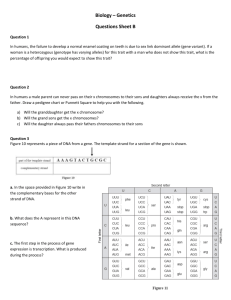
Vocabulary Notes: Inheritance: passing of genetic information from
advertisement

Vocabulary Notes: Inheritance: passing of genetic information from one generation to the next Father of Genetics: Gregor Mendel, performed experiments using pea plants Cells: Animal Cells Cell Membrane Nucleus (the center portion of the cell) Organelles are also located inside the cell: they perform many function essential for life. DNA: inheritance messenger Inside the nucleus: Chromosomes: Look something like below. DNA is coiled into structures called chromosomes. Come in pairs (2) 1 from mom, 1 from dad Alleles: areas on chromosomes that hold specific genetic information *Two alleles on the paired chromosomes work together = A GENE. SO FAR: 1. nucleus contain chromosomes 2. chromosomes come in almost identical pairs 3. chromosomes have specific active locations called alleles 4. two alleles in identical locations on paired chromosomes constitute a gene A gene controls a trait (ex. Fur color) Genotype: combination of alleles in an organism chromosomes (we use uppercase or lowercase letters to identify the alleles) Dominant alleles: more influential alleles (represented by an uppercase letter) Recessive alleles: less influential alleles (represented by a lowercase letter) Genotype is how we identify phenotypes. Phenotype: the way something looks (physical appearance) *Organisms have unique genotype, composed of paired alleles on paired chromosomes. Those genes produce unique traits in those organisms. The traits that the genotype produces results in the organisms phenotype.