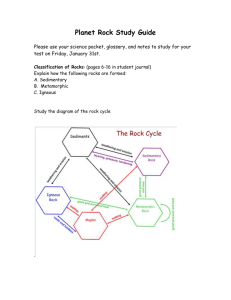
Rocks Study Guide
advertisement

Study Guide: Earth’s Changing Surface Abrasion and Glaciers Full Name: ________________________ #: ______ What to Study… Big Idea: Moving water, ice, and wind break down rock (abrasion/weathering), transport materials (erosion), and build up the earth’s surface (deposition). Rocks: 1. Which 2 rocks wear down the fastest? Pumice and Sandstone (**Pumice wears down the fastest!) 2. Which 2 rocks wear down the slowest? Quartzite and Slate Abrasion: 1. Understand abrasion and what the result of it is on the earth 2. What is abrasion? Rocks grinding down other rocks 3. Abrasion is likely to break down the earth’s surface. 4. Abrasion is a form of: weathering (one of earth’s natural processes) 5. Weathering (breaks down the earth) can cause glacial striations and glacial polish Glaciers: 1. How are glaciers formed? Lots of snow built up over hundreds of thousands of years, cold weather year-round, ice formed- flowing downhill 2. Glacial Deposition (builds up the earth) can cause: a. Erratics- when a glacier retreats, melting ice deposits the boulders b. Moraines- glacier melts and carries sediment, ice pushes the debris into mounds or ridges REVIEW THE EXPERIMENTS FROM CLASS!!!! 1. Quartzite experiment (grinding of 3 different rock types): a. What happened when you used quartzite on the soft, medium, hard rock types? Study Guide: Earth’s Changing Surface Abrasion and Glaciers 1. Vocabulary Make o o o o o o Full Name: ________________________ vocabulary cards to study from!!! Abrasion- rocks grinding down other rocks Glacier- a long-lasting mass of ice and snow Sediment- materials that glaciers carry Gravity- makes glaciers move Erratic- a large rock that is moved by a glacier Moraine- a pile of sediment deposited by a glacier #: ______