Gas Exchange in Lungs: Biology Exam Questions
advertisement
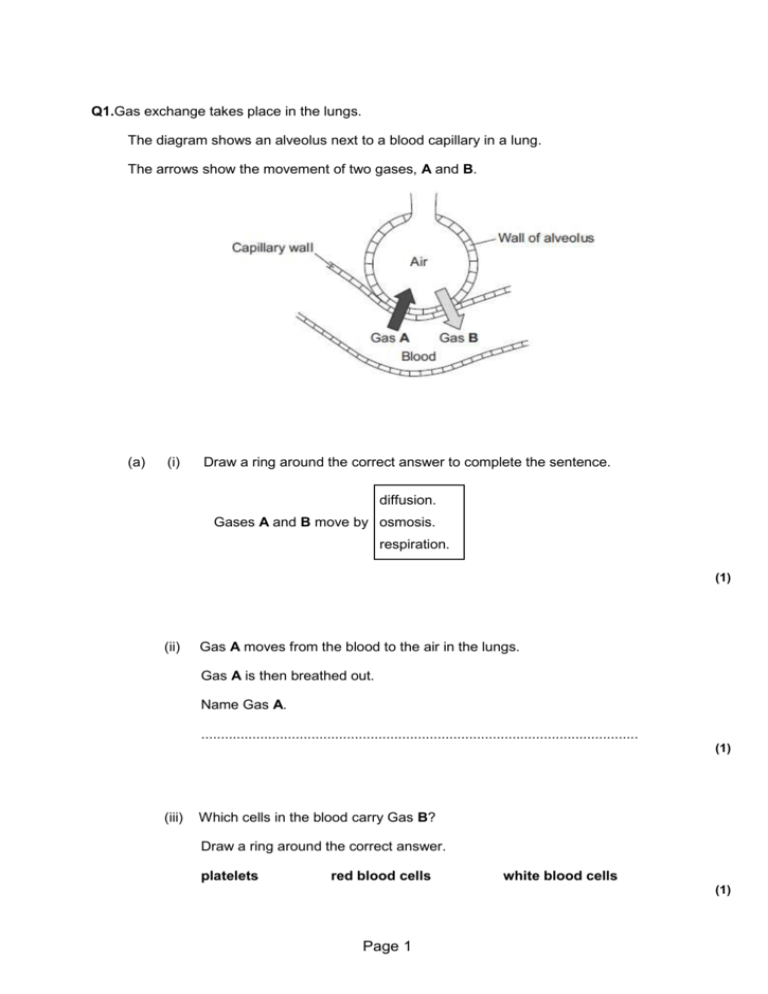
Q1.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. (a) (i) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. diffusion. Gases A and B move by osmosis. respiration. (1) (ii) Gas A moves from the blood to the air in the lungs. Gas A is then breathed out. Name Gas A. ............................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Which cells in the blood carry Gas B? Draw a ring around the correct answer. platelets red blood cells white blood cells (1) Page 1 (b) The average number of alveoli in each human lung is 280 million. The average surface area of 1 million alveoli is 0.25 m2. Calculate the total surface area of a human lung. ........................................................................................................................ Answer ...................................................................... m2 (2) (c) An athlete trains to run a marathon. The surface area of each of the athlete’s lungs has increased to 80 m2. Give one way in which this increase will help the athlete. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (1) (Total 6 marks) Q2.(a) Diagram 1 shows part of the breathing system. Diagram 1 (i) Use words from the box to name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. alveolus diaphragm Page 2 lung rib trachea A ......................................................... B ......................................................... C ......................................................... D ......................................................... (4) (ii) Parts B and C move when we breathe in. Part B moves ......................................................................................... Part C moves ......................................................................................... (2) (b) A student used the apparatus shown in Diagram 2 to measure the maximum volume of air that he could breathe in one breath. When the student breathes in, the piston moves upwards. The piston moves back down after the student has breathed out. Diagram 2 The student breathes in through the apparatus three times. The drawings show the position of the piston after each of the three breaths. The volumes are measured in cm3. Page 3 (i) Read the volume of each breath and write the volume in the table. Volume in cm3 Breath 1 Breath 2 Breath 3 ..................... ..................... ..................... (3) (ii) Calculate the mean volume of air breathed in. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... Mean volume of air breathed in = ....................................... cm3 (2) (c) A teacher asks the student to investigate if students who take part in sports activities can breathe in a larger volume of air than students who do not take part. Describe briefly how the student could use the same apparatus to do the investigation. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ Page 4 ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (3) (d) Photograph 1 shows a different piece of apparatus used to measure the volume of air that a person can breathe in one breath. Photograph 1 When the student breathes out through the apparatus the pointer on the scale moves. The pointer stays in the same position when the student has finished. Explain one advantage, apart from size, of using this apparatus rather than the apparatus described in part (b). ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (2) (e) Photograph 2 shows one type of mechanical ventilator. Page 5 Photograph 2 (i) Use information from Photograph 2 to suggest how this type of ventilator works. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Use information from Photograph 2 to suggest two disadvantages of this type of ventilator. 1............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................... 2............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................... (2) (Total 20 marks) Q3.Diagram 1 shows a yeast cell. Diagram 1 Page 6 (a) Name structures A and B. A ............................................................ B ............................................................ (2) (b) Yeast cells can respire anaerobically. The equation for anaerobic respiration in yeast is: glucose alcohol + carbon dioxide (+ energy) Give one way in which anaerobic respiration in yeast cells is different from anaerobic respiration in human muscle cells. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (1) (c) Yeast can use other types of sugar instead of glucose. Some scientists investigated the effect of three different types of sugar on the rate of anaerobic respiration in yeast. The scientists: • used the apparatus shown in Diagram 2 with glucose sugar • kept the apparatus at 20 °C • repeated the investigation with fructose sugar and then with mannose sugar • repeated the investigation with water instead of the sugar solution. Diagram 2 Page 7 (i) Give two control variables the scientists used in this investigation. