Unit 2 Objectives
advertisement

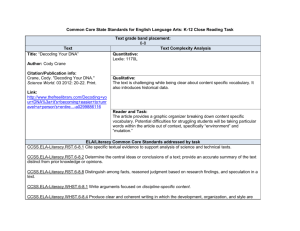
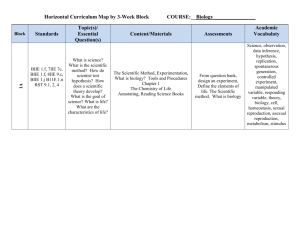
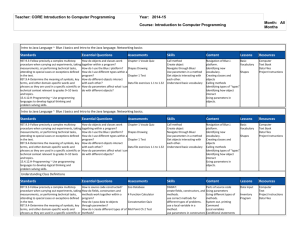
Cellular Metabolism Unit 2 Objectives Draw a lock and key model of an enzyme and describe what enzyme specificity means State how enzymes function List the four ways in which the speed of enzyme catalyzed reactions can be altered (how can they be sped up or slowed down?) Differentiate between catabolic, hydrolysis reactions and anabolic, dehydration synthesis reactions Define cellular respiration and state why it takes place in all living organisms Explain the structure and function of ATP Model the process of cellular respiration in the form of a game List the main steps of cellular respiration Describe the “big idea” of glycolysis Explain how the 2 pyruvate molecules are modified before the Kreb’s cycle takes place Describe the “big idea” of the Kreb’s cycle State what happens to all the original carbons in the glucose molecule In detail, draw and explain what happens in the electron transport chain (how is ATP created, what molecules play a role in the cycle, what is the concentration gradient?) o Specifically explain how the concentration gradient in the ETC creates ATP State how cyanide can interrupt the ETC and kill cells very quickly (less than 5 minutes!) Describe the structure of DNA Label the parts of a nucleotide and describe how they interact with a whole DNA molecule Read and provide an opinion on a “Creepy or Cool” article regarding DNA being used for art Describe the importance of DNA replication Explain the steps of DNA replication, including the necessary enzymes in the process State what the complementary base pairing rule is and how it relates to DNA Describe the structure of RNA Model the process or transcription and translation, describing the steps and enzymes in the process Explain how environmental factors can cause mutations in cellular processes or to DNA itself Recognize the various types of mutations that can happen to DNA and RNA Practice scientific argumentation while building science literacy skills when researching relevant topics regarding genetic modification NGSS: HS-LS1-6 Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for how carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen from sugar molecules may combine with other elements to form amino acids and/or other large carbon based molecules HS-LS1-7 Use a model to illustrate the cellular respiration is a chemical process whereby the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and the bonds in new compounds are formed resulting in a net transfer of energy HS-LS1-1 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out essential functions of life through systems of specialized cells HS-LS3-1 Ask questions to clarify relationships about the role of DNA and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristics passed from parents to offspring o Students should have had this in Biology 1, thus review will be brief HS-LS3-2 Make and defend a claim based on evidence that inheritable genetic variations may result from: 1) new genetic combinations through meiosis, 2) viable errors occurring during replication, and/or 3) mutations caused by environmental factors o Students should have had this in Biology 1, thus focus will be on mutations during cellular processes or caused by the environment Common Core: RST.11-12.1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts, attending to important distinctions the author makes and to any gaps or inconsistencies in the account. RST.11-12.2 Determine the central ideas or conclusions of a text; summarize complex concepts, processes, or information presented in a text by paraphrasing them in simpler but still accurate terms. RST.11-12.3 Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks; analyze the specific results based on explanations in the text RST.11-12.4 Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and other domain-specific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant to grades 11-12 texts and topics. RST.11-12.6 Analyze the author’s purpose in providing an explanation, describing a procedure, or discussing an experiment in a text, identifying important issues that remain unresolved. RST.11-12.7 Integrate and evaluate multiple sources of information presented in diverse formats and media (e.g., quantitative data, video, multimedia) in order to address a question or solve a problem. RST.11-12.9 Synthesize information from a range of sources into a coherent understanding of a process, phenomenon, or concept, resolving conflicting information when possible RST.11-12.10 By the end of grade 12, read and comprehend science/technical texts in grades 1112 text complexity band independently and proficiently. WHST.11-12.1A Introduce precise, knowledgeable claim(s), establish the significance of the claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that logically sequences the claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. WHST.11-12.1D Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone while attending to the norms and conventions of the discipline in which they are writing. WHST.11-12.4 Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. WHST.11-12.5 Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. WHST.11-12.6 Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products in response to ongoing feedback, including new arguments or information. *Not every part of the standards listed above will be completed within this unit. Many of these standards will be addressed multiple times in multiple lessons throughout the year.