probing oral questions
advertisement

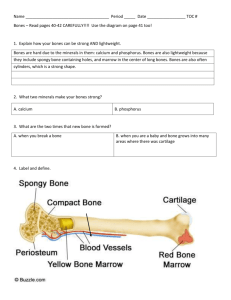
PROBING ORAL QUESTIONS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT 1. What is the difference between the functions of the osteoblasts and osteoclasts? Osteoclasts are cells that break down these specialized organs (bones.) Osteoblasts are cells that form these specialized organs (bones.) 2. Compact bone and spongy bone have completely different structures. This is because they have different functions. Explain the differences. Spongy Bone: Spongy bone is located towards the end of long bones like your thigh and upper arm. Spongy bone has many small open spaces that make the bones lightweight. In the center of long bones are large opening called cavities. These cavities and spaces in spongy bone are filled with marrow. Some marrow is yellow and is made f fat cells. Red marrow produces red blood cells at a rate of 2-3 million per second. Compact Bone: This is located directly under the periosteum. Calcium and phosphate components make compact strong. Bone cells and blood vessels are found in this layer. Compact bone is arranged in circular structures called the Haversian system. This system consists of tiny connected channels through which blood vessels and nerve fibers pass. 3. Describe the four types of joints and give examples of each. Ball and Socket: This a ball with a rounded end that fits in the cavity of another bone. Swinging arms and legs in any direction is an example of this motion. Hinge: This joint has a smaller range and has a back and forth motion like a door. These joints are found in elbows, knees and fingers. Gliding: This joint is where one part of the bone slides over another and they also move back and forth. They are found in wrists ankles and in between vertebrae Pivot: One bone rotates in a ring of another bone that does not move. Turning your head is an example. 4. Explain how the form and function of muscle cells varies. Skeletal muscles: these are muscles that move bones. Cardiac muscle: These type of muscles are found only in the heart. The cardiac muscle is striated and it contracts about 70 times per minute every day all day. Smooth muscle: These muscles are found in the intestines, bladder, blood vessels and other internal organs. They are non-striated and they contract and relax slowly. 5. Temperature control is critical to the health of our bodies. Explain the relationship of the muscular and skeletal system and how they contribute to controlling temperature for the purpose of homeostasis. As the muscle contracts the chemical energy is then change to mechanical energy (movement) and then to thermal energy (heat.) Maintaining a consistent body temperature is critical to the maintenance of homeostasis in the human body. If the body temperature needs to be lowered heat is released from the body in the form of sweat. If the body is to cold, the muscles shiver to generate body heat. 6. Describe the processes that occur in the periosteum and how they contribute to homeostasis. Blood vessels contained within the periosteum carry nutrients to the bone. Calcium and phosphate are components that make compact bones strong. Cells involved in the growth and repair of bones are also found in the periosteum. Growth and repair is also necessary for homeostasis.