Content creation and level design - Serious Games Pathway within
advertisement

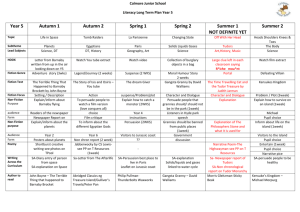
Course Name…………… Content creation and level design ……………….. Course Code ……………………??? ……………… No. of student working Hours…200 hours ……… Prerequisite……………………………………………….. Student should have knowledge or have these topics covered before taking this course: 1. General Knowledge about Gaming: Student should have knowledge about game theory, history of various types of games, survey of computer game categories and major game components including an overview of the game development process. Ref. 1] 2. Familiar with Process of Game Design: Student should have covered the skills and tools needed for story and character development, game design, production, testing, , interface, and content development. [Ref. 1 ] 3. Game Design Strategies: Student should explored game design concepts, such as challenge, reward, penalties, game balance, and level of difficulty, artificial intelligence, game genres and the social aspects of gaming. [1] Course Description .......................................................................................................................................... ...... Level design is the art of creating believable environments, stages and missions for games. Upon completion of this class student will have a strong foundation and understanding of how to analyze game levels and break them down into their basic components, purpose does it serve, level functionality and how does the current level ties to previous features serve. Students will also learn about level pacing and flow and the importance of visuals. The fun factor will also be covered, as a way of tying the individual components together [3]. The course will explore topics including architecture, flow, pacing and puzzles and the usage of a level editor. Students will investigate technical design issues including the construction, texturing, lighting and scripting of modern game levels. The roles, duties and challenges of the level designer will also be discussed [5]. A combination of lecture, discussion and hands-on applications are used to teach issues addressed by game and level designers. The course integrates theories and skills to demonstrate and simulate the decisions, skills, tools, problems and working conditions of a level designer who is responsible for designing the game spaces in which the player competes.[2] Course aims and objectives .................................................................................................................................... On completion of the course the student will be able to: ● Discuss and employ basic principles and practices within level design as well as analyses and discuss own and others work within the area ● Develop a theoretical model of a playable level ● Define and demonstrate solutions by applying methods and practices such as brainstorming, concept art and GGD. ● Build and test a playable level in an existing game engine by applying ● ● ● ● ● ● methods and practices such as templeting and prototyping Perform in a team Students will gain a more in depth understanding of the design process [6] Understanding of architecture, theories of flow and balance in game play, and a firm grasp of the Unreal Editor[4] Students develop original level design concepts The student will develop advanced skills in preproduction, modeling, rigging, weight mapping, and texturing game characters Other skills in: [2]: ○ Story and scripting ○ sound ○ Multi-player systems ○ Game documentation ○ Play testing I. Intended Learning Outcomes of Course (ILOs) a. Knowledge and Understanding On completing the course, students should be able to: K.1 Discuss and employ basic principles and practices within level design as well as analyse and discuss own and others work within the area K.2 Develop a theoretical model of a playable level K.3 K.4 K.5 Apply and test a playable level in an existing game engine by applying methods and practices such as templating and prototyping b. Intellectual/Cognitive Skills On completing the course, students should be able to: I.1 Make a feasibility study for a specific game leveling system. I.2 Differentiate the design process I.3 Choose architecture, theories of flow and balance in game play, and a firm grasp of the Unreal Editor. I.4 The ability to develop original level design concepts …. I.5 Perform in a team a team c. Practical/Professional Skills On completing the course, students should be able to: P.1 Select, Build and apply test for a playable level in an existing game engine by applying methods and practices such as templating and prototyping P2. Design, devise, and evaluate a computer game d. General and Transferable Skills On completing the course, students should be able to: T.1 T2. Participate in and lead game projects T.2 T4. Provide a scientific basis in computer games and serious gaming to future studies and to prepare for a career in the area, gather and interpret information and research findings on computer games and serious gaming. T.3 Provide/Participate in creating methodologies for production quality game levels.[4] II. Course Matrix Contents Duration (student working hours) K&U History of game level design [7] 1 WEEK K1,k2 Level Purpose and Theme[3] 1 WEEK K1 Level Goals and Objectives[3] 1 WEEK K1 P1 Environmental Modeling[3] 1 WEEK K1 P2 Pacing and Flow[3] 1 WEEK K1 Topics 1- learn how to critically evaluate game design [7] Level Transition using 3- reward systems [7] 2- 4- Working with sound [7] 5- Moving to Dimension the Third 1WEEK Course ILOs Covered by Topic (By ILO Code) K1 1WEEK K1 1WEEK K1 1WEEK P.S. G.S. P3 K1 Moving to Multiplayer 1 WEEK K1 Testing Levels 1 WEEK K1 Designing for third-person camera and gameplay 1 WEEK Designing for games based on real spaces and vice versa. 1 WEEK The world as a puzzle. Designing level mechanics 1 WEEK Designing for swimming, flying, vehicles, and more 1 WEEK Total student working hours I.S. K1 K1 K1 K1 P4 200 hours III. List of References The Hows and Whys of Level Design 2nd Edition, by Sjoerd “Hourences” De Jong" Essential http://www.hourences.com/the-hows-and-whys-of-level-design-about/ Text Level Up!: The Guide to Great Video Game Design, by Scott Books Rogers Course notes Recomm ended books Periodica ls, Web sites, etc … Theory of Fun for Game Design by Raph Koster [4] Architecture: Form, Space, & Order by Francis D. K. Ching A Pattern Language: Towns, Buildings, Construction by Christopher Alexander Towards a Ludic Architecture by Steffen Walz [1] : http://www2.itttech.edu/campus/desc.cfm?prog_id=2251#GD375 [2]: https://www.sheridancollege.ca/academics/programs-andcourses/game-level-design.aspx [3]: http://www.fullsail.edu/degrees/online/game-designbachelors/courses/level-design-GDN-3631 [4]http://www.seriousgameuniversity.com/index.php?option=com_co ntent&view=article&id=7&Itemid=65 [5]http://www.cdm.depaul.edu/academics/pages/courseinfo.aspx?Subj ect=GAM&CatalogNbr=341 –GAM 341: Introduction to Level Design Ref. [6] https://docs.google.com/file/d/0B_emGO_CgNZHWE8zX1JORE95T zg/edit?pli=1 http://www.bellevue.edu/resources/courses/courselisting.aspx?concentration=GAME [7]http://www.reddit.com/r/gamedev/comments/y8ker/level_design_ii _syllabus_chapman_university/ Note: Ref. [7] : EXCELLENT SOURCE FOR TOOLS, COMMUNITY … IV. Facilities required for teaching and learning