Stephen Teet
advertisement

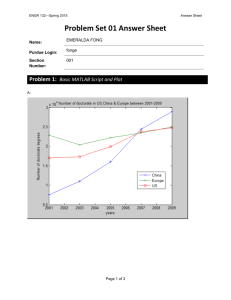
Stephen Teet Lab1 1. The wavelength regions represented are blue, green, red, near infrared, mid infrared and thermal infrared. 2. The most realistic color combination is using band 3 for red, band 2 for green and band1 for blue. 3. Setting red as band 2, green as band 3 and blue as band 4 gives a Duke blue look to the image. 4. Band 4 red, band 3 green and band 2 blue gives red vegetation. 5. Setting red, green and blue all to the same band gives a grey scale image. 6. At this image resolution I can see large water bodies (rivers, lakes), forested areas, farms, towns, large buildings, bare soil areas like the lake shoreline. 7. The screen RGB are the values of the colors used for the pixel to display, more of a visual representation. The data RGB values represent the reflectivity of the surface in each wavelength region. 8. The image is on the North Carolina Virginia border, a little east of central NC. 9. 10. Water has a low value over all wavelengths, it is highest at blue and drops off quickly to near infrared and more gradually through near and mid infrared. The forest and farm start slightly higher at blue and also taper at first but quickly jump back up at the green wavelength. The forest then steadily decreases through mid-infrared while the farm keeps a high value through near infrared before declining. The four land cover types have different spectral signatures because they have different reflectance properties and values at all/most wavelengths. 11. The greenest areas are north and south of the river almost centered east to west and an area in the southeast corner. 12. The areas east side of the figure, narrow in the north tapering out to the south, as well as in the west around the lake have the highest NDVI year round. 13. The Southwest region of the figure changes the most, this area seem to have a lot of farms. 14. 15. The four temporal signatures are extremely varied, all of them unique at almost every band (wavelength region?). Water has the most unique signature, while the farm and forest are the most similar. The differences in signatures are due to the different vegetation, or lack thereof, in the represented pixels. 16. At this resolution, I can see farms, forested areas, the lake and river and can barely make out the small town. I can no longer see buildings or other small and more narrow features that I could see in the other image. 17. 18. The surface profile depicts the reflectance values of the figure, with the raised areas being the higher values. The bumpier areas have a more divers land-use, giving more varied values.