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (ii) The graph shows the scientists’ results. Time in minutes From this information, a company decided to use fructose to produce alcohol and not mannose or glucose. Explain the reason for the company’s choice. Page 8 ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) Q4. (a) The diagrams show cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Into which cell, A, B, C or D, will oxygen move the fastest? Write your answer, A, B, C or D, in the box. (1) (b) Draw a ring around the correct word to complete each sentence. diffusion (i) Oxygen is taken into cells by the process of Page 9 osmosis . respiration (1) breathing (ii) Cells need oxygen for photosynthesis . respiration (1) membranes (iii) The parts of cells that use up the most oxygen are the mitochondria . nuclei (1) diffusion (iv) Some cells produce oxygen in the process of photosynthesis . respiration (1) (Total 5 marks) Q5. The diagram shows a small part of a lung. Page 10 (a) The arrow on the diagram shows the movement of oxygen from the air in the alveolus to cell X. Complete the sentences by drawing a ring around the correct answer. platelet (i) Cell X is a red cell white cell (1) diffusion (ii) Oxygen moves from the air in the alveolus into cell X by filtration respiration (1) Page 11 glycogen (iii) The substance in cell X that combines with oxygen is called haemoglobin lactic acid (1) a cell membrane (iv) Cell X does not have cytoplasm a nucleus (1) (b) On the diagram, draw an arrow to show the movement of carbon dioxide during gas exchange. (1) (Total 5 marks) Q6. Paula is training for a marathon. When she runs, her heart beats faster than it does when she is resting. Complete the sentences, using words from the box. blood breathe heat nitrogen carbon dioxide oxygen glucose respire When she is running, Paula‘s muscle activity increases. To do this, her muscle cells ................................................. at a faster rate to give her more energy. Her muscles need to Page 12 be supplied with ........................................... and .................................................................... more quickly. Her heart beats faster to increase the flow of.................................................... which carries the products ................................................................................................ and ............................................................ away from her muscles. (Total 6 marks) Q7. The diagram shows a part of a lung that is involved in gaseous exchange in a human. (i) Draw and label, on the diagram, one arrow to show the direction of movement of oxygen between the alveolus and capillary. (1) (ii) Draw and label, on the diagram, one arrow to show the direction of movement of carbon dioxide, between the alveolus and capillary. (1) Page 13 (iii) Give the function of the red blood cell in this process. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 3 marks) Q8. A student breathed out into an empty breathing bag five times. After breathing out five times the volume of air in the bag was measured. The volume was 3000 cm3. (a) Complete the following sentences. The air the student breathed in would contain more ........................................ than the air the student breathed out. The air the student breathed out would contain more ...................................... than the air the student breathed in. (2) Page 14 (b) The student then did some exercise for two minutes. The volume breathed out in five breaths was again measured. This time there was 9000 cm3 of air in the bag. What does this tell you about the effect of exercise on breathing? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) (i) Name the chemical process that releases energy when it takes place in the cells of the body. ................................................ (1) (ii) Name the substances produced by this process. .......................................................... and .......................................................... (2) (iii) Explain as fully as you can why this process has to take place more rapidly during exercise. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) Q9. In an investigation four groups of athletes were studied. The maximum rate of oxygen consumption for each athlete was measured and the mean for each group was calculated. The athletes then ran 10 mile races and the mean of the best times was calculated for each group. The results are shown in the table below. Page 15 (i) What is the relationship between maximum rate of oxygen consumption and time for a 10 mile race? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Suggest an explanation for this relationship. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 4 marks) Q10. The diagram shows part of the breathing system in a human. Page 16 (a) Use words from the list to label the parts on the drawing. alveoli bronchiole bronchus diaphragm trachea (windpipe) (4) (b) Where in the lungs does oxygen enter the blood? