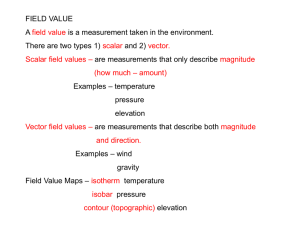
Unit 2 Topographic Maps
advertisement
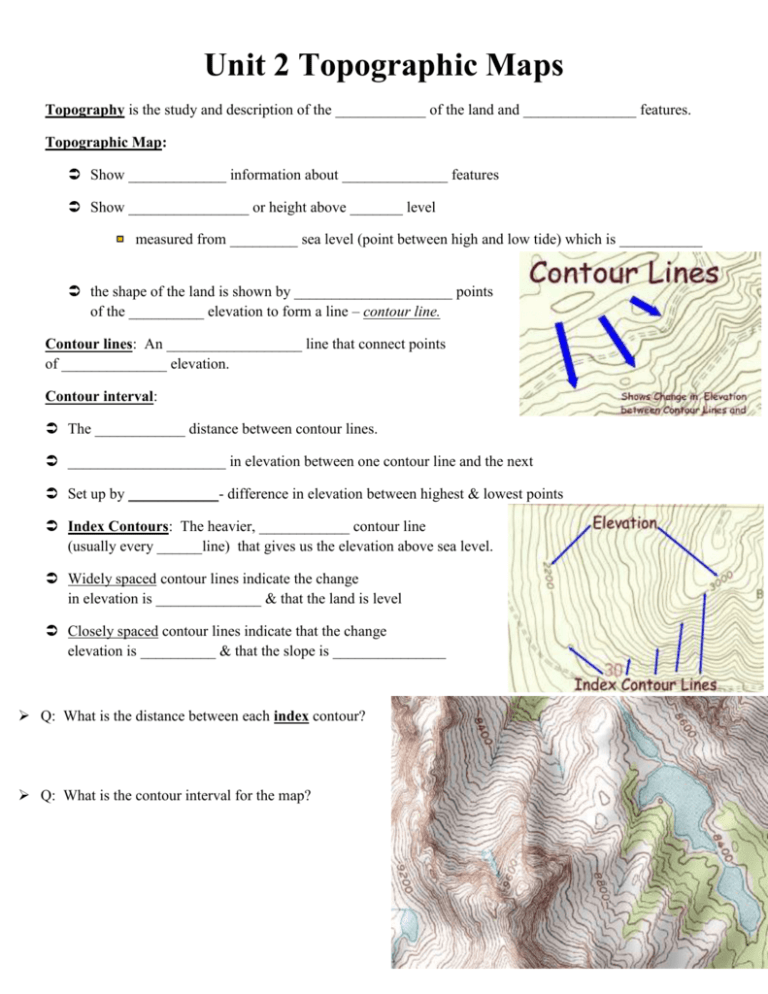
Unit 2 Topographic Maps Topography is the study and description of the ____________ of the land and _______________ features. Topographic Map: Show _____________ information about ______________ features Show ________________ or height above _______ level measured from _________ sea level (point between high and low tide) which is ___________ the shape of the land is shown by _____________________ points of the __________ elevation to form a line – contour line. Contour lines: An __________________ line that connect points of ______________ elevation. Contour interval: The ____________ distance between contour lines. _____________________ in elevation between one contour line and the next Set up by ____________- difference in elevation between highest & lowest points Index Contours: The heavier, ____________ contour line (usually every ______line) that gives us the elevation above sea level. Widely spaced contour lines indicate the change in elevation is ______________ & that the land is level Closely spaced contour lines indicate that the change elevation is __________ & that the slope is _______________ Q: What is the distance between each index contour? Q: What is the contour interval for the map? in Contour Properties Contour lines form a _____ when crossing streams. The V always points _______________ to mouth of river V-shaped contour lines show a ________________, (V points to _____________ end of valley) Contour lines that form closed _________ indicate a _______________ or mountain peak. Concentric circles with short straight ________ indicate a closed ___________________. Maps & Globes Earth’s Shape: Oblate spheroid – polar ___________________ and equatorial bulge, caused by rotation Latitude: lines showing North and South of the equator (_________________) ___________________ is 0 º Each latitude has _____ equal parts known as ________________. Each minute equals ________ km (symbol ’) Each minutes has 60 equal parts known as __________________ (symbol”) FRACTIONS OF A DEGREE 1 degree = 60 minutes or 1 minute is 1/60th of a degree Use minutes if location is ______ directly on the latitude/longitude line Written ----- Degree/minute = ______° ______’ compass direction Longitude: lines showing _________ and ________ of the prime meridian (meridians) ____________ Meridian: 0º pass through Greenwich, England Meridian ______________ prime meridian is 180º 180º ____ prime meridian 0º 180º _____ Distance between longitudes depends on __________ you measure Distance in between each line ____________________ as you move from the equator to the poles LONGITUDE & TIME The world rotates (spins) __________° in _____ hours. 360° / 24 hours = _________° per hour The world has 24 _____________ zones, each l5° apart. THERE IS A _____HOUR TIME DIFFERENCE FOR EVERY 15° OF _____________________ Greenwich, England is the _______________ point for time zones The world rotates __________ to __________ (counterclockwise), time zones to the east are ______________ of the those time zones to the west Great circles: any circle that divides the globe into ______________ Equator is only _______________ that is a great circle Any _______ longitudes across from each other is a great circles Used for ______ travel and _______ travel PARTS of a MAP Legend: list of _____________ and their _______________ Direction: Maps drawn with north at _____, east at the __________, _________ at the left, and ____________ at the bottom ↑N Scale: shows relationship between _______________ on map to distance on ___________ Types of Scales Graphic Scale: printed line divided into ___________ parts and labeled Verbal Scale: a ___________ statement Ex: one centimeter equals one kilometer Fractional Scale: (ratio) 1 ________ of distance on map to same unit on the __________