Learning Center: High School Science
advertisement
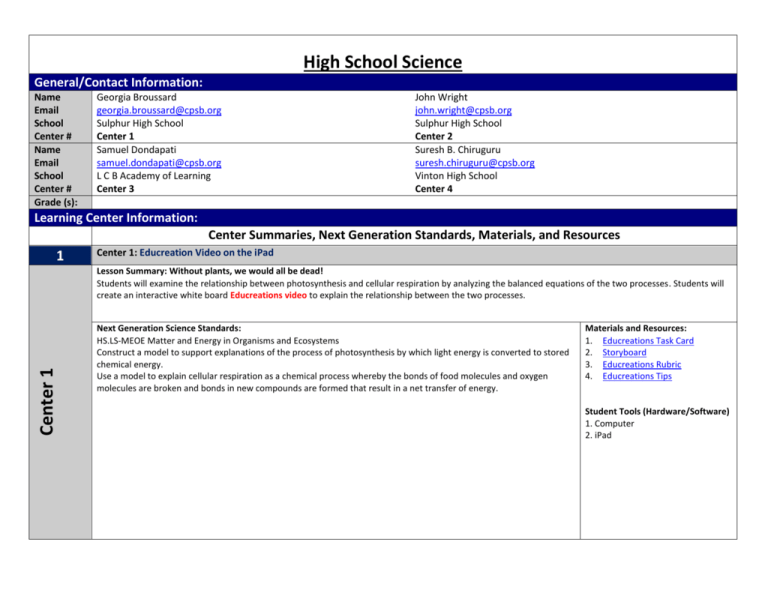
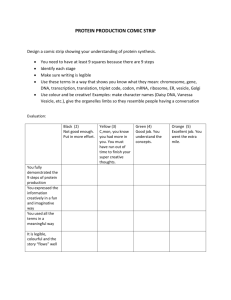
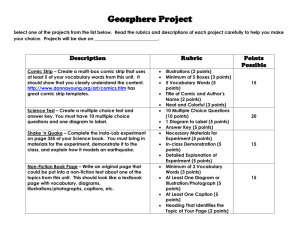
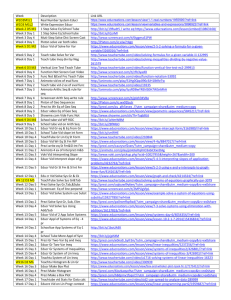
High School Science General/Contact Information: Name Email School Center # Name Email School Center # Grade (s): Georgia Broussard georgia.broussard@cpsb.org Sulphur High School Center 1 Samuel Dondapati samuel.dondapati@cpsb.org L C B Academy of Learning Center 3 John Wright john.wright@cpsb.org Sulphur High School Center 2 Suresh B. Chiruguru suresh.chiruguru@cpsb.org Vinton High School Center 4 Learning Center Information: Center Summaries, Next Generation Standards, Materials, and Resources 1 Center 1: Educreation Video on the iPad Center 1 Lesson Summary: Without plants, we would all be dead! Students will examine the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration by analyzing the balanced equations of the two processes. Students will create an interactive white board Educreations video to explain the relationship between the two processes. Next Generation Science Standards: HS.LS-MEOE Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems Construct a model to support explanations of the process of photosynthesis by which light energy is converted to stored chemical energy. Use a model to explain cellular respiration as a chemical process whereby the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and bonds in new compounds are formed that result in a net transfer of energy. Materials and Resources: 1. Educreations Task Card 2. Storyboard 3. Educreations Rubric 4. Educreations Tips Student Tools (Hardware/Software) 1. Computer 2. iPad 2 Center 2: Comic Strip Center 2 Lesson Summary: The Ultimate Battle of Good Versus Evil Students will construct a short comic strip of the ultimate battle (balanced ionic compound) showing that both sides are evenly balanced using Marvel comic strip heroes to represent cations and Marvel comic strip villains to represent anions. This will also explain what causes atoms to form ionic bonds and why elements bond with other elements in varying amounts. Next Generation Science Standards: HS-PS1-b. Use the periodic table as a model to predict the relative properties of elements based on patterns of electrons in the outer energy level of atoms. [Clarification Statement: An example of a pattern that predicts element properties would be Group I of the periodic table. These elements all have one electron in the outermost energy level and as such are all highly reactive metals. Other properties could include types of bonds formed with other elements, number of bonds formed, and reactions with oxygen.] Materials and Resources: 1. Comic Strip Task Card 2. Ionic Naming Worksheet 3. Ions List 4. Heroes and Villains Guide 5. Making a Comic Directions 6. Comic Strip Rubric HS-PS1-i. Construct an explanation to support predictions about the outcome of simple chemical reactions, using the structure of atoms, trends in the periodic table, and knowledge of the patterns of chemical properties. [Clarification Statement: Examples of chemical reactions would include the reaction of sodium and chlorine, or carbon and oxygen, or carbon and hydrogen.] [Assessment Boundary: Chemical reactions not readily predictable from the element’s position on the periodic table (i.e., the main group elements) and combustion reactions are not intended. Reactions typically classified by surface level characteristics (e.g., double or single displacement reactions) are not intended.] Student Tools (Hardware/Software) 1. computer 2. Website: http://marvelkids.marvel.com/game s/play/75/create_your_own_comic 3 Center 3: Prezi Center 3 Lesson Summary: Beat the Stoichiometric Challenge Students will conduct a lab how stoichiometry works, showing that if concentrations and amounts of the starting materials are known that the theoretical yield can be calculated from a balanced chemical equation. They will create a Prezi explaining how much SO2 is released in to the air from the local refinery and calculate how much lime stone is required to contain SO2 pollution in to the air. 4 Next Generation Science Standards: PS1.B: Chemical Reactions: 1. Substances react chemically in characteristic ways. In a chemical process, the atoms that make up the original substances are regrouped into different molecules, and these new substances have different properties from those of the reactants. (a),(b) 2. The total number of each type of atom is conserved, and thus the mass does not change. (a),(c) http://nextgenscience.org/next-generation-science-standards Materials and Resources: 1. Prezi Task Card 2. Stoichiometric Lab Sheet 3. Prezi Rubric Student Tools (Hardware/Software) 1. Computer 2. http://prezi.com/ Center 4: MovieMaker Video Lesson Summary: Saving One Species At a Time Center 4 Students will examine several ways that species are being threatened with extinction globally, which types of threats are having the largest impact on biodiversity, and how humans cause extinctions. Students will create a public service announcement in the form of a short TV documentary (using Windows Movie Maker) about saving the endangered species. Next Generation Science Standards: Materials and Resources: HS.LS-IRE: Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems Students who demonstrate understanding can: E. Use evidence to construct explanations and design solutions for the impact of human activities on the environment and ways to sustain biodiversity and maintain the planet’s natural capital. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. MovieMaker Task Card Storyboard 1 Storyboard 2 MovieMaker QuickTips MovieMaker Rubric http://www.fws.gov/ http://www.fws.gov/le/lawsregulations.html http://www.fws.gov/endangere d/ Student Tools (Hardware/Software) 1. Computer 2. Flipcam