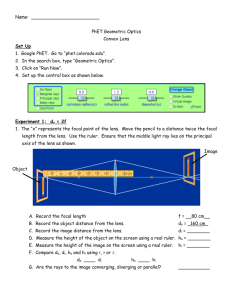
Solution
advertisement

Physics 112 Exam 3 Summer 2015 41. A beam of light in air strikes a slab of glass (n 1.50) at a 30.0° angle to the vertical. What is the angle of refraction? A) B) C) D) E) 30.0° 25.7° 19.5° 15.0° 10.3° Solution: n1 sin 1 n2 sin 2 sin 2 1.0 1 sin 30 ; 1.5 3 sin 2 n1 sin 1 n2 2 19.5° 42. A diver shines a flashlight upward from beneath the water at a 60.0° angle to the vertical. Index of refraction water is 1.33. At what angle does the light leave the water? A) B) C) D) E) 60° 50° 40° 30° It does not leave the water Solution: The critical angle for the total internal refractions is given by the equation: c 48.8 60.0 . sin c n2 n1 sin c 1 1.33 43. The speed of light in a certain substance is 89% of its value in water. What is the index of refraction of this substance? A) B) C) D) E) 1.00 1.21 1.49 1.60 3.00 Solution: c n We find the index of refraction from the equation: v ; v 0.89 vwater 0.89 c c 1.33 n n 1.33 / 0.89 , which gives n 1.49. Page 1 of 8 Physics 112 Exam 3 Summer 2015 44. Which statement concerning mirrors is wrong? A) B) C) D) E) Real image is always inverted Inverted image is always real Virtual image is always erect Erected image is always virtual Real and virtual images could be erect or inverted Solution: In mirrors and lenses real image is always inverted; it cannot be erect. 45. Which statement concerning lenses is wrong? A) B) C) D) E) Real image is always inverted Inverted image is always real Virtual image is always erect Erected image is always virtual Real and virtual images could be erect or inverted Solution: In mirrors and lenses real image is always inverted; it cannot be erect. 46. A 4.0-cm-tall object is placed 10 cm in front of a spherical mirror. It is desired to produce a virtual image 6.0 cm tall. What is the focal length of the mirror? A) B) C) D) E) 30 cm 25 cm 20 cm 15 cm 10 cm Solution: Virtual image is allays erect. We find the image distance from the magnification: m hi di ho do di d o hi ho di 10cm 6.0cm 15cm . 4.0cm We find the focal length from the equation: 1 1 1 ; d o di f 1 1 1 , which gives f 30cm. 10cm 15cm f Note! To produce a larger virtual image the mirror should be concave. As expected f>0. Virtual image is located behind the surface of the mirror. As expected, di 0. The image is located 15cm behind the surface. Page 2 of 8 Physics 112 Exam 3 Summer 2015 47. Find magnification, if a real image is located at the same distance from a mirror as the object? A) B) C) D) E) 1 -1 2 -2 It is impossible to have this kind of image Solution: If d o di , then from equation m di follows that magnification m=-1. do 48. Parallel light rays are directed from air into a double convex glass lens. These rays will converge at: A) B) C) D) E) Focal point Two focal distances from the lens One half of the focal from the lens At the center of the lens On the surface of the lens Solution: By definition, focal point is the point where parallel rays converge. 49. Monochromatic light falls on two very narrow slits. Successive fringes on a screen 5.00 m away are 6.5 cm apart near the center of the pattern. What is the distance between the slits if the wavelength of the light is 650 nm? A) B) C) D) E) 500 µm 100 µm 50 µm 25 µm 5.0 µm Solution: d sin m m We use equations: tan y x For small angles: dy m x m d x y1 d 650 10 9 m 5.0m 6.5 10 2 m 5.0 10 5 m 50m Page 3 of 8 Physics 112 Exam 3 Summer 2015 50. Monochromatic light falls on a slit that is 2.60 10 3 mm wide. If the angle between the first dark fringes on either side of the central maximum is 30.0° (dark fringe on one side to dark fringe on another side), what is the wavelength of the light used? A) B) C) D) E) 450 nm 511 nm 585 nm 627 nm 673 nm Solution: The angle from the central maximum to the first minimum is 1 = 30.0° /2 =15.0° We find the wavelength from equation: D sin m m D sin 1 2.60 10 6 msin 15.0 , which gives 6.73 10 7 m 673nm 51. The separation between adjacent maxima in a double-slit interference pattern using monochromatic light is A) B) C) D) E) Greatest for red light Greatest for green light Greatest for blue light The same for all colors of light It is smallest for green light Solution: Conditions for constrictive interference: d sin m m . For given index m, angle m is increasing with increasing wavelength . Maximum value of m is for the maximum value of , which is for red light. 