Monday Oct 19, 2015 Earth`s Interior Standard(s): 17.1.1 4.) Explain
advertisement

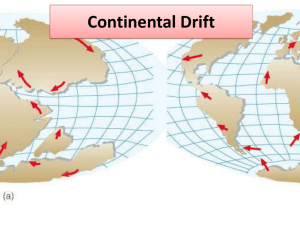
Monday Oct 19, 2015 Earth’s Interior Standard(s): 17.1.1 4.) Explain the plate tectonic theory. Example: using terminology such as continental drift, seafloor spreading, lava, magma, eruption, epicenter, focus, seismic wave, and subduction zone • Describing types of volcanoes and faults • Determining energy release through seismographic data Example: using data from the Mercalli scale and the Richter scale Bell ringer (Activate prior knowledge – Showing what you know): What are tectonic plates Before/ Purpose: Students will watch Brain Pop Video on Tectonic Plates During/ Purpose: Students will discuss what tectonic plates are. Students will research meaning of the following words: seismic waves, pressure, crust, basalt, granite, mantle, lithosphere, asthenosphere, outer core, and inner core. After/ Purpose: Students will discuss in whole group what they learned from the day’s lesson. Outcome: Students will be able to discuss what plate tectonics are. Assignment: Students will begin working with their partners. Work book pages 69-72 . Accommodations (IEP): Respective students have been given preferential seating, extra time on assignments, assignments modifications have been made and copy of the teacher notes provided. Tuesday Oct 20, 2015 Earth’s Interior Standard(s): 17.1.1 4.) Explain the plate tectonic theory. Example: using terminology such as continental drift, seafloor spreading, lava, magma, eruption, epicenter, focus, seismic wave, and subduction zone • Describing types of volcanoes and faults • Determining energy release through seismographic data Example: using data from the Mercalli scale and the Richter scale Bell ringer (Activate prior knowledge – Showing what you know): How do scientist find out what’s inside the Earth? Before/ Purpose: Students read pages 122 – 131. Students will read about the exploration inside earth along with learning about the Earth’s crust and mantle. During/ Purpose: Students will discuss what tectonic plates are. Students will discuss the meaning of the following words: seismic waves, pressure, crust, basalt, granite, mantle, lithosphere, asthenosphere, outer core, and inner core. Students will work on workbook pages 69-72 during discussion. After/ Purpose: Students will discuss in whole group what they learned from the day’s lesson. Outcome: Students will be able to discuss the exploration inside the Earth. Students will be able to discuss the Earth’s crust and mantle. Assignment: Students will continue working with their partners. Work book pages 69-72 . Accommodations (IEP): Respective students have been given preferential seating, extra time on assignments, assignments modifications have been made and copy of the teacher notes provided. Wednesday Oct 21, 2015 Continental Drift Standard(s): 17.1.1 4.) Explain the plate tectonic theory. Example: using terminology such as continental drift, seafloor spreading, lava, magma, eruption, epicenter, focus, seismic wave, and subduction zone • Describing types of volcanoes and faults • Determining energy release through seismographic data Example: using data from the Mercalli scale and the Richter scale Bell ringer (Activate prior knowledge – Showing what you know): What was Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis about the continent? What evidence supported Wegener’s hypothesis? Why was Wegener’s theory rejected by most scientist of his day? Before/ Purpose: Students read pages 136-140. Students will read and learn about Continental Drift During/ Purpose: Students will discuss the theory of Continental Drift. Students will work on workbook pages 74-75 during discussion. After/ Purpose: Students will discuss in whole group what they learned from the day’s lesson. Outcome: Students will be able to discuss the Wegener’s rejected theory. Students will be able to discuss the theory of continental drift. Assignment: Students will continue working with their partners. Work book pages 74-75 . Accommodations (IEP): Respective students have been given preferential seating, extra time on assignments, assignments modifications have been made and copy of the teacher notes provided. Thursday Oct 22, 2015 Sea-floor Spreading Standard(s): 17.1.1 4.) Explain the plate tectonic theory. Example: using terminology such as continental drift, seafloor spreading, lava, magma, eruption, epicenter, focus, seismic wave, and subduction zone • Describing types of volcanoes and faults • Determining energy release through seismographic data Example: using data from the Mercalli scale and the Richter scale Bell ringer (Activate prior knowledge – Showing what you know): What is the process of sea floor spreading? What is the evidence for sea-floor spreading? What happens at deep-ocean trenches Before/ Purpose: Students read pages 141-146. Students will read and learn about Sea-floor spreading and the evidence supporting it. Students will work on workbook pages 78-80 during discussion. After/ Purpose: Students will discuss in whole group what they learned from the day’s lesson. Outcome: Students will be able to discuss Sea-floor spreading. Assignment: Students will continue working with their partners. Work book pages 78-80 Students will begin working on interactive notebook section: Tectonic Plates . Accommodations (IEP): Respective students have been given preferential seating, extra time on assignments, assignments modifications have been made and copy of the teacher notes provided. Friday Oct 23, 2015 Theory of Plate Tectonics Standard(s): 17.1.1 4.) Explain the plate tectonic theory. Example: using terminology such as continental drift, seafloor spreading, lava, magma, eruption, epicenter, focus, seismic wave, and subduction zone • Describing types of volcanoes and faults • Determining energy release through seismographic data Example: using data from the Mercalli scale and the Richter scale Bell ringer (Activate prior knowledge – Showing what you know): What is the theory of Plate Tectonics? What are the three types of plate boundaries? Before/ Purpose: Students read pages 150-153. Students will read and learn about how Plate boundaries: Divergent boundaries, Convergent Boundaries, and Transform Boundaries. After/ Purpose: Students will discuss in whole group what they learned from the day’s lesson. Outcome: Students will be able to discuss plate boundaries Assignment: Students will continue working with their partners. Work book pages 81-83 Students will continue working on interactive notebook section: Tectonic Plates . Accommodations (IEP): Respective students have been given preferential seating, extra time on assignments, assignments modifications have been made and copy of the teacher notes provided.