Habitat and Niche
advertisement

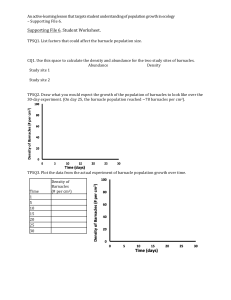
Habitat and Niche Habitat: where an organism lives Niche: the role an organism plays in its community…how an organism lives 2 types of Niches 1. Fundamental Niche: the entire range of resource opportunities an organism is potentially able to occupy. 2. Realized Niche: The part of its fundamental niche that an organism actively occupies. Barnacle Experiment Intertidal Zone: Shallow, unstable environment. It is higher in salt content, waves crashing and greater temperature fluctuations. C.S. barnacles live here. They can withstand the extreme conditions. Deep Water Zone: Deep water offers a more stable environment. This is the preferred habitat. S.B. barnacles live here. The S.B. barnacle is the better competitor because it occupies the deep water zone, however, the S.B. barnacle is not good at extreme conditions. What was observed during the experiment?: When the S.B. barnacles were removed from the deep water zone the C.S. barnacles replaced them. Conversely, when the C.S. barnacles were removed the S.B barnacles DID NOT move to the intertidal zone. Results of the Experiment: The C.S. barnacles’ fundamental niche is both the intertidal zone (shallow water) and the deep water zone. HOWEVER, the C.S. barnacles’ realized niche is the intertidal zone (shallow water) because they cannot occupy the deep water zone because the S.B. barnacles are already there. The S.B. barnacles’ fundamental niche is the deep water zone and its realized niche is the deep water zone. Conclusion: competition occurs in nature and can explain the distinction between a fundamental niche and a realized niche.