Classification
advertisement

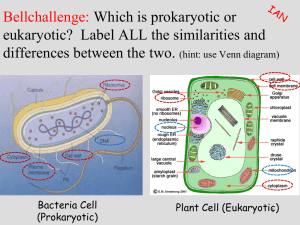
SC.912.L. 15.6 Discuss distinguishing characteristics of the domain and kingdoms of living organisms. CC: RST. 11-12.1, SL.11-12.4, MP.4 Polar bears and Brown Bears are their common names but how can we scientifically name them? How do you know the cat on the left? • Puma • Mountain lion • Florida panther • Cougar Puma concolor= cougar Puma concolor coryi= florida panther COMMON NAME SCIENTIFIC NAME Vary among languages and from place to place • Cougar, mountain lion, puma, panther Binomial Nomenclature- two word naming system • Created by botanist Carolus Linnaeus • Written in italics • First word begins with a capital letter • Second word is lowercased Different species can have the same common name • Buzzard (UK)- hawk • Buzzard (USA)- vulture First part of the name is the Genus to which the organism belongs. • Genus- group of similar species Second part of the name is unique to each species. • Description of an important trait or the organism’s habitat Example: Polar Bear Example: Ursus maritimus Used to identify organisms Series of paired statements or questions that describe alternative possible characteristics of an organism. System that organized species into taxa that formed a hierarchy or set of ordered ranks. Taxa Description Species Group of individuals capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. Genus (plural: genera) Group of similar species Family Several Genera that share similar characteristics. Order Closely related families are grouped into the next larger rank. Class Similar orders Phylum Classes are grouped into a phylum Kingdom Largest and most inclusive Problems with Traditional Classification • Linnaeaus System is based on similarities and differences • The crab, barnacles, and limpet share some similarities and differences. • Under traditional classification, crabs would be classified into a separate group. BUT LOOKS can be deceiving! Look more closely! LIMPET BARNACLE Limpet and barnacle larvae are very different. Barnacles have jointed limbs. Limpets DON’T ! Barnacles have a segmented body Limpets DON’T ! Barnacles have an exoskeleton that molts. Limpets DON’T ! CRAB Look more closely! LIMPET CRAB BARNACLE Crab and barnacle larvae are very similar Barnacles have jointed limbs. So do CRABS ! Barnacles have a segmented body So do CRABS ! Barnacles have an exoskeleton that molts. So do CRABS ! LIMPET SNAIL Limpets have an internal anatomy more like snails, which are MOLLUSKS. Because of these characteristics, scientists have concluded that barnacles are more closely related to crabs than to MOLLUSKS BOTH crabs and barnacles have been classified as CRUSTACEANS Scientists today try to assign species to a larger group in ways that reflect how closely members of those groups are related to each other. Evolutionary Classification- grouping organisms based on evolutionary history. • Phylogeny: evolutionary history of lineages. Common ancestors get placed in higher taxa whose members are more closely related to one another than to any other group. This classification system groups organisms into groups called CLADES. Clades- group of species that includes 1. single common ancestor 2. and all descendants of that ancestor—living and extinct. • Links groups of organisms by showing how evolutionary lines, or lineages, branches off from common ancestors. Derived Characters- a trait that arose in the most recent common ancestor of a particular lineage and was passed along to its descendants. • certain kinds of characters are looked at when assigning organisms into clades unlike Linnaeaus classification. Linnaean Class Reptilia is not a clade because it does NOT include modern birds. Birds are descendants of reptiles, which can be seen from the cladogram on the right! Genes can be derived characters. The more derived GENETIC characters two species share, the more recently they shared a common ancestor and the more closely they are related in evolutionary terms. • • • • • • • • • • Prokaryote- unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus Eukaryote- organisms whose cells contain a nucleus Peptidoglycan- serves a structural role in the walls of bacteria. Cellulose- provides strength and rigidity to plant cells Chitin- tough, protective covering or structural support for certain organisms. Chloroplast- organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy. Multicellular- two or more cells in an organism Unicellular- organism is made up of one cell. Autotroph- organism that is able to capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food from inorganic compounds—producer. Heterotroph- organism that obtains food by consuming other living things— consumer.