Guide-to-probity - Victorian Government Procurement
advertisement

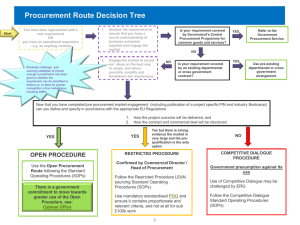
Managing probity – procurement guide Governance Policy Complexity and Capability Policy Market Analysis and Review Policy Market Approach Policy Contract Management and Disclosure Policy What is probity? Probity signifies integrity, fairness and honesty. Government often refers to probity in a general sense to mean good process demonstrated by transparency of actions, equity, confidentiality and managing conflicts of interest, whether actual or perceived. In the procurement sector, probity relates to proper and ethical conduct, and propriety in dealings with the market. Probity is integral to the goal of achieving value-for-money outcomes. Why is probity important? Good probity practice is important for: business and community confidence in the integrity of government procurement processes; encouraging and enabling purchasers and businesses to deal with each other on the basis of mutual trust and respect; and improving the defensibility of market engagement processes and procurement outcomes. When to apply probity Probity should underpin every aspect of every procurement activity. How to apply probity To achieve an ethical and transparent approach, procurement processes must be clear, open, wellunderstood and applied by all parties in the process. In practice, probity requires: acting with integrity and impartiality; ensuring market equality by applying an appropriate level of competition and contestability relevant to the procurement activity; consistent and transparent processes; secure and confidential market engagement information; identifying and managing conflicts of interest; allocating appropriate capability to elements of the procurement process; and engaging a probity practitioner(s) where the complexity of the procurement warrants independent process oversight. Table 1 (overleaf) provides a more detailed look at probity in practice. Note: For more information, see the Guide to engaging a probity practitioner which accompanies the VGPB’s Market Approach Policy. Using this guide This guide accompanies the Victorian Government Purchasing Board’s (VGPB) new procurement framework. Refer to the policies for mandatory requirements. For more information, visit the Procurement Victoria website at www.procurement.vic.gov.au Table 1: Probity in practice Requirement Recommended actions Acting with integrity and impartiality Organisations demonstrate integrity by: being honest, open and transparent in their dealings using their powers responsibly addressing improper conduct managing any real or apparent conflicts of interest, and striving to earn and sustain a high level of public trust. Organisations demonstrate impartiality by: making decisions and providing advice based on merit—without bias, caprice, favouritism or self-interest, and acting fairly by objectively considering all relevant facts and fair criteria. Ensure compliance with government legislation and codes, including: Public Administration Act 2004 Freedom of Information Act 1982 Code of Conduct for Victorian Public Sector Employees State Services Authority (SSA) Ethics Framework SSA Conflict of Interest Policy Framework SSA Gifts, Benefits and Hospitality Policy Framework, and Commonwealth legislation and relevant trade agreements. Ensuring market equality All suppliers (existing and potential) must be provided with the same information Consistent and transparent processes Apply transparency and fairness throughout the procurement cycle. Maintain records throughout the process, providing enough information to regarding the procurement activity. enable independent review. Ensure any change or variation to process and/or scope does not unfairly Secure and confidential market engagement information preference any bidder and minimises additional costs. Set up procurement processes to ensure that information from suppliers, in particular intellectual property, remains confidential. Identifying and resolving conflicts Set up and apply procedures and processes to identify and address actual and perceived conflicts of interest. of interest Record all action taken to address any actual or perceived conflict of interest. Allocating appropriate capability Align procurement processes with capability, ensuring staff and systems match each element of the procurement process. to elements of the procurement process Engaging a probity practitioner(s) Ensure that probity practitioner services add value to the capability of the organisation in conducting the procurement process. (Refer to Guide to engaging where the complexity of the a probity practitioner.) procurement activity warrants independent process oversight State of Victoria 2014 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Australia licence. You are free to re-use the work under that licence, on the condition that you credit the State of Victoria as author. The licence does not apply to any images, photographs or branding, including the Victorian Coat of Arms, the Victorian Government logo and the Department of Treasury and Finance logo. Copyright queries may be directed to IPpolicy@dtf.vic.gov.au Managing probity – procurement guide Last updated 8 August 2012 2