A2 The energy continuum
advertisement

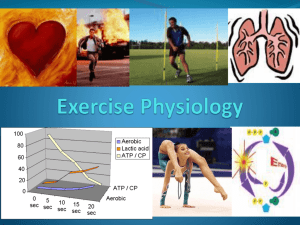
The energy continuum The energy continuum is the interaction of the 3 energy systems to provide energy to resynthesise ATP. It shows the predominant system or percentage of each system dependant on the intensity and duration of the activity. At the beginning of exercise all 3 energy systemsstart. The dominant system initially is the ATP/PC as shown on the diagram. As the PC is exhausted (ATP-PC/lactic acid threshold) the lactic acid system takes over. Depending on the intensity of the activity, the lactic acid/aerobic threshold is reached between 1-3 mins. The aerobic system now becomes the main provider of energy for ATP resynthesis. The diagram does not show the initial depletion of ATP – so the energy systems begin after approx 2-3 secs. This is shown on the next diagram. Onset of blood lactate accumulation (OBLA) During higher intensity activity lactate levels rise. Blood lactate levels at rest and during aerobic activity (remember during aerobic activity lactic acid is not produced) is aprox 2mmol/L(2 millimoles per L of blood). When blood lactate begins to rise during anaerobic activity and lactate levels reach 4 mmol/L, it is said to be the onset of blood lactate accumulation – OBLA. If the activity intensity continues or increases OBLA will continue to rise. The result of this is: - Lower blood pH (increased blood acidity) - Inhibition of enzyme action - Pain receptors stimulated - Muscle fatigue/pain - Reduction in performance This diagram adds a little more detail – Initial ATP depletion/thresholds. The shape of the line representing the lactic acid system in particular will change depending on the intensity of the activity – so, therefore will the threshold where the aerobic system will take over as the predominant system for ATP resynthesis. This explains the small difference between the two diagrams. Key points to learn related to the diagram: -Start points of each system -Shape of each system (relate to the timings/duration of each system) -Time of the thresholds – ATP-PC/lactic acid and lactic acid/aerobic. Remember the thresholds are the point where the one energy system takes over as the predominant (main supplier) energy supplier, not the point at which the energy system stops. This point will show good understanding and get a mark within an exam. Fitness levels - can change the thresholds. An aerobic athlete will have a more efficient cardiovascular and respiratory systems. They will have a greater ability to transport and use O2 to breakdown glycogen and FFAs (aerobically) to resynthesise ATP. Aerobic athletes will be able to work at higher intensities before their lactate threshold and OBLA will be reached. Aerobic athletes will reach OBLA at approx 85-90% of their VO2 max (compared to 50-55% for average person) An anaerobically trained athlete can also delay the ATP-PC/lactic acid threshold by increasing : ATP/PC/glycogen stores. Increased anaerobic enzymes (creatinekinase/ GPP/PFK) Increased tolerance of lactic acid. Team sports require the 3 systems to be used at different times. You need to be able to explain where each system is used within the game. Be specific in terms of time and intensity as well as the description of the movements. This is a popular exam Q! Possible exam Q-Factors affecting energy system used: Test your knowledge – use following key words – add details to each point. (revision book p168-171) 1 Intensity and duration of exercise. 2 Fitness level : - OBLA - Energy system thresholds - O2 availability - Enzyme activity - Fuel availability