Respirator - WordPress.com
advertisement

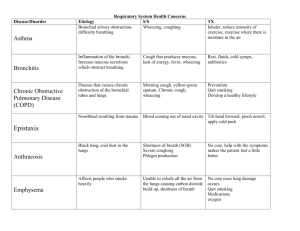
Laura Spenceley Respiratory – Task 1 A&P Task 1 – Respiratory Systems –Shortness of Breath during exercise Shortness of breath during or after exercise is common in many people, there may be a number of possible reasons for shortness of breath occurring which must be taken into account for diagnosis and treatment. Lifestyle factors often play a significant role in shortness of breath during or following exercise. Factors may include; Smoking - Medical evidence has shown that smoking is the main cause of many respiratory diseases. Cilia in the nasal cavity are very sensitive filament like structures which are easily damaged by cigarette smoke and may even be destroyed all together. Tar from cigarettes may also paralyse cilia preventing any movement, subsequently meaning any mucus holding dust particles will remain in the nasal cavity and bacteria will not be cleared into the digestive system potentially causing a build up in nasal cavity which may impede breathing. Alcohol – People who consume excessive amounts of alcohol are also at risk of an increased number of upper respiratory infections and pneumonias related to a decreased functioning of the immune system associated with alcohol overuse. Chronic lung conditions such as emphysema, bronchitis or COPD (chronic obstruction pulmonary disease) are aggravated by the use of alcohol. Fitness - Overdoing exercise when first starting a routine is one of the most common causes of shortness of breath while exercising. Your body needs to generally increase duration and exertion when exercising in order to increase aerobic benefits, burn fat, and increase muscular endurance and stamina. Trying to do too much too soon causes excess stress on the lungs and increases the heart rate as the heart and lungs try to maintain adequate oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood flow to the muscles. Age – It is easy to assume shortness of breath may be related largely to the age of the individual, however this assumption may not always be correct. The fitness and health of the person is a much higher factor when looking at shortness of breath in exercise than the age of the person. Stress – Anxiety and stress may cause panic which may be aggravated by exercise if a person does not feel comfortable in their surroundings or of their ability. Breathing becomes much shorter and harder when someone is anxious and this must be taken into account during exercise. Diagnostics One of the most common symptoms of shortness of breath is rapid, shallow breathing, Rapid breathing means you’re not getting as much oxygen as you should. Your body needs adequate amounts of oxygen for optimal function. A feeling of light-headedness is also a symptom of shortness of breath that can be caused by exertion or exercise. The light-headedness or faintness you feel is because your cells aren’t receiving adequate amounts of oxygen. When cells are lacking or starved for oxygen, they cease to function as they should. During exercise, shortness of breath may result in clients showing symptoms such as blue lips or skin. The most common reason for blue lips/skin is a low level of oxygen in the blood or poor circulation. This blueness is known as Cyanosis, when limbs, hands and feet show signs of cyanosis, often affected areas become cold to touch, this Laura Spenceley Respiratory – Task 1 A&P is usually due to poor circulation due to a blockage in the blood flow ( possible blood clot) or possibly Raynaud’s Disease. General blueness of lips and/or skin is usually a sign of low levels of oxygen in the blood, this may be as a result of problems with the lungs, airways, heart or other underlying factors. Conditions affecting breathing rate A number of health conditions may affect breathing rate. Conditions which effect breathing rate should always be considered before and during exercise and monitored closely especially if they cause difficulty or become a danger to participant health. Such conditions which effect breathing rate for different reasons may include: Asthma – causes a narrowing of the airways, restricting oxygen intake. Bronchitis – inflammation to the lining of the bronchi, restricting gaseous exchange. Emphysema – inflammation of alveoli, slowing blood flow to lungs ( more common in elderly) Hayfever – Wheezing due to pollen allergies, weakens lung strength. Pneumonia – Inflammation of lungs due to bacterial and viral infections As mentioned earlier, poor circulation also causes problems with oxygen transportation to the lungs during exercise, this poor circulation may be due to heart conditions such as; Pulmonary hypertension – high blood pressure in lungs. Pulmonary fibrosis – hardening of lung tissue. Structures affected The structures of the lower respiratory tract are most affected during shortness of breath due to afore mentioned reasons. Structures such as the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli and the diaphragm, are all affected in different ways, when there is a reduced amount of oxygen reaching each of these structures they cease to work to their full potential and this is where problems arise and a shortness of breath becomes apparent. Trachea – as detailed in Task 2, the trachea’s primary function is to allow the movement of air into the lungs, any blockage caused or health conditions such as asthma may narrow the airways and mean the trachea cannot function efficiently. Bronchi – as detailed in Task 2, the bronchi