Plant Systems AG2
advertisement
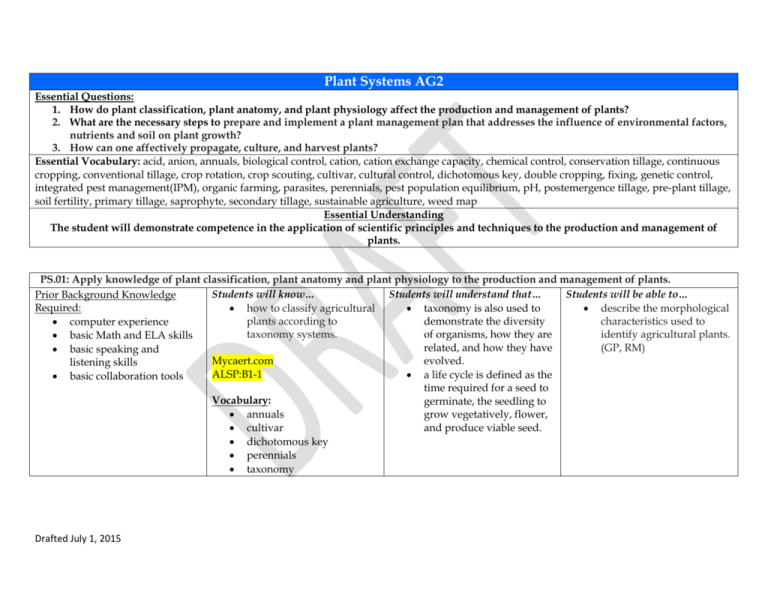
Plant Systems AG2 Essential Questions: 1. How do plant classification, plant anatomy, and plant physiology affect the production and management of plants? 2. What are the necessary steps to prepare and implement a plant management plan that addresses the influence of environmental factors, nutrients and soil on plant growth? 3. How can one affectively propagate, culture, and harvest plants? Essential Vocabulary: acid, anion, annuals, biological control, cation, cation exchange capacity, chemical control, conservation tillage, continuous cropping, conventional tillage, crop rotation, crop scouting, cultivar, cultural control, dichotomous key, double cropping, fixing, genetic control, integrated pest management(IPM), organic farming, parasites, perennials, pest population equilibrium, pH, postemergence tillage, pre-plant tillage, soil fertility, primary tillage, saprophyte, secondary tillage, sustainable agriculture, weed map Essential Understanding The student will demonstrate competence in the application of scientific principles and techniques to the production and management of plants. PS.01: Apply knowledge of plant classification, plant anatomy and plant physiology to the production and management of plants. Students will know… Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to classify agricultural taxonomy is also used to describe the morphological plants according to demonstrate the diversity characteristics used to computer experience taxonomy systems. of organisms, how they are identify agricultural plants. basic Math and ELA skills related, and how they have (GP, RM) basic speaking and Mycaert.com evolved. listening skills ALSP:B1-1 a life cycle is defined as the basic collaboration tools time required for a seed to Vocabulary: germinate, the seedling to annuals grow vegetatively, flower, and produce viable seed. cultivar dichotomous key perennials taxonomy Drafted July 1, 2015 PS.02: Prepare and implement a plant management plan that addresses the influence of environmental factors, nutrients and soil on plant growth. Students will know… Students will understand that … Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to prepare growing soil fertility involves the determine the hydraulic media for use in plant storage of nutrients and conductivity for soil and computer experience systems. refers to the availability of how the results influence basic Math and ELA skills those nutrients for plants. irrigation practices. (GP) how to develop and basic speaking and implement a fertilization soil pH is the measure of discuss the influence of pH listening skills plan for specific plants or acidity or alkalinity of the and cation exchange basic collaboration tools crops. soil. capacity on the availability of nutrients. (GP) soil productivity can be Mycaert.com affected by organic matter, ALSP:D3-2 soil depth, surface slope, soil organisms, and Vocabulary: nutrient balance. acid anion cation cation exchange capacity pH soil fertility PS.03: Propagate, culture and harvest plants. Students will know… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to demonstrate plant propagation techniques. computer experience how to develop and basic Math and ELA skills implement a plant basic speaking and management plan for crop listening skills production. basic collaboration tools how to develop and implement a plan for integrated pest management. how to apply principles Drafted July 1, 2015 Students will understand that … Students will be able to… there are a variety of tillage explain pollination, crosssystem options available to pollination and selfthe crop producer. pollination of flowering plants. (GP) conservation tillage is a tillage program aimed at demonstrate sowing reducing erosion by leaving techniques and provide crop residues on a rough favorable conditions