HCA Lactation Consultant Workgroup Final Draft 5-12-10/8-31
advertisement

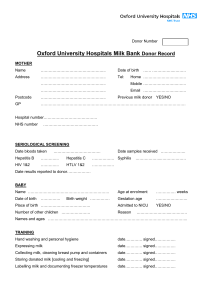
HCA Lactation Consultant Workgroup Final Draft 5-12-10/8-31-10 PURPOSE: To provide clinical guidelines for the use of pasteurized banked donor milk. BACKGROUND: Human milk is the standard food for infants and young children including premature and sick newborns with rare exceptions. Human milk provides optimal nutrition, promotes normal growth and development, and reduces the risk of illness and disease. The unique composition of human milk includes nutrients, enzymes, growth factors, hormones, and immunological and anti-inflammatory properties that have not been duplicated. Exclusive breastfeeding for six months is recommended with introduction of complementary nutritionally adequate foods at about this time. In situations where mothers’ own milk is not available, provision of pasteurized, screened donor milk is the next best option particularly for ill or high-risk infants. DEFINITION: Pasteurized Donor Milk: milk that has been processed per Human Milk Banking Association of North America (HMBANA) guidelines. POLICY: Parent/legal representative of every infant will be informed of the availability of donor milk as an option when supplementation is medically indicated and mother’s own milk is not available in adequate volumes. STORAGE: Refer to Collection, Storage and Handling of Human Milk for the Hospitalized Infant. PROCEDURE: PROCEDURE Notify parents(s)/legal representative of recipient infant of the need for and use of pasteurized banked donor milk with an opportunity to ask questions and accept or refuse the use of donor milk. Obtain order to use donor milk. Obtain parent(s)/legal representative Donor Milk Consent Form. Verify signed original consent in recipient infant’s medical record prior to use. Store and handle donor breastmilk per HCA Perinatal Clinical Services Group Guidelines for the Collection, Storage and Handling of Human Milk for the Hospitalized Infant. RESPONSIBILITY MD/NP/RN/IBCLC MD/NP/RN/IBCLC MD/NP RN/IBCLC RN/IBCLC A. Remove frozen donor milk from freezer and label with recipient infant’s electronic medication label or identification label including infant’s name and medical record number. Record date and time milk is removed from the freezer along with staff initials on the label. B. Document lot number and expiration date of donor milk on infant’s record. REFERENCES: CPQCC Nutrition Toolkit Appendices, 2008. Appendix 1-E1: Example of Nutrition Dashboard; Appendix 1-F: VON: Potentially Better Nutritional Practices; Appendix 4-C: Nutritional Support of the VLBW Infant; Appendix 4-D: Nutritional Support of the VLBW Infant. www.cpqcc.org CPQCC Nutrition Toolkit Appendices, 2008, Attachment A (Heat Processed, Banked Donor Breastmilk Information Sheet) and Attachment A1 (Fresh Donor Breastmilk Information Sheet for Recipient Parent) 1 HCA Lactation Consultant Workgroup Final Draft 5-12-10/8-31-10 Vaucher,Y, Wight,N. CPQCC Care and Management of the Late Preterm Infant Toolkit: Nutrition (2007), pp 1-7. www.cpqcc.org AAP Policy Statement http://aappolicy.aappublications.org/cgi/reprint/pediatrics;115/2/496.pdf Renfrew MJ, Craig D, et al. “Breastfeeding promotion for infants in neonatal units: a systematic review and economic analysis.” Health Technology Assessment NIHR HTA programme, www.hta.ac.uk, August, 2009; Vol 13: No. 40. CDC Maternity Care practices, CDC Guide to Breastfeeding Interventions: Maternity Care Practices. http://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/pdf/BF_guide_1.pdf CDC National Survey of Maternity Practices in Infant Nutrition and Care (mPINC), 2007. http://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/pdf/Maternity_Care_Practices.pdf Protecting, Promoting and Supporting Breastfeeding: The Special Role of Maternity Services, a joint WHO/UNICEF statement published by the World Health Organization. http://www.unicef.org/newsline/tenstps.htm HMBANA: The Value of Human Milk, Position Paper on Donor Milk Banking. http://www.hmbana.org/downloads/position-paper-donor-milk.pdf Jones F, “History of North American Donor Milk Banking: One Hundred Years of Progress.” J Hum Lact 19 (3), 2003 Arnold Lois D.W., “Milk Banks and Milk Banking: Clinical Uses of Donor Milk” J Hum lact 6(3), 1990 2