Evolution Study Guide: Vocabulary, Natural Selection, Speciation
advertisement
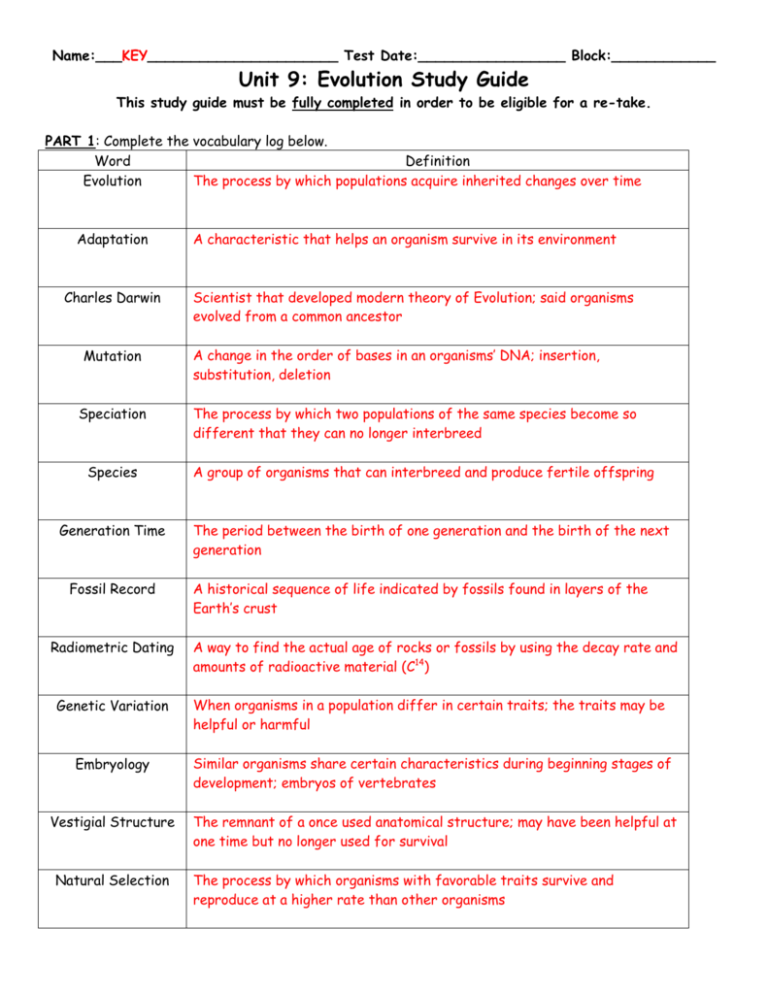
Name:___KEY______________________ Test Date:_________________ Block:____________ Unit 9: Evolution Study Guide This study guide must be fully completed in order to be eligible for a re-take. PART 1: Complete the vocabulary log below. Word Definition The process by which populations acquire inherited changes over time Evolution Adaptation Charles Darwin Mutation Speciation Species Generation Time Fossil Record Radiometric Dating A characteristic that helps an organism survive in its environment Scientist that developed modern theory of Evolution; said organisms evolved from a common ancestor A change in the order of bases in an organisms’ DNA; insertion, substitution, deletion The process by which two populations of the same species become so different that they can no longer interbreed A group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring The period between the birth of one generation and the birth of the next generation A historical sequence of life indicated by fossils found in layers of the Earth’s crust A way to find the actual age of rocks or fossils by using the decay rate and amounts of radioactive material (C14) Genetic Variation When organisms in a population differ in certain traits; the traits may be helpful or harmful Embryology Similar organisms share certain characteristics during beginning stages of development; embryos of vertebrates Vestigial Structure The remnant of a once used anatomical structure; may have been helpful at one time but no longer used for survival Natural Selection The process by which organisms with favorable traits survive and reproduce at a higher rate than other organisms PART 2: Identify the four steps of natural selection and explain what happens in each stage. 1. Overproduction: an organism produces more offspring than can survive to maturity. Ex. A sea turtle or alligator lay many eggs, but not all will hatch and survive to adulthood. 3. Struggle to Survive: Offspring will have to fight for available resources as they grow and develop (food, water, living space, mates). They may also face predation. Ex, Baby sea turtles may get eaten by birds or fish as they go out to sea. 2. Genetic Variation: the offspring will have some variation (differences) in appearance or behaviors. Ex. Some sea turtle babies might have a difference in shell color or size. 4. Successful Reproduction: This is the KEY to Natural Selection – the organisms that have beneficial adaptations that aid in survival will get to reproduce and pass on their genes. Ex. Baby sea turtles with larger/stronger front flippers may have an advantage of getting out to sea faster than others, aiding in survival. PART 3: Identify the 3 steps of speciation and explain what happens in each step. 1. Separation: Part of a population becomes isolated from the rest. This could be caused by a geographic disruption (new mountain range, canyon, river, lake, etc. or Environmental reasons (eating, living, or mating behaviors) 2. Adaptation: The two groups of the population slowly adapt to their changed environment through natural selection. Beneficial adaptations aid in survival. 