for soil surface. seed germination. (GP) major pest groups and their define micropropagation, biology knowledge is discuss advantages required to ensure success associated with the practice and practices of sustainable agriculture to plant production. how to harvest, handle and store crops. Mycaert.com APSR:D2-4 APSR:E5-1 APSR:E5-5 APSR:E5-6 Vocabulary: biological control chemical control conservation tillage continuous cropping conventional tillage crop rotation crop scouting cultural control double cropping fixing genetic control integrated pest management(IPM) organic farming parasites pest population equilibrium postemergence tillage pre-plant tillage primary tillage saprophyte secondary tillage Drafted July 1, 2015 in reducing crop losses due to pests. the goal of managing pest populations is to avoid a profit reduction. integrated pest management (IPM) is an organized program in which the best management methods available are used to keep pest populations below the economic injury level. there are many benefits of IPM to agriculture and the environment. bacteria spread easily, but there are various methods for control. different species of bacteria affect plants in different ways. one of the keys to a successful integrated pest management program is regular monitoring of field crop conditions and pest infestations. scouting for weeds is necessary to determine the need to control weeds that can compete with crops for light, water, and nutrients. insect pests can be monitored in several ways, and several methods of and outline the four main stages of the process. (FO) explain the principles behind recombinant DNA technology and the basic steps in the process. (GP) give examples of the risks and advantages associated with genetically modified plants. (GP) inspect propagation material for evidence of pests or disease. (PM) prepare soil for planting with the addition of amendments. (SO) prepare growing media for planting. (SO) identify types of plant pests and disorders. (PM) identify major local weeds, insect pests and infectious and noninfectious plant diseases. (PM, RM) design and implement a crop scouting program. (PM) describe damage caused by plant pests and diseases. (PM) diagram the life cycles of major plant pests and diseases. (PM) describe pest control strategies associated with integrated pest sustainable agriculture weed map scouting are utilized. Drafted July 1, 2015 management. (PM) describe types of pesticide controls and formulations. (PM) explain risks and benefits associated with the materials and methods used in plant pest management. (PM) explain procedures for the safe handling, use and storage of pesticides. (PM) evaluate environmental and consumer concerns regarding pest management strategies. (PM) explain sustainable agriculture and objectives associated with the strategy. (GP, FO, RM) describe sustainable agriculture practices and compare the ecological effects of traditional agricultural practices with those of sustainable agriculture. (GM) identify harvesting methods and harvesting equipment. (GP) assess the stage of growth to determine crop maturity or salability and demonstrate proper harvesting techniques. (GP) PS.04: Employ elements of design to enhance an environment. (NA) Drafted July 1, 2015 explain reasons for calculating crop yield and loss. (GP) evaluate crop yield and loss data. (GP) implement plans to reduce crop loss. (GP) explain the proper conditions to maintain the quality of plants and plant products held in storage. (GP) explain the reasons for preparing plants and plant products for distribution. (GP) demonstrate techniques for grading, handling and packaging plants and plant products for distribution. (GP)








![NAME PLS 205 Final [Total Points in Exam = 100] March 12, 2014](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007026756_1-7a438545e3b67fbfb78298e89562cbf1-300x300.png)