PAP Test Review KEY
advertisement

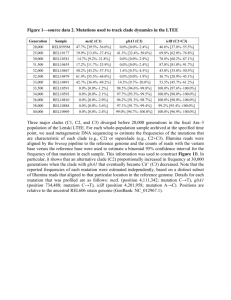
Name: __________________ Date: ______ PAP Molecular Genetic and Biotechnology Test Review Key 1. DNA mRNA AA TAC AUG CGC GCG TCC GCC GTC AGG CGG CAG GAC CUG Period: _____ ACT UGA Meth----Ala-------Arg----Arg----Glu------Leu-----Stop 2. Circle the correct suspect This technique is done through Gel Electrophoresis and this is known as DNA Fingerprinting 3. Put the events of genetic expression in the correct order. (Protein-RNA-DNA-Amino Acid-Genetic Expression) DNA-RNA-Amino Acid-Protein-Genetic Expression 4. When there is a mutation in the gamete of an organism, where will it be most likely transferred to? Offspring 5. What is selective breeding and give an example. Selective breeding: directed breeding to produce plant and animal with desirable traits. Ex: breeding plants to produce larger fruits/vegetable 6. If a gene that expresses a color is inserted into the DNA of another organism, how can a scientist determine if the gene is transcribed and translated? It will express the trait (show the color) 1 7. a. What process is shown in X? DNA Replication b. What process is shown in Y? Transcription c. What process is shown in Z? Translation 8. How does DNA in cells determine an organisms complex traits? DNA contains codes for proteins, which are necessary for the growth and functioning of an organism Word Bank: Anti-Codon rRNA mRNA tRNA Nucleus Answer the following question using the diagram above 9. What does E represent? Anti-Codon 10. What does A represent? Nucleus 11. What does D represent? tRNA 12. What does C represent? rRNA 13. What does B represent? mRNA 14. What does the technique of Chromosome painting allow for in different species? To compare the genomes of different species 15. Why is the sequence of bases in DNA important? It provides the instructions for the trait(s) of an organism 16. Put the following events of mutations in the correct order 3. Appearance of characteristic 1. A change in the sequence of DNA bases 2. Joining amino acids in sequence 2 17. What type of molecule is being produced from the DNA strand above? Messenger RNA 18. True or False A mutation is least likely to affect a cell when the mutation produces a triplet that codes for the same amino acid as that original triplet. True Matching; Match the correct mutation with the correct diagram 19. B Duplication Mutation 20. C Inversion Mutation 21. D Translocation Mutation 22. A Deletion Mutation A B C D 23. DNA segment is changed from TTGCCA to TTGGCCA. This is a Insertion mutation 24. DNA segment is changed from TTGCCA to TAGCCA. This is a Substitution mutation 25. What causes a frameshift mutation? A Deletion or Insertion of a base, which cause the DNA sequence to sift. 26. What type of biomolecule molecule will turn yellow to dark purple in the present of Lugol’s iodine? Polysaccharide (Starch) 27. Birds can exhibit symbiotic relationships between the different species. For instance, a cuckoo bird may lay its eggs in the nest of a nearby warbler bird. The cuckoo’s young will then be raised by the warbler, as the warbler’s young have been displaced. The symbiotic interaction this describes is Parasitism 3 28. What location of the cell does the synthesis of new proteins occur? In the ribosomes that are bound to the endoplasmic reticulum 29. When chromosomes crossover during meiosis what will increase in the offspring? Genetic Variation 30. Circle which organism that would have the greatest biomass in an ecosystem. Bird Frog Water Rock Pond grass Fly 31. Describing the process of cloning. The nucleus is removed from a body cell in one organism and is placed in an egg cell that has had its nucleus removed. This results in the production of an organism that is genetically alike. 32. Which will most likely cause a variation to occur within a species? Mutation 33. Label each diagram as the process of mitosis or meiosis Mitosis Meiosis 4 34. The graph below show the basic changes in a forest community after a disturbance occurred. What suggest the changes was cause by? Succession after a fire Matching: Match the correct mutation with the definition 35. AB Mutation that results from a change in a single nucleotide. 36. D Mutation from the deletion of a single nucleotide. 37. BC Mutation from the insertion of single nucleotide. 38. A Mutation where the amino acid does not change. 39. B Mutation when one amino acid is changed. 40. C Mutation when there is a premature stop signal. A. Silent mutation (point mutation) B. Missense mutation (point mutation) C. Nonsense mutation (point mutation) D. Deletion mutation (frameshift mutation) AB. Substitution mutation (point mutation) BC. Insertion mutation (frameshift mutation) 5 6 7