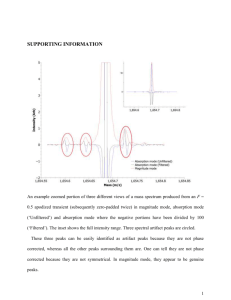
schematic peak
advertisement

The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Science Chemistry Department Instrumental Analysis B Mid Exam Questions Professor Nizam M. El-Ashgar Sample 1 I) a) Draw a schematic diagram the diffuse reflectance spectrometer and discuss its principle and applications. b) What are the handling processes of liquid samples of IR spectroscopy? c) Calculate the vibrational frequency, and wavelength of the fundamental absorption peak due to NH molecule. (N = 14, H = 1, K = 5x102 N/m, speed of light = 3x1010 cm/s). d) Discuss the overtones and coupling vibration phenomena in IR spectroscopy. II) a) Derive the bond vibrational frequency () using the quantum model. b)Derive a relation between the source frequency and interferometer frequency. c) Calculate the frequency of a modulated signal from a Michelson interferometer with a mirror velocity of 0.2 cm/s for a visible radiation of 650 nm. d)) What is the path length of an empty liquid cell exhibits 25 interference peaks in the range of 3200-1800 cm-1? II) a) Arrange the following: 1) CH3CH2CH2COHCH2CH3 CH3OH CH2CH2CH2OH (according to increase in C-O stretching vibration frequency) 2) C-Br, C-H, C-I, C-C, C-I (According to increase in single bond stretching vibrations) b) Explain the drive mechanism of interferometer. c)What are the main applications of FTIR in chemistry areas. d) What are the main factors that affect the extent of coupling in IR. 1 Sample 2 Answer the following questions: I) Comment on the following: 1- Homonuclear diatomic molecules do not absorb IR radiation. 2- CO2 gives two IR peaks, while SO2 gives three peaks. 3- IR quantitative measurements are less precise than UV-Vis. 4- Overtones signals occur at higher frequency than fundamental signals in IR. 5- TGS transducer could be used in FTIR but not bolometers. II) a) Calculate the approximate wave number and wavelength of the fundamental absorption peak due to N-H stretching vibration. (N = 14, H = 1, K = 5x102 N/m, speed of light = 3x1010 cm/s). b) What are the advantages of FTIR spectrometer compared with the dispersed instrument? c) What are the methods of solid sample handling in IR spectroscopy? III) a) Draw the schematic diagram of a double beam dispersive instrument showing all components. b) What are the principles of attenuated total reflectance spectrometry? c) Mention some applications of near IR absorption spectroscopy. d) draw and discuss the Michelson interferometer. Sample 3 Answer the following questions: I) 1) Calculate the approximate wave number and wavelength of the fundamental absorption peak due to C≡N stretching vibration. (C = 12, N = 14, K = 1.5x103 N/m, speed of light = 3x1010 cm/s). 2) The wavelength of the fundamental O-H stretching vibration is about 1.4 m. What is the approximate wavenumber and wavelength of the first overtone peak for the O-H stretch? 3) Arrange the following according to increasing in starching vibrational frequency: C=C, C-H, C-C, C-I, C-D, C-Cl, CC II) 1) Explain how a molecule absorbs IR. 2) Arrange the following compounds according to increasing C-O stretching frequency: 2-butanol, methanol and ethanol. Explain your answer. 3) How many IR normal modes that could be obtained from C5H12 molecule? 2 Sample 4 4) Write briefly about the null system in IR spectroscopy. III) Comment on the following: 1) IR technique mainly is useful in qualitative analysis over quantitative analysis. 2) Generally; the number of IR peaks observed experimentally is different from the theoretical number of normal modes. 3) Vibration of a real molecule not described perfectly by a harmonic oscillator. 4) Sample and reference compartments are always located between the source and monochromator in IR. 5) The force constant of a carbon monoxide bond is so much larger than the force constant of the bond in O2. IV) 1) Draw the schematic diagram of non-filter IR photometer and discuss its operation. 2) What are main advantages and uses in chemistry areas of FTIR? 3) Mention some applications of Far IR absorption spectroscopy. 4) What length of mirror drive in FT spectrometer would be required to provide a resolution of a) 0.02 cm-1 and b) 2.0 cm-1 Answer the following questions: II) a) Comment on the following: 6- Homonuclear diatomic molecules are IR inactive. 7- Linear triatomic molecules give two IR peaks, while nonlinear triaomic molecules give three peaks. 8- Not only fundamental peaks observed in IR spectra. b) Calculate the approximate wave number and wavelength of the fundamental absorption peak due to S-H stretching vibration. (S = 32, H = 1, K = 5x102 N/m, speed of light = 3x1010 cm/s). c) Mention some applications of near IR absorption spectroscopy. II) a) Draw as schematic diagram of a non fitter IR photometer and discuss its operation and applications. b) Derive the vibrational frequency equation using the mechanical model treatment. c) What is the path length of an empty liquid cell exhibits 20 interference peaks in the range of 3200-11800 cm-1? d) Mention the main types of molecular vibrations. e) What are the principles of attenuated total reflectance spectrometry? 3 4