File - Hopkins
advertisement

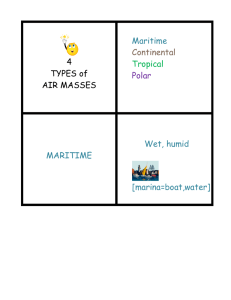
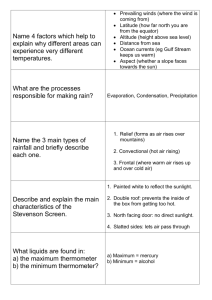
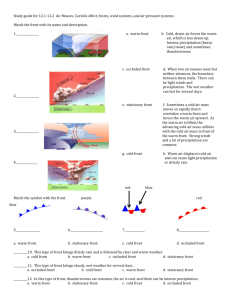
Weather Factors Test # Multiple Choice: -1. We have studied meteorology for almost a month now, so what is meteorology? -a. The study of weather and the factors that change it. -b. The study of rocks, minerals, and factors that change the earth’s surface. -c. The study of weather maps and air pressure. -d. The study of meteors. -2. Air pressure is measured using a ________________. -e. Thermometer -f. Isobars -g. Barometer -h. Triple Beam Balance -3. Prevailing Westerlies are winds that... -a. Blow from the east to the west around the equator. -b. Blow from the west to the east around the equator. -c. Blow from east to west between 30 and 60 degrees. -d. Blow from west to east between 30 and 60 degrees. -4. What is the name of an air mass that is cold and wet? -e. Continental Polar -f. Continental Tropical -g. Maritime Polar -h. Maritime Tropical -5. _____________ is a circular pattern in the sky that heats up the troposphere. -a. Conduction -b. Convection -c. Radiation -d. Convaduction -6. On a weather map this is shown as an alternating red and blue line. -e. Cold Front -f. Low Pressure System -g. Stationary Front -h. Occluded Front -7. When air cools down, air pressure… -a. Rises -b. Falls -c. Stays the same -d. Drops in temperature -8. During a day at the beach the _______ will heat up faster since the sun only has to heat a small amount of it. -e. Water -f. land -9. A cold front will bring… -a. Colder temperatures and heavy rains. -b. Warmer temperatures and heavy rains. -c. Colder temperatures and no rain. -d. Warmer temperatures and no rain. -10. We live in the… -e. Thermosphere -f. Mesosphere -g. Stratosphere -h. Troposphere -11. The rays from the sun heat up the earth, this is called… -a. Conduction -b. Convection -c. Radiation -d. Convaduction -12. Shown as a blue line with small triangles, this is a... -e. Cold Front -f. Low Pressure System -g. High Pressure system -h. Occluded Front -13. As you rise in altitude it gets harder to breathe, this is due to the… -a. Low air pressure -b. High air pressure -c. Warm temperatures -d. Cold temperatures -14. The curving of the winds due to the rotation of the earth, called… -e. Global Winds -f. Prevailing Winds -g. Doldrums -h. Coriolis Effect -15. The most dense weather front is… -a. Cold front -b. Warm Front -c. Maritime Polar -d. Maritime Tropical -16. Blocking meteorites is the job of this layer... -e. Thermosphere -f. Mesosphere -g. Stratosphere -h. Troposphere -17. When the ground heats the air that is touching it, this is called… -a. Conduction -b. Convection -c. Radiation -d. Convaduction -18. On a weather map, this usually means you will have clear skies. -e. Low Pressure -f. Cold Front -g. High Pressure -h. Warm Front -19. Warm air creates… -a. Lower Pressure -b. Higher Pressure -c. Occuded Pressure -d. Makes it rain -20. When traveling from the west coast to the east coast; this global wind will push the plane, and make the travel time less than flying from the east coast towards the west coast. -e. Easterly Trade Winds -f. Horse Latitudes -g. Prevailing Westerlies -h. Polar Easterlies -21. What air mass is warm and dry? -a. Maritime Polar -b. Maritime Tropical -c. Continental Polar -d. Continental Tropical -22. What are the two layers that have an increase in temperature? -e. Troposphere and Mesosphere -f. Stratosphere and Thermosphere -23. Shows equal areas of air pressure on a weather map? -a. Barometer -b. Thermometer -c. Isobars -d. Thermograph -24. When air becomes less dense… -e. Air pressure rises -f. Air pressure drops -g. Air pressure stays the same -h. Air becomes occluded -25. What global wind moves cold air from the poles? -a. Easterly Trade Winds -b. Horse Latitudes -c. Polar easterlies -d. Prevailing Westerlies -26. This air mass moves warm dry air north from Mexico… -e. Continental Polar -f. Continental Tropical -g. Maritime Polar -h. Maritime Tropical -27. What layer absorbs solar radiation from the sun and blocks it from hitting the earth ? -a. Troposphere -b. O-zone Layer -c. Mesosphere -d. Thermosphere -28. During the night at the beach the ______ is now warmer because it can hold heat better since it is so thick. -a. sun -b. land -c. water -d. moon -29. Shown as a red line with half circles... -a. Warm Front -b. Cold Front -c. Stationary Front -d. Occluded Front -30. How is air temperature measured? -e. Barometer -f. Thermometer -g. Isobars -h. Thermosphere -31. What local wind blows at night when the ocean is warmer than the land? -a. Land Breeze -b. Sea Breeze -c. Trade Wind -d. Convection -32. If a warm front brings no moisture, what kind of air mass made this front? -e. Continental Polar -f. Continental Tropical -g. Maritime Polar -h. Maritime Tropical -33. What layer contains all of Earth’s weather? -a. Stratosphere -b. Thermosphere -c. Troposphere -d. Mesosphere -34. What local wind blows during the day when the land is warmer than the ocean? -e. Land Breeze -f. Sea Breeze -g. Trade Wind -h. Convection -35. When observing weather on a weather map, weather typically moves… -a. From east to west -b. From west to east -c. From north to south -d. south to north -36. Wind is defined as the horizontal movement of air from areas of… -e. High to low pressure -f. Low to high pressure -g. Cold to warm temperature -h. Warm to cold temperature -37. Low pressure systems; air moves up, towards the center, and… (use your hand model) -a. Clockwise -b. Counter-clockwise -c. Downward -d. Upward -38. High pressure systems; air moves down, away from center, and… (use your hand model) -e. Clockwise -f. Counter-clockwise -g. Downward -h. Upward -39. What is the most abundant gas in earth’s atmosphere? -a. Carbon dioxide -b. Nitrogen -c. Oxygen -d. Dihydrogen Monoxide -40. What is the name of when a warm and a cold air front collide? -e. Cold Front -f. Warm Front -g. Occluded Front -h. Stationary Front Paragraph: Answer the following incomplete sentences. Simply bulleting the information will not allow you to gain full credit. -41-46. In detail explain how radiation, conduction, and convection heat Earth’s atmosphere. -47-50. Draw a Sea Breeze, include the following: -location of high pressure -location of low pressure -labeled sea breeze -time of day (Sun = daytime, moon = nighttime)