Name: : :______ Study Guide for Genetic Test Define these terms
advertisement

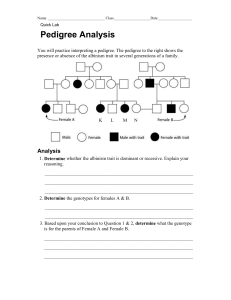
Name: ______________________________________Date:____________________Period:___________ Study Guide for Genetic Test 1. Define these terms: use your notes please! a. Traits b. Genes c. Alleles d. Dominant e. Recessive f. Genotype g. Phenotype h. Homozygous i. Heterozygous j. Hybrid k. Genetic Disorder l. Carrier m. Pedigree 2. Who is Gregor Mendel? What did organism did he study? Father of genetics, pea plants 3. What are his laws of inheritance? 1. Dominance 2. Segregation 3. Independent Assortment 4. Who determines the sex of the offspring the male or the female? a. XY = male b. XX = female 5. Know these Genetic Disorders – use your notes a. Hemophilia b. Cystic Fibrosis c. Sickle-Cell Anemia Disease d. Tay-sachs 6. Monohybrid cross (using one trait) a. Punnett Squares: A father has a widow’s peak (ww) and a mother doesn’t have a Widow’s peak but is a Hybrid for the trait (Ww). They want to know what are the chances of their children having a widow’s peak? The W represents what trait: Without a widow’s peak The w represents what trait: With a Widow’s Peak W w W Ww ww Ww ww W What are the possible Genotypes? Write them down: ____2Ww 2ww What are the chances of having a widow’s peak 50%; not having a widow’s peak 50% b. Do a Punnett Square for the following problems. i. A dwarf pea plant is crossed with a pure bred tall pea plant. tt x TT all tall heterozygous ii. Two pea plants that are heterozygous for round-shaped seeds. Rr x Rr = 1 RR; 2 Rr; 1 rr or 75% round and 25% wrinkle 7. Dihybrid Cross: (uses two traits) a. List all % of offspring showing certain traits i. Cross a left-handed Blue –eyed woman with a man brown eyed and right handed, who is heterozygous for both traits. R – right; r – left; B – Brown; B – Blue rrbb (woman) x RrBb (man) 25% Brown Right; 25% Brown Left; 25% Blue Right; 25% Blue Left ii. Cross a pea plant that is heterozygous for all the tall traits with terminal flowers with a plant that is dwarf and heterozygous for the axial trait. T – tall; t – short; A – axial; a – terminal Ttaa x ttAa 25% Tall axial; 25% Tall terminal; 25% Short axial; 25% Short terminal 8. Review how to do sex-linked traits and incomplete dominance. a. Complete the following crosses. i. In some plants there is an intermediate height (medium) as a result of the heterozygous condition. Cross two intermediate height Brassica plants. T = tall; S = Short; TS = Medium TS x Ts = resulting in 1 TT; 2 TS and 1 SS ii. In humans, colorblindness is sex-linked. Cross a female who carries the recessive colorblind gene with a normal male. XcX x XY gives you one Male normal, one male colorblind, one female normal and one female carrier 9. Blood typing. a. List All the possible Genotypes for the following Blood Types Blood type A B AB O Genotype AA, AO BB, BO AB OO b. A man with type AB Blood marries a woman with type A (heterozygous). Show the results in a Punnett Square. (make sure to have percentages) AB X AO = 50% TYPE A ; 25% TYPE AB; 25% Type B c. Cross an O parent with an AB Parent OO X AB RESULTS IN 50% TYPE A AND 50% TYPE B d. Cross A parent with B parent (use all possibilities; multiple punnett squares) AA X BB; AO X BO; AO X BB; AA X BO 10. Pedigrees Analysis For Questions 1-9, use the pedigree chart shown below. Some of the labels may be used more than once. C_____ 1. A male A 2. A female B________ 3. A marriage A 4. A person who expresses the trait C 5. A person who does not express the trait D 6. A connection between parents and offspring 3_______ 7. How many generations are shown on this chart? Assuming the chart above is tracing the dominant trait of "White Forelock (F)" through the family. F is a tuft of white hair on the forehead. ff________8. What is the most likely genotype of individual “A”? (FF, Ff or ff?) Ff________9. What is the most likely genotype of individual “C”? (FF, Ff or ff?) Example Trait: Falconi anemia Forms of the trait: The dominant form is normal bone marrow function - in other words, no anemia. The recessive form is Falconi anemia. Individuals affected show slow growth, heart defects, possible bone marrow failure and a high rate of leukemia. A typical pedigree for a family that carries Falconi anemia. Note that carriers are not indicated with half-colored shapes in this chart. Ff ff Ff F- Analysis Questions. To answer questions #1-5, use the letter "f" to indicate the recessive Falconi anemia allele, and the letter "F" for the normal allele. 1. What is Arlene's genotype? ff 2. What is George's genotype? Ff 3. What are Ann & Michael's genotypes? Ff 4. Most likely, Sandra's genotype is FF 5. List three people from the chart (other than George) who are most likely carriers of Falconi anemia. Sam; Daniel; Alan; Ann, Michael *Draw your own Pedigree - Case study Instructions: 1. Draw a pedigree showing all the individuals described in the problem. (Include their names if given.) 2. Label the genotypes of as many individuals in the pedigree as possible. 3. Shade in half of the symbol if you know that the individual is heterozygous or a carrier. Condition of Interest: Albinism Albinism is a condition in which there is a mutation in one of several possible genes, each of which helps to code for the protein melanin.. This gene is normally active in cells called melanocytes which are found in the skin and eyes. Albinism involves a significant reduction or absence of the production of melanin, giving affected individuals a lack of normal coloration to their skin/eyes. Inheritance Pattern: normal melanin protein is produced by an autosomal dominant allele; albinism results from a lack of melanin and is caused by an autosomal recessive allele. Use the letter A or a to represent dominant/recessive forms of albinism. Two normally-pigmented parents have 3 children. The first child (a girl) and their second child (a boy) have normal pigmentation. Their third child (a girl) has albinism. That girl marries a normally pigmented male and they have four children. The first three (two girls and a boy) have normal pigmentation. Their fourth child (a girl) has albinism like her mother. Aa ? Aa aa ? Aa Aa Aa Aa aa