MOLECULAR BIOLOGY I Tissue preparation for DNA isolation
advertisement

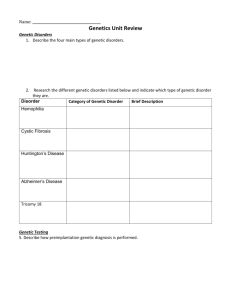
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY I Tissue preparation for DNA isolation Principle: DNA can be isolated by an isolation kit based on DNA adsorption on silicate. Material for examination (bird blood or other tissue) is lysed by lysis buffer (it contains detergents that dissolve cell membranes and denature proteins), enzyme proteinase K (it splits proteins including histons bound to DNA) and enzyme RNase A (it splits RNA). Material after lysis is transferred into isolation column with silicate on surface (SiO2 - glass). In the presence of chaotrope salts (part of the lysis buffer), DNA adheres to silicate. The column with DNA adhered to silicate is rinsed with buffers and finally DNA is released by elution buffer. General instruction: Each student will prepare one sample, students will work in groups and share set of pipettes and all other material. Required volume can be set on pipette - be careful not to rewind the pipette out of given volume range. To prevent contamination of pipette, chemicals and samples, new tips are used for each step of the procedure. To prevent contamination of pipette by DNA, filtered tips are used during working with DNA. To ensure accurate pipetting, tips should be properly set to a pipette. To obtain required volume, pipette should be pressed to the first position and tips should be merged into solution. By relaxing the pressing the liquid is sucked. After transferring the solution into other tube, the pipette should be pressed to the second position to release transferred material. The homogenization of liquid in a tube is done by repeated sucking into the pipette and emptying (three times) Tubes should be marked with the group number and student number Process of Lysis: 1. Tissue: take a piece of tissue (required size corresponding to two pinheads) and transfer it into microtube (1.5 ml) marked by marker. (Blood: take fresh or thawed blood and transfer (use tip with filter) 10 μl into microtube (1.5 ml) marked by marker. 2. Tissue: use micropestle to grind the tissue and add 200 μl GT Buffer (Blood: add 200 μl GT Buffer) 2. Add 20 μl proteinase K using new tips 3. Close the microtube, shake in your hands and let it incubate 2 minutes in room temperature. 4. Add 200 μl buffer for lysation (GBT Buffer) using new tip. 5. Close the microtube, shake it and place it into thermoblock (or water bath) to incubate at 55 oC. Tissue: incubate for 6 -18 hours (Blood: incubate for 10 minutes) 6. Lysed samples will be stored at room temperature for next week. MOLECULAR BIOLOGY II DNA isolation and PCR DNA isolation: 1. Add 200 μl 96% ethanol to lysed sample (from previous week). 2. Close the microtube and shake it by repeated turnover of the microtube. 3. Take a column with collecting microtube and mark the cover of column by marker. 4. Pour the content of microtube into the column. 5. Centrifuge for 2 min at 14 000 rpm (rounds per minute). 6. Pour off collecting microtube and use it again 7. Add 400 μl washing solution 1 (W1 Buffer) into the column using new tip. 8. Centrifuge for 1 minute at 14 000 rpm. 9. Pour off collecting microtube and use it again. 10. Add 600 μl washing solution 2 (W2 Buffer) into the column using new tip. 11. Centrifuge for 3 minutes at 14000 rpm. 12. Transfer the column into a new microtube (1.5 ml) marked by marker (discard the used collecting microtube). 13. Add 100 μl elution solution into the center of column (elution buffer) 14. Incubate for 2 minutes in room temperature. 15. Centrifuge for 1,5 minute at 14000 rpm 16. Discard the column and close the microtube that contains isolated DNA. PCR: 1. Each group of students prepares PCR mixture into one microtube (1.5 ml) according to the sample number (n + one extra): Mixture for one sample: 10 μl - PCR master mix (mixture of nucleotides (dNTP), DNA polymerase and Mg2+ ions) 0.2 μl - primer PP (TCTGGATCGCTAAATCCTTT) 0.2 μl - primer P8 (CTCCCAAGGATGAGRAAYTG) 7.6 μl - PCR water 2. Add 18 μl PCR mixture into PCR microtube (0.2 ml) marked by marker on the cover and side of tube. 3. Add 2 μl isolated DNA using new filtered tip. 4. Close PCR microtube, place it into thermocycler and run the appropriate PCR programme. 