Human Anatomy and Physiology Unit 02 Basic Chemistry Matter
advertisement

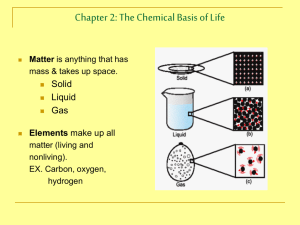
Human Anatomy and Physiology Unit 02 Basic Chemistry Matter and Energy __________________________________- anything that occupies spaces and has mass __________________________________- the ability to do work o Chemical o Mechanical o Electrical o Radiant Composition of Matter __________________________________ o Fundamental Units of Matter 96% of the body is made from four elements o ___________________________________ o ___________________________________ o ___________________________________ o ___________________________________ ___________________________________ o Building blocks of elements Atomic Structure o Nucleus ___________________________ o Outside of Nucleus ___________________________ ___________________________ Molecules and Compounds Molecule- two or more of the ____________________________ atom combined chemically o Ex: Compound- two or more ___________________________atoms combined chemically o Ex: Chemical Reactions Atoms are united by ______________________________ ____________________________ Atoms ____________________________from other atoms when chemical bonds are ___________________________ Electrons and Bonding ___________________________________ involves interactions between electron in the outer shell Chemical Bonds ______________________________________ o Forms when electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another o Ions Charged particles Anions are _______________________ Cations are _______________________ Either donate or accept electron 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology _____________________________________ o Atoms become stable through shared electrons o Single covalent bonds share __________ electron o Double covalent bonds share __________ electrons o Polarity Covalent bonded molecules Some are ____________________________________ o Electrically neutral as a molecule o ______________________________________ Unit 02 Basic Chemistry Some are ___________________________________ o Have a positive and negative side ______________________________________ o Weak chemical bonds o Hydrogen is attracted to negative portion of polar molecule o Provides attraction between molecules Patterns of Chemical Reactions Synthesis reaction ________________________________________ o Atoms or molecules combine o Energy is absorbed for bond formation Decomposition reaction __________________________________ o Molecule is broken down o Chemical energy is released Exchange reaction ________________________________________ or _______________________________________ o Ex: _________________________________________________ o Involves both synthesis and decomposition Biochemistry: Essentials for Life Organic Compounds o Contain ________________________ and _________________________ o Most are ________________________________ bonded o Example: _____________________________________ Inorganic Compounds o Lack _____________________________ o Tend to be simpler compounds o Example: _____________________________________ 2 Human Anatomy and Physiology Unit 02 Basic Chemistry Important Inorganic Compounds Water o Most abundant inorganic compound Vital Properties High heat capacity: ________________________________________________________________ Polarity/solvent: ________________________________________________________________ Chemical reactivity: ________________________________________________________________ Cushioning: ________________________________________________________________ Salts o Easily dissociate into ions in the presence of water o Vital to many body functions o Include _________________________________________ which conduct electrical currents pH Acids o Can release detectable hydrogen ions Bases o Proton Acceptors Measuring relative concentration of __________________________________ ions o pH 7= _____________________________ o pH below 7= _____________________________ o pH above 7= _____________________________ o Buffers: chemicals that can regulate pH change Macromolecules Carbohydrates Monomer _______________________ Polymer _______________________ Example _______________________ Lipids _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ Proteins _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ Nucleic Acids _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ 3 Human Anatomy and Physiology Carbohydrates o Contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen o Include sugars and starches o Classified according to size ______________________________________ – simple sugars Unit 02 Basic Chemistry ______________________________________ – two simple sugars joined by dehydration synthesis ______________________________________ – long branching chains of linked simple sugars Lipids o Contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen Carbon and hydrogen outnumber oxygen o Insoluble in water o Common lipids in the human body Neutral fats (triglycerides) Found in ___________________________________ Composed of fatty acids and glycerol Source of _________________________________ Phospholipids Steroids Include cholesterol, bile salts, vitamin D, and some hormones Form _____________________________________ Cholesterol: the basis for all ___________________________ made in the body Proteins o Made of ___________________________________ Contain carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur o Account for over half of the body’s organic matter Provides for construction materials for body tissues Plays a vital role in cell function o Act as ______________________________, ______________________________, and _____________________________ Enzymes act as biological catalysts Increase the rate of chemical reactions 4 Human Anatomy and Physiology Unit 02 Basic Chemistry Nucleic Acids o Provide blueprint of life o Nucleotide bases A = Adenine G = Guanine C = Cytosine T = Thymine U = Uracil o __________________ pairs with ______________ o _________________ pairs with ______________ o Make DNA and RNA o Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) Organized by complimentary bases to form double helix Replicates before cell division Provides instruction for every protein in the body Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) o Chemical energy used by all cells o Energy is released by breaking high energy phosphate bond o ATP is replenished by oxidation of food fuels 5