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Which process in cells produces carbon dioxide? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 6 marks) Page 17 Q11. The pie chart shows the composition of the air we breathe in. The table shows the composition of the air we breathe out. Gas Percentage Carbon dioxide 5 Nitrogen 80 Oxygen 15 (a) Complete the pie chart below for the composition of the air we breathe out. Remember to label the chart. Page 18 (3) (b) Use the information from the two pie charts to give two differences between the air we breathe in and the air we breathe out. the air we breathe in contains more ........................................................................ . the air we breathe out contains more ....................................................................... . (2) (c) Name the process in the body which produces carbon dioxide. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 6 marks) Q12. (i) What is the name of the process which takes place in living cells in your body and which releases energy from oxygen and glucose? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Name the two products of the process in part (i). ............................................................... and .............................................................. (1) (Total 2 marks) Page 19 Q13. (a) (i) Complete the word equation for the process of aerobic respiration. Glucose + ........................... → carbon dioxide + water (1) (ii) Which organ removes carbon dioxide from your body? ................................................................................................................. (1) (b) Use names from the box to complete the two spaces in the passage. carbon dioxide lactic acid nitrogen oxygen water Anaerobic respiration can occur when an athlete does vigorous exercise. This is because there is not enough ....................................................... in the body. The product of anaerobic respiration is ................................................................. . (2) (Total 4 marks) Q14. (a) The air you breathe in and the air you breathe out are different. Use the names of gases from this box to complete the three spaces. argon vapour carbon dioxide nitrogen oxygen water Compared to the air you breathe in, the air you breathe out contains: Page 20 • more ..................................................................................................................... • more ..................................................................................................................... • less ........................................................................................................................ (3) (b) The process of aerobic respiration takes place in your cells. (i) Complete the space in the word equation for this process. ........................ + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water (1) (ii) Complete the space to give the main energy transfer which takes place in this process. chemical energy → ............................... energy (1) (iii) What is the name of the organ where oxygen from the air passes to your blood? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (c) The athlete is taking part in vigorous exercise. Page 21 Complete the two spaces in the passage. The cells in our muscles respire anaerobically during vigorous exercise. This results in ........................................debt and the production of ....................................... acid. (2) (Total 8 marks) Q15.Scientists measured the amount of energy used by four people, A, B, C and D. The scientists also measured the amount of energy taken in as food by each person. The chart shows the scientists’ results. Page 22 Mean energy in kJ per day (a) (i) What was the mean amount of energy used by D? ...................................................................... kJ per day (1) (ii) The amount of energy used by D is different from the amounts of energy used by A, B and C. Suggest two reasons why. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (2) (b) The data in the bar chart was collected over twelve months. Which person, A, B, C or D, would gain body mass over the twelve months? Give a reason for your answer. Page 23 ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (2) (c) In the UK many people are obese. Doctors advise obese people to lose mass. Suggest two different ways an obese person could lose mass. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (2) (Total 7 marks) Page 24 M1.(a) (i) diffusion 1 (ii) carbon dioxide accept CO2 / CO2 do not accept CO2 1 (iii) red blood cells 1 (b) 70 if no / incorrect answer then 70 000 000 or 280 x 0.25 gains 1 mark ignore doubling the answer 2 (c) allows more gas / oxygen / CO2 (exchange) do not accept air 1 [6] M2.