PhET Geometric Optics
advertisement
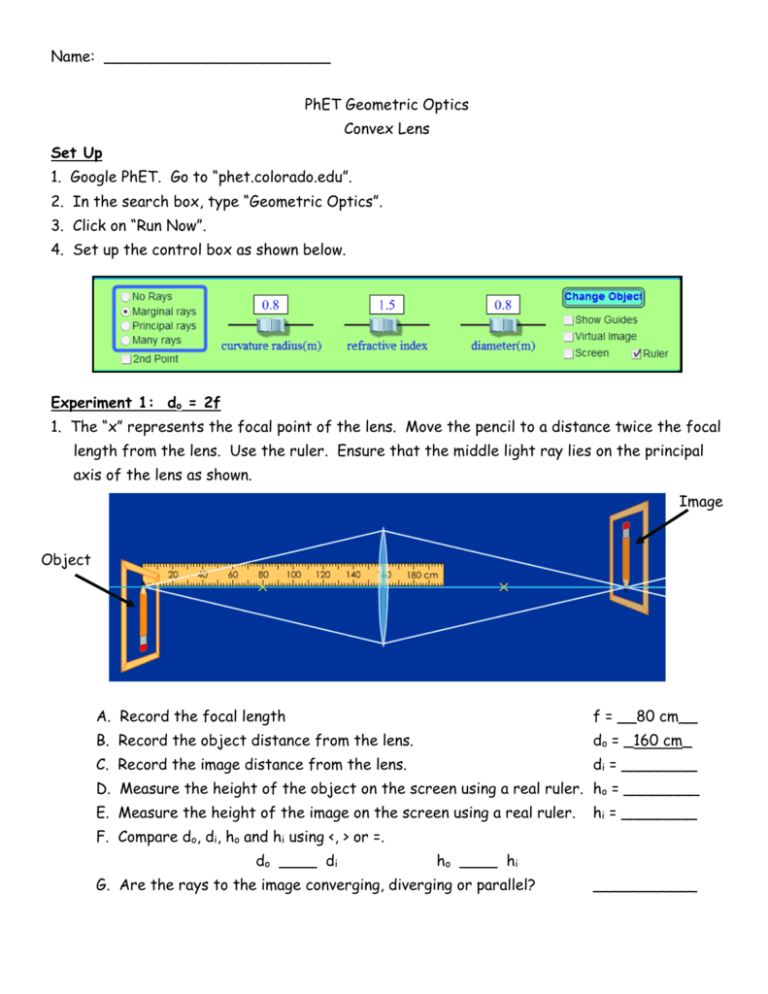
Name: ________________________ PhET Geometric Optics Convex Lens Set Up 1. Google PhET. Go to “phet.colorado.edu”. 2. In the search box, type “Geometric Optics”. 3. Click on “Run Now”. 4. Set up the control box as shown below. Experiment 1: do = 2f 1. The “x” represents the focal point of the lens. Move the pencil to a distance twice the focal length from the lens. Use the ruler. Ensure that the middle light ray lies on the principal axis of the lens as shown. Image Object A. Record the focal length f = __80 cm__ B. Record the object distance from the lens. do = _160 cm_ C. Record the image distance from the lens. di = ________ D. Measure the height of the object on the screen using a real ruler. ho = ________ E. Measure the height of the image on the screen using a real ruler. hi = ________ F. Compare do, di, ho and hi using <, > or =. do ____ di ho ____ hi G. Are the rays to the image converging, diverging or parallel? ___________ Experiment 2: do = 3f 1. Move the pencil to a distance 240 cm from the lens. Again use the ruler. Ensure that the middle light ray lies on the principal axis of the lens. A. Record the focal length f = ________ B. Record the object distance from the lens. do = _______ C. Record the image distance from the lens. di = ________ D. Measure the height of the object on the screen using a real ruler. ho = _______ E. Measure the height of the image on the screen using a real ruler. hi = ________ F. Compare do, di, ho and hi using <, > or =. do ____ di ho ____ hi G. Are the rays to the image converging, diverging or parallel? ___________ Experiment 3: do = 1.5f 1. Move the pencil to a distance 120 cm from the lens. Ensure that the middle light ray lies on the principal axis of the lens. A. Record the focal length f = ________ B. Record the object distance from the lens. do = _______ C. Record the image distance from the lens. di = ________ D. Measure the height of the object on the screen using a real ruler. ho = _______ E. Measure the height of the image on the screen using a real ruler. hi = ________ F. Compare do, di, ho and hi using <, > or =. do ____ di ho ____ hi G. Are the rays to the image converging, diverging or parallel? ___________ Experiment 4: do = f 1. Move the pencil to a distance 80 cm from the lens. If you have the pencil exactly on the x you will get the light rays bending crazily down. Place it slight before or after the x. Ensure that the middle light ray lies on the principal axis of the lens. A. Record the focal length f = ________ B. Record the object distance from the lens. do = _______ C. Are the rays converging, diverging or parallel? ___________ Experiment 5: do = 0.5f 1. Move the pencil to a distance 40 cm from the lens. Ensure that the middle light ray lies on the principal axis of the lens. Also, click on “Virtual Image” in the control box. You may click the “Virtual Image” on and off to see that this is a virtual image. A. Record the focal length f = ________ B. Record the object distance from the lens. do = _______ C. Record the image distance from the lens. di = ________ D. Measure the height of the object on the screen using a real ruler. ho = _______ E. Measure the height of the image on the screen using a real ruler. hi = ________ F. Compare do, di, ho and hi using <, > or =. do ____ di ho ____ hi G. Are the light rays (white lines) converging, diverging or parallel? ___________ Summary Answer the following questions using <, > or =. We performed 5 specific experiments. I would like you to generalize your answer. Your answer may include a range of distances. Go back and move the pencil around again if you are unsure of an answer. 1. When do you get a smaller image (i.e. di < do)? __When do is greater than 2f (do > 2f)__ 2. When do you get a larger image (i.e. di > do)? _______________________________ 3. When do you get no image (i.e. when the image light rays are parallel)? _______________________________ 4. When do you get an inverted image? _______________________________ 5. When do you get an upright image? _______________________________ 6. When do you get a real image? _______________________________ 7. When do you get a virtual image? _______________________________