Fractions Review Sheet
advertisement

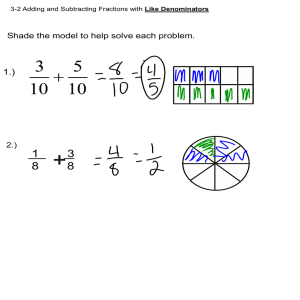
Name: ___________________________________________ Date: _____________________ Fractions Study Guide Fraction Vocabulary & Definitions o o o o o o o o o Fraction- A part of a whole object or set of objects. Fractions represent a division sentence. An object or set is divided into equal groups and each part or group is one fraction of the whole. Numerator- The top number in a fraction. It represents how many parts of the whole are being talked about or used. For example the 3 in ¾ is the numerator. Of the four equal parts a whole is divided into we are looking at/using 3 of them. Denominator- The bottom number in a fraction. It represents how many parts there are to the whole. For example the 4 in ¾ is the denominator, the whole is divided into four equal parts. Common Denominator- Denominators that are the same. Example: ¾ and ¼ both have 4 as the denominator and have common denominators. Equivalent fractions- Fractions that name the same amount. Example: 2/4 and 4/8 are both naming one half of an object or set. Fraction of a Set- Part of a group of objects. For example ½ of a bag of candy or ¼ of the books on a shelf. Fraction of a Whole- Part of one object. For example ¼ of a cake or ½ of an apple are both parts of one whole object. Improper Fraction- A fraction where the numerator is GREATER than its denominator. Example: 16/4. Mixed Number- A whole number and a fraction. It represents a whole, and some parts. Example: 2 ½. Equivalent Fractions o Check if two fractions are equivalent by cross multiplying: Example 1: 2 4 4 8 4x4=16 2x8=16 *The answers are the same so they are equivalent. Example 2: 3 4 5 8 4x5=20 3x8=24 *The answers are NOT the same so they are NOT equivalent. Ordering Fractions o To order fractions with the same denominator from smallest to greatest: Look at the numerators. Order them from smallest to largest. The smaller the numerator the smaller the fraction. Example: Biggest Smallest o 3 9 5 9 8 9 To order fractions with the same numerator from smallest to greatest: Look at the denominators. Order them from largest to smallest. The larger denominators are the smallest fractions since the whole is being broken into more pieces—each piece is smaller. (If you share a cake with 3 friends you get more than if you have to share that same cake with 10 friends). Example: Biggest Smallest o 2 9 2 9 2 6 2 4 2 3 To order fractions with different denominators and numerators: Find a common denominator for all fractions then compare numerators. Example: 2 6 1 4 1. Find a common denominator: 6, and 4 both go into 12 so 12 is the common denominator. 2. Convert fractions to twelfths. 2 6 = 4 12 1 4 3. Compare numerators. 4 12 > 3 12 = 3 12 Adding/Subtracting Fractions o When the denominators are the same you can add the numerators and keep the denominators. THIS WILL BE ON TEST! Example 1: 2 4 o 1 4 2 + 1= 4 3 4 1 4 2 - 1= 4 1 4 Example 2: 2 4 o + - When the denominators are NOT the same you must find a common (same) denominator then add the numerators. THERE WILL ONLY BE EXTRA CREDIT PROBLEMS LIKE THIS ON THE TEST! Example1: 2 4 + 1 3 Step 1: Find a common denominator. 4x3=12 so 4 and 3 are both factors of 12 and 12 is a common denominator. Step 2: Convert fractions to common denominator. 2 4 6 12 = 1 3 = 4 12 Step 3: Add numerators, keep the denominator. 6 + 4 6+4 = 12 12 12 = 10 12 Example 2: 2 4 - 1 3 Step 1: Find a common denominator. 4x3=12 so 4 and 3 are both factors of 12 and 12 is a common denominator. Step 2: Convert fractions to common denominator. 2 4 6 12 = 1 3 = 4 12 Step 3: Subtract the numerators, keep the denominator. 6 - 4 6-4 = 12 12 12 = 2 12 Practice Adding and Subtracting Fractions with Common Denominators - - - - - Practice Comparing Fractions (You must find a common denominator BEFORE comparing!) Practice Adding and Subtracting Fractions with Unlike Denominators THIS WILL ONLY BE EXTRA CREDIT ON TEST (You must find a common denominator BEFORE adding or subtracting!)