52. A 3500 lines/cm grating produces a third-order fringe at a 28.0° angle. What wavelength of light is being used? A) B) C) D) E) 421 nm 447 nm 502 nm 631 nm 680 nm Solution: We find the wavelength from equation: d sin m; 1 2 10 m / cm sin 28.0 / 3 , which gives 3500lines / cm d sin / m 4.47 107 m 447nm. Page 4 of 8 Physics 112 Exam 3 Summer 2015 53. An important reason for using a very large diameter objective in an astronomical telescope is A) B) C) D) E) To increase the magnification To increase the resolution To form a virtual image To form a real image To increase the width of the field of view Solution: Recall Rayleigh criterion: R 1.22 D . Increasing diameter we increase resolution. 54. A lens appears greenish yellow ( 570 nm is strongest) when white light reflects from it. What minimum thickness of coating n=1.25 is used on such a glass (n 1.52) lens? A) B) C) D) E) 570 nm 512 nm 450 nm 321 nm 228 nm Solution: There are phase shifts on both surfaces: air-film and film-glass. For constructive interference we have: 2t m film m / n film , and tmin 2nfilm 570nm 2 1.25 228nm. 55. What is Brewster’s angle for a diamond submerged in water if the light is hitting the diamond (n 2.42 ) while traveling in the water (n =1.33)? A) B) C) D) E) 33° 41° 52° 61° 72° Solution: Because the light is coming from water to diamond, we find the angle from the vertical from tan p ndiamond 2.42 1.82, which gives p 61.2. nwater 1.33 Page 5 of 8 Physics 112 Exam 3 Summer 2015 56. What kinds of image observe people wearing glasses? A) B) C) D) E) Always real Always virtual Real if glasses’ power is positive, and virtual if glasses’ power is negative Real if glasses’ power is negative, and virtual if glasses’ power is positive It could be real and virtual for any power of glasses Solution: Image produced by glasses is on the same side from glasses as object. Also, erect image is always virtual. 57. A person has a far point of 14 cm. What power glasses would correct this vision if the glasses were placed 2.0 cm from the eye? A) B) C) D) E) +2.0 -2.0 -4.6 -6.5 -8.3 Solution: With the glasses, an object at infinity would have its image 14 cm from the eye or 14cm 2cm 12cm from the lens; di 12cm. P 1 1 1 1 1 8.3D f do di 0.12m 58. A nearsighted person wears contact lenses whose power is -5.0D. What is the person's far point? A) B) C) D) E) 5 cm 10 cm 20 cm 50 cm 1.0 m Solution: If d 0 , then d i f 1 / P 1 / 5.0m 1 0.20m 20cm . So, far point is 20cm Page 6 of 8 Physics 112 Exam 3 Summer 2015 59. A small insect is placed 5.0 cm from a 6.00-cm-focal -length lens. Calculate the angular magnification. A) B) C) D) E) 1.2 2.4 4.1 5.0 6.0 Solution: Magnification is M ' 25cm 25cm 5.0 d0 5.0cm 60. An astronomical telescope has an objective with focal length 85 cm and a 35-D eyepiece. What is the total magnification? A) B) C) D) E) -15 -20 -30 -35 -41 Solution: The magnification of the telescope is given by f M o f o P e 0.85m 35m 1 29.75 fe Page 7 of 8 Physics 112 Exam 3 Summer 2015 Record Sheet You may fill in this sheet with your choices, detach it and take it with you after the exam for comparison with the posted answers 41 C) 19.5° 51 A) Greatest for red light 42 E) It does not leave the water 52 B) 447 nm 43 C) 1.49 53 B) To increase the resolution 44 54 E) Real and virtual images E) 228 nm could be erect or inverted 45 55 E) Real and virtual images D) 61° could be erect or inverted 46 A) 30 cm 56 B) Always virtual 47 B) -1 57 E) -8.3 48 A) Focal point 58 C) 20 cm 49 C) 50 µm 59 D) 5.0 50 E) 673 nm 60 C) -30 Page 8 of 8