5. PCR product will be stored in fridge after finishing PCR programme. Programme of PCR amplification: Initial DNA denaturation 94°C 1 min 30 sec Primer attachment (annealing) 49°C 45 sec Synthesis of complementary DNA strains (extension) 72°C 1 min 30x DNA denaturation 94°C 1 min Completion of DNA synthesis (final extension) 72°C 10 min MOLECULAR BIOLOGY III Restriction reaction with PCR products, DNA electrophoresis, visualization and evaluation Principle: Bird sex can be detected by analysis of CHD gene (Chromo-Helicase-DNA binding gene), which encodes a protein that regulates transcription on the chromatin level. In birds, this gene is located on sex chromosomes. Males are homogametic with sex chromosomes ZZ Females are heterogametic with sex chromosomes ZW The PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is used to amplify DNA fragment corresponding to a part of gene located on chromosome W (CHD-W) and on chromosome Z (CHD-Z). PCR products is cleaved by restriction endonuclease (restrictase) Hae III (isolated from bacteria Haemophilus aegyptius) in specific restriction site. 5´-GG↓CC-3´ 3´-CC↑GG-5´ This restriction site is present only in the PCR product of gene CHD-Z, thus the enzyme cleaves it into two fragments, while PCR product of gene CHD-W is not cleaved (doesn´t contain restriction site). DNA fragments are then separated by gel electrophoresis, visualized under UV light and the result is evaluated. Gel electrophoresis and DNA visualization Principle: Gel electrophoresis is used to separate DNA fragments according to their size. Gel electrophoresis is based on the movement of negatively charged DNA molecules in electric field towards anode. DNA movement is inversely proportional to DNA size (smaller molecules move faster). Electrophoresis is preceded in suitable carrier, usually in agarose or polyacrylamide gel (in the practical, agarose will be used). Agarose gel is prepared in different concentration (% of agarose). Agarose is dissolved in buffer, which is also present in electrophoretic bath as an electrolyte. In the practical, TBE buffer containing Tris. boric acid and EDTA will be used. The samples are applied to wells made in the gel by a comb. The size of DNA fragment is estimated by comparing to the size of fragments of DNA ladder (molecular weight marker; DNA cleaved into fragments with defined size) that is applied into one of the wells. Prior to sample loading, each sample is mixed with the loading buffer to facilitate DNA loading. DNA is visualized by staining with DNA-binding dye, such as ethidiumbromide (in the practical, MIDORI Green will be used). PROCEDURE Restriction reaction: 1. Add 1.2 µl of mixture of restrictase Hae III and reactivating buffer into new PCR microtube (0.2 ml) marked with marker. 2. Add 10 µl PCR products using a new filtered tip. 3. Incubate it for 45 min at 37°C in the thermocycler. 1.2 % agarose gel preparation: One agarose gel will be prepared for all students. 1. Weigh 1.2 g agarose and put it into an Erlenmeyer flask. 2. Measure 100 ml TBE buffer with a glass cylinder, pour it into the flask and mix. 3. Place the flask into the microwave oven and boil it at maximal temperature for 2 minutes (stop the oven if agarose starts to babble, mix the content of the flask gently, not to generate bubbles in it); use gloves! 4. After 2 minutes, take the flask out of the microwave oven and cool it under flowing water to 60 °C (so that you can hold the flask for several seconds without gloves). 5. Add 3 µl MIDORI Green (10 thousand times concentrated solution) using a new tip and mix the content gently. 6. Prepare electrophoretic form and pour off warm agarose from the flask into the form up to 8 mm height. 7. Place the comp into the form and remove eventual air bubbles by tip. 8. Agar gel will be rigid after 30 min. Horizontal gel electrophoresis: 1. Remove the comb from the gel, turn the gel in form and submerge the gel into TBE buffer. 2. Apply 3 µl of DNA ladder (size standard, already stained) into one well (the central one is the best). 3. Apply 10 µl of mixed PCR product into one of the well (mixed PCR product = mixture of all your samples prior to restriction). 4. Apply 10 µl of stained sample (PCR product after restriction) into a gel well using a new tip (be careful not to tear the gel). 5. Cover the electrophoretic bath with a lid, plug it in, set constant voltage of 160 V for at least 20 min and switch it on. 6. After the electrophoresis is finished, place the gel on UV-transluminator and evaluate the results. Use plastic cover to observe the result! EVALUATION Female sex: (ZW) two bands are present on gel. The larger one corresponds to non-restricted CHD-W (with the same size as a non-restricted PCR product) and the second one (restricted CHD-Z) is smaller in about 50 bp (base pairs). Male sex: CHD-Z is cleaved, thus there is just one shorter fragment present in the gel. 100 bp 200 bp 300 bp 400 bp 500 bp 1 2 3 4 Fig. The result of gel electrophoresis: 1 – size marker, 2 – non-restricted PCR product, 3 – male, 4 – female