Speciation - Science at NESS
advertisement

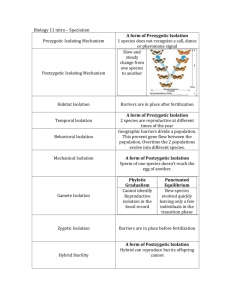
Speciation name:__________________________ Species: A group of organisms capable of interbreeding =_______________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 1)______________________________________________________________________ 2)______________________________________________________________________ Two Reproductive Isolation Mechanisms: 1) Prezygotic Isolating Mechanisms:_______________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Eg._____________________________________________________________________ 2)Postzygotic Reproductive Isolation:_____________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Eg.1)___________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Eg.2)___________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Causes of Reproductive Isolation Mechanisms: Prezygotic Isolation Habitat Isolation Temporal Isolation Behavioral Isolation Mechanical Isolation Definition Example Postzygotic Isolation Definition Example Gamete Isolation Zygote Isolation Hybrid Sterility F2 Fitness Process of Speciation Speciation:____________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Allopatric Speciation:________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ Sympatric Speciation:________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Eg._____________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Pace of Speciation: 2 Hypothesis that address the pace of speciation 1) Phyletic Gradualism Model: 2) Punctuated Equilibrium: How do Both Models Explain the lack of Transition Fossils in the Fossil Record? Phyletic Gradualism:_________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Punctuated Equilibrium:____________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Questions: 1) Compare and Contrast the way gradualism and punctuated equilibrium happen. 2) How do punctuated equilibrium and gradualism explain the lack of transition fossils in the fossil record. 3) Compare and contrast between allopatric and sympatric speciation. 5) Which type of reproductive isolation is depicted in the following Example of Reproductive Isolation 1) An inlet is closed and the salt water slowly turns into freshwater. The population of crabs slowly adapts to freshwater. They can no longer travel over to the saltwater population to interbreed. 2) A liger is a cross between a lion and tiger. Ligers are sterile animals. 3) A flowering plant is crossed with a different species to form a reproductive hybrid. When the reproductive hybrids are crossed together they form a sterile plant. 4) A purple ringed topsnail spawns at the same time as another species of topsnail. Although the eggs are fertilized and the embryo starts to develop it dies shortly after fertilization. 5) One population of frogs have a low pitch breeding call. A mutation in one spawn produces offspring with a high pitch call. This call is not recognized by the original population creating two isolated populations 6) Several species of coral mass spawn in one night. One species produces a thick shelled egg. The sperm of another species tries to enter the egg but cannot pass through the egg’s shell. 7) Rednecked duck eggs were placed in a canvas back ducks nest. The rednecked ducks learned the mating dance of the canvas back not his own species. Although they performed the canvas mating dance well they were not able to impress the rednecked females. Prezygotic or Postzygotic Isolation Type of Isolation Prezygotic or Postzygotic Isolation