3. Division: The two populations of organisms have become so different that they can no longer interbreed. This means that they are no longer the same species! PART 4:Identify the 6 pieces of Evidence for Evolution, and explain how they are used to support the theory of evolution. Fossil Record: The only way to know about life forms that are now extinct. By studying layers of rock, scientists can identify which fossils are oldest & most recent by relative dating. DNA: Similar organisms have similar DNA, showing a link to common ancestry. Mice and humans share >97% of the same DNA. Radiometric Dating: This is a way that scientists can determine the exact age of fossils by finding the amounts of radioactive elements left in organic material. Ex. Carbon14 Dating Comparative Embryology: The embryos of different vertebrates are very similar during the earliest stages of life. Vertebrate embryos share a few characteristics: gill slits, tail, backbone and nerve chord. Anatomical Similarity: Vertebrate organisms that have a similar skeletal structure may have come from a common ancestor. Ex. A human, bat, dolphin, and cat all share similar forelimb anatomy. Vestigial Structures: Sometimes organisms HAVE structures that they DO NOT use; These structures may have been useful at one point in time, but are no longer needed for survival. Ex. Leg bones in whales, Eyespots in blind mole-rats, Wisdom teeth in humans. PART 5: Choose an organism that either lives in a desert or forest biome. Draw a picture of the animal and label its adaptations. List at least 3 adaptations. PART 6: Short Answer: 1. The solidified remains or imprint of a previously existing organism is called: A fossil_________________________________________________ 2. Compare the age of fossils found deep in the Earth’s crust compared to those found closer towards the surface. What type of dating is this? Fossils found deep in the Earth’s crust are older than fossils found near the surface of the Earth. This is called relative dating.________________________________ 3. Explain why individuals in a population that has traits or abilities that give them a competitive advantage over other population members are more likely to survive and reproduce. Individuals with beneficial traits are more likely to get the food and other resources they need for survival. They might even become more attractive to a mate. These individuals will be more likely to survive and have successful reproduction.__ 4. According to Darwin, the four steps in natural selection are: __1. Overproduction 2. Genetic variation 3. Struggle to survive 4. Successful reproduction______________ 5. The “key” or the most important step of natural selection is_ Successful reproduction _. 6. The opposable thumb allows humans to grasp objects firmly. Because this feature helped humans to survive over time, it is called a(n)_adaptation___. 7. After 1850, dark peppered moths became more abundant than pale peppered moths. What factors caused the moths to turn black? Pollution from factories turned tree trunks black; moths with darker color mutation survived to reproduce 8. A newly formed canyon, mountain range, or lakes are a few of the ways that the first step of _speciation_ can occur. 9. In order for the American Bald Eagle to produce fertile offspring, who should it mate with and why? It should mate with a member of its own species or the offspring will not be fertile and will not be able to reproduce_ _______________ 10. If organisms share similar DNA, embryology, and skeletal structures, what does that mean? __They most likely share a common ancestor___________