Microscope Comparison Web Quest: Biology Worksheet
advertisement
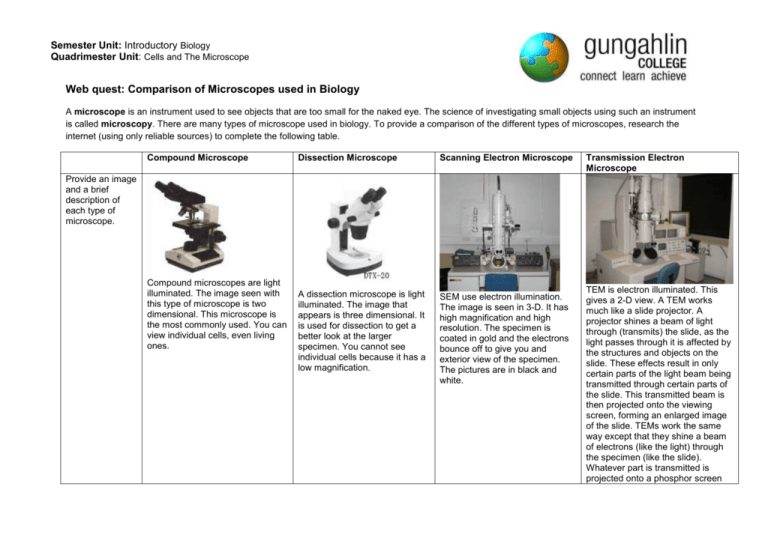
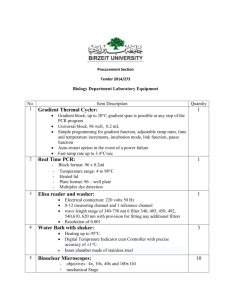
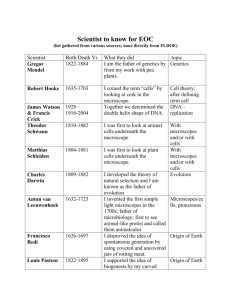
Semester Unit: Introductory Biology Quadrimester Unit: Cells and The Microscope Web quest: Comparison of Microscopes used in Biology A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy. There are many types of microscope used in biology. To provide a comparison of the different types of microscopes, research the internet (using only reliable sources) to complete the following table. Compound Microscope Dissection Microscope Scanning Electron Microscope A dissection microscope is light illuminated. The image that appears is three dimensional. It is used for dissection to get a better look at the larger specimen. You cannot see individual cells because it has a low magnification. SEM use electron illumination. The image is seen in 3-D. It has high magnification and high resolution. The specimen is coated in gold and the electrons bounce off to give you and exterior view of the specimen. The pictures are in black and white. Transmission Electron Microscope Provide an image and a brief description of each type of microscope. Compound microscopes are light illuminated. The image seen with this type of microscope is two dimensional. This microscope is the most commonly used. You can view individual cells, even living ones. TEM is electron illuminated. This gives a 2-D view. A TEM works much like a slide projector. A projector shines a beam of light through (transmits) the slide, as the light passes through it is affected by the structures and objects on the slide. These effects result in only certain parts of the light beam being transmitted through certain parts of the slide. This transmitted beam is then projected onto the viewing screen, forming an enlarged image of the slide. TEMs work the same way except that they shine a beam of electrons (like the light) through the specimen (like the slide). Whatever part is transmitted is projected onto a phosphor screen Semester Unit: Introductory Biology Quadrimester Unit: Cells and The Microscope When was this microscope invented and who invented it? What is the approximate cost? What is the range of magnification? What is the source of Illumination? What are the specimens mounted on? Provide an example of an image seen through this type of microscope. In the late 1590’s Hans Lippershey and his son, Zaccharias Hanssen were experimenting with a variety of lenses in a tube and were amazed to see that the object at the end of the tube was magnified significantly beyond the capability of a magnifying glass. Philip O. Gravelle, a chemist, developed the dissecting microscope in the 1920’s to compare bullets for identification in forensics. Co-invented by Germans, Max Knoll and Ernst Ruska in 1931, Ernst Ruska was awarded half of the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1986 for his invention. for the user to see. Co-invented by Germans, Max Knoll and Ernst Ruska in 1931, Ernst Ruska was awarded half of the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1986 for his invention. $150 - $1500 $100-$1500 more than $50,000 more than $50,000 x40 – x400 (without oil immersion lens) Up to x30 about x10 to x1,000,000 about x10 to x1,000,000 visible light visible light electrons electrons glass slides Specimens are not mounted but are generally viewed on a glass petri dish. Onion epidermis Lepidoptera Mounted on metal stubs (such as aluminium) and then covered in an ultrathin coating of conductive material such as gold or platinum.. A seed of a tobacco plant Thin films of collodion or other supporting material on copper grids. C. elegans (nematode) egg