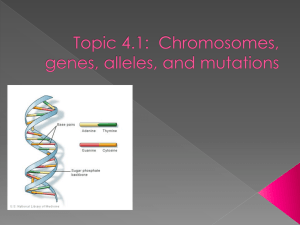
Mutation 1 The following is the beginning of the gene that produces
advertisement

Mutation 1 The following is the beginning of the gene that produces normal hemoglobin: TAC GTG CAC CTG CCT CCT GAG GAG AAG 1. Transcribe and translate the DNA sequence to produce a normal hemoglobin protein. Sickle-Cell Anemia is a blood disorder that results in abnormally-shaped red blood cells. These cells cannot carry nearly as much oxygen as normal red blood cells and they get caught more easily in the capillaries, cutting off blood supply to vital organs. The following is the beginning of the gene that produces sickle-celled hemoglobin: TAC GTG CAC CTG CCT CCT GTG GAG AAG 2. Transcribe and translate the DNA sequence to produce a mutated hemoglobin protein. 3. Describe the mutation in the DNA sequence and how that affects this protein chain. Mutation 2 The following is part of the NOD2 gene, which produces an important immune protein that recognizes bacterial molecules in the intestinal tract: CGG TCA CAA TCT AAA GAG ACG ACC 1. Transcribe and translate the DNA sequence to produce a normal protein from the NOD2 gene. Crohn’s Disease is an inflammatory bowel disease that is caused by a combination of genetics, exposure to microbes, and other environmental factors. A mutation in the NOD2 gene is a known cause in the development of Crohn’s Disease. The following is the beginning of the gene that produces a mutated NOD2 protein: CGG TCA ACA ATC TAA AGA GAC GAC C 2. Transcribe and translate the DNA sequence to produce the mutated protein of the NOD2 gene. 3. Describe the mutation in the DNA sequence and how that affects this protein chain. Mutation 3 The following is part of the FBN1 gene, which produces a protein called fibrillin. Fibrillin aids in the development and support of elastic fibers found in the smooth muscle of arteries. AAT CTC GTA CTG AGA TCC CAA GTT GAG CGA 1. Transcribe and translate the DNA sequence to produce a normal protein from the FBN1 gene. The following is part of the gene with a mutation in the FBN1 gene. AAT CTC GTA CTG AGA TCC CAA GTC GAG CGA 2. Transcribe and translate the mutated FBN1 sequence. A mutation in the FBN1 gene is associated with Marfan Syndrome. Marfan Syndrome has a wide variety of defects in the skeletal, cardiovascular, nervous, and respiratory systems. 3. Even though this individual has a mutation in the FBN1 gene, they do not have Marfan Syndrome. Explain why.