(a) (i) A lung 1 B rib 1 C diaphragm 1 D alveolus / alveoli 1 Page 25 (ii) (B moves) up(wards) / out / up and out 1 (C moves) down(wards) / flattens do not allow inwards ignore outwards if neither mark gained allow 1 mark for correct reference to muscle contraction 1 (b) (i) 1640 1 1440 1 1720 allow max 1 for 3 correct values using of bottom of piston: 1380 + 1180 + 1480 to 1485 1 (ii) 1600 correct answer gains 2 marks if answer incorrect allow 1 mark for evidence of (1640 + 1440 + 1720) ÷ 3 allow ecf from (b)(i) allow use of two numbers divided by two if one is considered anomalous: = 1680 for 2 marks 2 (c) two groups of students − one group sports activity participants, other not allow students as a group 1 fair test eg groups same height / same mass / same sex 1 measure air breathed in by each student / repeat previous experiment then calculate mean for group 1 (d) pointer remains still after breathing / cylinder will move down after breathing (in) 1 Page 26 error reading volume less likely allow more accurate / reliable 1 (e) (i) operator squeezes bag 1 air forced / pushed into lungs or positive pressure ventilator 1 (ii) any two from: • • • air pressure / volume not regulated operator will tire / must be present at all times / variable intervals too much / too little air allow may ‘overbreathe’ the patient 2 [20] M3.(a) A = cytoplasm 1 B = (cell) membrane 1 (b) in yeast: ’it’ equals yeast makes alcohol / makes CO2 / does not make lactic acid do not allow uses / involves alcohol / CO2 1 (c) (i) any two from: allow amount of yeast • volume of yeast / suspension • volume of sugar / solution• of sugar = max 1 for sugar Page 27 concentration of sugar amount • temperature (total) volume = 1 mark if no other volume ignore concentration of yeast 2 (ii) most / more CO2 given off with fructose or ’it’ equals fructose faster CO2 production or faster respiration allow faster fermentation 1 do not allow aerobic respiration so (rate of) alcohol production will be greatest / more (with fructose) 1 [7] M4. (a) A 1 (b) (i) diffusion 1 (ii) respiration 1 (iii) mitochondria 1 (iv) photosynthesis 1 [5] M5. (a) (i) red cell 1 Page 28 (ii) diffusion 1 (iii) haemoglobin 1 (iv) a nucleus 1 (b) (on diagram) arrow from any part of blood to air 1 [5] M6. (a) respire 1 2 blood 1 2 [6] M7. (i) oxygen into the blood stream arrow must start inside alveolus and finish outside the capillary 1 (ii) carbon dioxide out of the blood stream arrow must start inside the capillary and finish inside the alveolus 1 Page 29 (iii) carries/takes up/releases oxygen or carbon dioxide accept forms oxyhaemoglobin 1 [3] ## (a) oxygen, carbon dioxide or water (vapour) for 1 mark each 2 (b) idea of more air per breath/deeper breaths for 1 mark 1 (c) (i) respiration for 1 mark 1 (ii) carbon dioxide, water for 1 mark each 2 (iii) more energy required, for increased muscular activity for 1 mark each 2 [8] Page 30 M9. (i) the higher the rate of oxygen consumption, the shorter the time taken to complete for 1 mark 1 (ii) the faster oxygen is taken into the blood, the faster energy can be released in the muscles, and the faster the athlete can run for 1 mark each 3 [4] M10. (a) trachea / windpipe bronchus alveoli diaphragm for 1 mark each 4 (b) alveoli / air sacs (reject capillaries) for one mark 1 (c) respiration for one mark 1 [6] M11. (a) plots all correct allow one mark for 1 / 2 correct plots 2 Page 31 all labels present and correct (in correct proportions) 1 (b) oxygen 1 carbon dioxide 1 (c) respiration do not accept anaerobic respiration 1 [6] M12. (i) (aerobic) respiration do not credit anaerobic respiration accept cellular respiration 1 (ii) carbon dioxide and water (vapour) both required do not credit heat 1 [2] M13. (a) (i) oxygen do not credit air 1 (ii) lung(s) do not credit blood or nose or windpipe alone but accept as a neutral answer if included with lungs 1 Page 32 (b) oxygen 1 lactic acid both words required 1 [4] M14. (a) more water vapour accept more water 1 more carbon dioxide 1 less oxygen 1 (b) (i) glucose accept carbohydrate(s) accept sugar(s) 1 (ii) heat or thermal or internal kinetic 1 (iii) lungs accept alveoli / alveolus do not credit air sacs do not credit capillaries both neutral if included with lungs 1 (c) oxygen Page 33 accept O2 1 lactic 1 [8] M15. (a) (i) 7500 ignore units 1 (ii) any two from if examples given they must be correct (differences in) • age • gender / sex • activity /amount of exercise allow job / lifestyle ignore fitness / health / medication • metabolism / metabolic rate allow BMR • genetic differences • body weight / mass / size / physique allow BMI • pregnancy • proportion of muscle to fat 2 (b) A if box empty, allow in explanation 1 Page 34 more energy taken in than used accept more food taken in than used allow correct numbers if comparative ignore incorrect numbers if comparison correct 1 (c) eat less (food / carbohydrates / fat / calories) accept a medical treatment such as gastric band / slimming pills / liposuction ignore balanced / healthy / diet allow go to weight watchers etc. ignore burn off more 1 exercise (more) or go to the gym 1 [7] Page 35