Sentence Combining and Conjunctions
advertisement

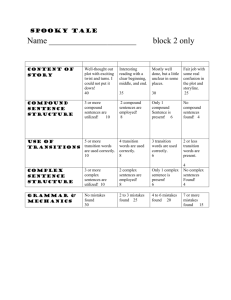
Sentence Combining and Conjunctions Mini Lesson Ms. Z. Aleman English IV Summary: As students read, they will be asked to identify and model compound and complex sentences. They will also use conjunctions appropriately in their own writing in order for sentences to become compound and complex. Students will utilize the Writer’s Choice Grammar book (grammar: sentence combining, coordinating/subordinating conjunctions section) and take notes on rules and practice with chosen exercises. Objectives: Learners will be able to; Identify conjunctions , compound and complex sentences Create compound and complex sentences Understand the effective use of compound and complex sentences Sunshine State Standards: The student will edit and correct the draft for standard language conventions. LA.1112.3.4.5 - varied sentence structure, including the elimination of dangling or misplaced modifiers, run-on or fused sentences, and unintended sentence fragments. Strategies: KWL Question/Answer Instructional Materials: Smart Board Internet Access Ms. Sentence Variety, 1 Microphone Pen and Paper Writer’s Choice Book Instructional Time: One class session or 40-50 minutes Directions: Write the following sentences on the board. The boy ran fast. The boy did not win the race. The boy ran fast, but he did not win the race. Show students breakdown: The boy ran fast, but he did not win the race. This is an independent clause This is an independent clause This is a coordinating conjunction. It joins the sentences with a comma so that two become one. A compound sentence formula is as follows: IC + Comma +CC+ IC=Compound Sentence. Coordinating conjunctions are also known as FANBOYS. (Acronym) For And Nor But Or Ye So Place a comma in front of these conjunctions and join two independent clauses to create a compound sentence. Now You TRY. Have students write their own 2 sentences and combine them using one of the FANBOYS Ms. Sentence Variety, 2 Culminating Activity ***Have student volunteers go to the board with their sentences and diagram them as previously modeled. Directions: Write the following on the board. Sandy went to the party even though she did not have permission. IC Subordinate Clause Both of these sentences are DC complex. Even though she did not have permission, Sandy went to the party. DC Comma IC Complex sentence formula: IC +DC DC + Comma +IC This is a great opportunity to ask students which subordinating conjunctions they are familiar with and offer suggestions: Common Subordinating Conjunctions After as though Provided (that) until Although because since when As far as before as long as whenever As if if though unless As soon as considering that than wherever Ms. Sentence Variety, 3 Culminating Activities: Now have student write 3 complex sentences. Make sure to have them diagram the sentences and have them share with the person to their right. That person is to diagram as modeled and share on the board. Once students are familiar with these varied sentences, begin the reading selection for the day. After reading the first paragraph, partner students and have them; Identify compound and complex sentences Diagram the sentences to show IC and DC Explain why the sentence is Compound or Complex Students will take an interactive quiz cooperatively (in class activity) Home Learning: Students will write and diagram 10 compound sentences using all the FANBOYS. Students will write and diagram 10 complex sentences using the formulas provided in class. Five sentences per formula. Ms. Sentence Variety, 4