Weak Chemical Bonds
advertisement
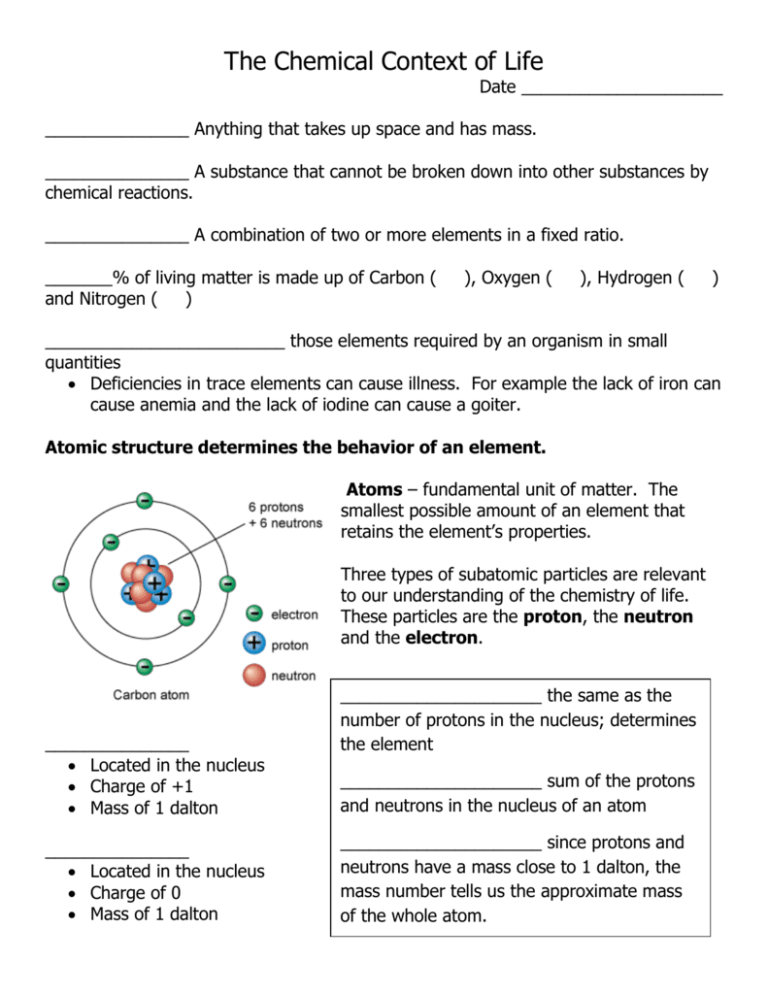
The Chemical Context of Life Date _____________________ _______________ Anything that takes up space and has mass. _______________ A substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions. _______________ A combination of two or more elements in a fixed ratio. _______% of living matter is made up of Carbon ( and Nitrogen ( ) ), Oxygen ( ), Hydrogen ( ) _________________________ those elements required by an organism in small quantities Deficiencies in trace elements can cause illness. For example the lack of iron can cause anemia and the lack of iodine can cause a goiter. Atomic structure determines the behavior of an element. Atoms – fundamental unit of matter. The smallest possible amount of an element that retains the element’s properties. Three types of subatomic particles are relevant to our understanding of the chemistry of life. These particles are the proton, the neutron and the electron. _______________ Located in the nucleus Charge of +1 Mass of 1 dalton _______________ Located in the nucleus Charge of 0 Mass of 1 dalton _____________________ the same as the number of protons in the nucleus; determines the element _____________________ sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom _____________________ since protons and neutrons have a mass close to 1 dalton, the mass number tells us the approximate mass of the whole atom. _______________ Located in a cloud around the nucleus Charge of -1 Mass is negligible Isotopes Isotopes have the same number of ___________ and ____________, but different numbers of ____________ Radioactive Isotopes Can cause mutations in DNA Useful in medical research and medicine as tracers Electron Orbital – the three dimensional space where an electron is found 90% of the time. Electron configuration and chemical properties The chemical properties of an atom depends mostly on the number of electrons in its outermost shell. ____________________ - electrons in the outermost shell ____________________- outermost energy shell Chemical Bonding When atoms with incomplete outer shells react, each atom gives up or acquires electrons so that partners end up with completed valence shells. Atoms do this by either sharing (______________________________) or transferring outer electrons (_____________________________) The strongest chemical bonds are covalent bond and ionic bonds _________________ bond – two atoms sharing one or more pairs of outer shell electrons. _________________ two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds. The number of single covalent bonds an atom can form is equal to the number of additional electrons needed to fill its outer shell. ____________________________ sharing of 2 pairs of electrons ____________________________ at atom’s attraction for the shared electrons of the bond. The more electronegative an atom, the more strongly it pulls atoms towards itself. Polar vs. Non-Polar Covalent Bonds ________________ Bond – attraction between ions of opposite charge __________ -- atom or molecule with an electrical charge resulting from the gain or loss of one or more electrons. Anion = ion with a __________________ charge Cation = ion with a __________________ charge Weak Chemical Bonds Weak bonds, unlike covalent bond, allow interactions between molecules to be brief The most important weak bond in living matter is the hydrogen bond. Hydrogen Bond = occurs when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted by another electronegative atom. In living cells, the electronegative partner involved is usually a nitrogen or oxygen atom.






