive demands than the previous levels) Level 4 (Extended thinking-requires complex reasoning and time to research, plan problem solve, and think) Cooperative learning Graphic organizers Hands-on, active participation Modeling/teacher demonstration Peer Tutoring Prediction Problem Solving Instruction Student Developed Glossary Use of Diagrams to teach cause & effect Visualizing Venn Diagram Formative Assessment: Summative Assessment: Parent Communication Plan: Observations Questioning Discussion Graphic Organizer Visual Representation Kinesthetic Assessment Constructive Quizzes State-mandated assessments(PARCC) District benchmark or interim assessments(Discovery) End-of-unit or -chapter tests End-of-term or -semester exams Progress reports every 3 weeks Remind App Phone calls to parents Emails to parents Teacher Unit Reflection: