BIOS 1300 SI REVIEW SESSION (Chapters 1
advertisement

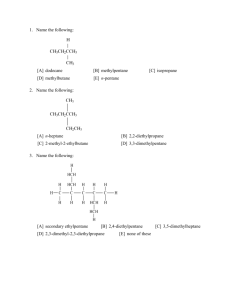
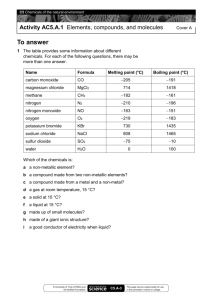
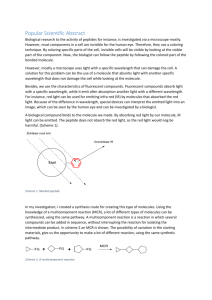
BIOS 1300 SI REVIEW SESSION (Chapters 1-3) SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries (mj983011@ohio.edu) 7 September 2014 EXAM 1 REVIEW ***SHAPE DETERMINES FUNCTION*** Multiple choice. Circle the correct answer. 1. The specialized study that analyzes the structure of individual cells is: a. Histology b. Microbiology c. Cytology d. Pathology 2. Homeostasis refers to: a. The chemical operations underway in the body b. Individual cells becoming specialized to perform particular functions c. Changes in an organism’s immediate environment d. The maintenance of a stable internal environment 3. The smallest living units in the body are: a. Elements b. Tissues c. Molecules d. Cells 4. Normal body temperature is 37 degrees Celsius. Suppose an individual’s body temperature is 36.7 degrees Celsius. This variation from the “normal” value may represent: a. An illness that has not been identified b. Individual variation rather than a homeostatic malfunction c. The need to see a physician immediately d. A variability that is abnormal 5. The study of general form and superficial anatomical markings is called: a. Developmental anatomy b. Surface anatomy c. Histology d. Systemic anatomy 6. The two regulatory systems in the human body include the: a. Nervous and endocrine b. Endocrine and reproductive c. Cardiovascular and nervous 7. The level of organization that reflects the interactions between chemicals is: a. Cellular level b. Tissue level c. Molecular level d. Organism 8. When a variation outside of normal limits triggers an automatic response that corrects the situation, the mechanism is called: a. Negative feedback b. Positive feedback c. Crisis management d. Homeostasis 9. The kidneys and liver are located in the ________________ cavity. a. Pericardial b. Thoracic c. Pleural d. Abdominopelvic 10. Moving from the elbow to the wrist is an example of moving in a _____ direction. a. Proximal b. Distal c. Medial d. Lateral 11. Making a coronal cut results in separation of: a. Anterior and posterior portions of the body b. Superior and inferior portions of the body c. Cranial and caudal portions of the body d. Right and left portions of the body 12. The plane that divides the body so the nose is split in half is the: a. Sagittal plane b. Frontal plane c. Transverse plane d. Oblique plane 13. Which of the following pairs of anatomical terms is correctly associated with its opposite? a. Distal, coronal b. Medial, lateral c. Proximal, lateral d. Distal, posterior 14. An accident victim has a collapsed lung. Which cavity has been entered? a. Mediastinal b. Pericardial c. Pleural 15. The equal sharing of electrons in a molecule is an example of: a. An ionic bond b. A polar covalent bond c. A nonpolar covalent bond d. A hydrogen bond 16. Of the following compounds, the one that is least likely to affect the concentrations of H+ and OH- ions is: a. A base b. A salt c. An acid d. A buffer 17. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are classified as: a. Eicosanoids b. Inorganic compounds c. Organic compounds d. Noncaloric compounds 18. The human body generates significant quantities of acids that may promote a disruptive: a. Decrease in pH b. Increase in pH c. pH of about 7.40 d. sustained muscular contraction 19. The three basic components of a single nucleotide of a nucleic acid are: a. Purines, pyrimidines, sugar b. Sugar, phosphate group, nitrogen base c. Guanine, cytosine, thymine d. Pentose, ribose, deoxyribose 20. The presence of an appropriate enzyme affects only the: a. Speed of the reaction b. Direction of the reaction c. Products that will be formed from the reaction 21. A solute that dissociates to release hydroxide ions and cause an increase in pH is: a. A base b. A salt c. An acid d. Water 22. Two simple sugars joined together form a disaccharide. The reaction necessitates: a. The removal of water to create a more complex molecule b. The addition of water to create a more complex molecule c. The presence of cations and anions to initiate electrical attraction d. The disassembling of molecules through hydrolysis 23. Compared to a solution with a pH of 8, a solution with a pH of 6 has: a. 2 times more H+ b. 100 times more H+ c. 100 times less H+ d. 2 times less H+ FILL-IN 1. The process that breaks a complex molecule into smaller fragments by the addition of a water molecule is ____________________________________ . 2. Molecules that have few if any polar covalent bonds and do not dissolve in water are described as ________________________________________. 3. What are the 3 components that make-up one nucleotide of ATP? ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ 4. A chemical with a charge of +1 due to the loss of one electron is called _______________________________ . 5. Elements are determined by the number of __________________ in an atom. 6. Strong acids dissociate ___________________ in a solution. 7. In a protein, the _____________________________ structure is several tertiary structures binding together. If any of the following statements is true, write T in the answer blank. If a statement is false, correct the underlined word and write the correction in the answer blank. ________________________ 1. All enzymes are triglycerides. ________________________ 2. The name of most enzymes ends in the suffix –ide. ________________________ 3. A cofactor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme before the substrates can bind. ________________________ 4. Enzymes increase the activation energy of biochemical reactions. ________________________ 5. The active site of an enzyme is the location of substrate attachment. ________________________ 6. Phospholipids are polarized molecules. ________________________ 7. Steroids are the major form in which body fat is stored. ________________________ 8. Water is an inorganic molecule. ________________________ 9. The universal energy currency of living cells is RNA. ________________________ 10. Hydrogen bonds are strong bonds that connect different molecules. ________________________ 11. The backbone of a nucleic acid molecule consists of sugar and lipid group. Match the terms in Column B with the descriptions in Column A. Enter the correct letters in the answer blanks. ____________ 1. Glycogen A. Amino acids ____________2. Class that includes cholesterol B. Carbohydrates ____________ 3. Building blocks of protein C. Lipids ____________ 4. Building blocks of nucleic acids D. Fatty acids ____________ 5. Sucrose E. Glycerol ____________ 6. Contains C, H, and O in the ratio CH2O F. Nucleotides ____________ 7. Essential for energy reserves and building structural components G. Proteins ____________ 8. Long chains of C and H with a carboxylic acid group at one end ____________ 9. Hemoglobin Use an X to designate which of the following are organic compounds. ______ Carbon dioxide _______ Fats _______ Proteins _______ H2O ______ Oxygen _______ KCl _______ Glucose _______DNA