Science 10Brakke/Baier/HeathcoteECA – Chemistry – Topic 01
advertisement

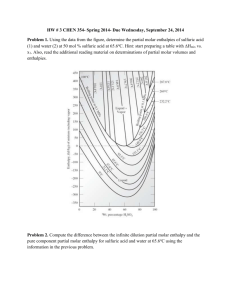
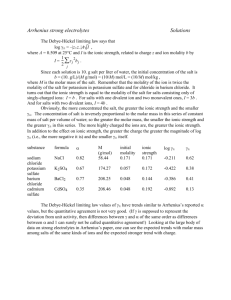
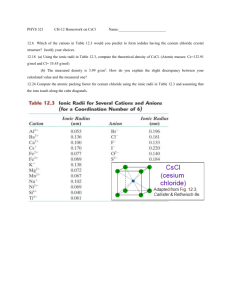
Science 10 Brakke/Baier/Heathcote ECA – Chemistry – Topic 01 CT01D02 – Heat Change Associated with the dissolving of Ionic Compounds Name ________________________________ All chemical and physical changes are accompanied by a change or flow of energy. When heat is liberated, the reaction is said to be exothermic. This energy is used to increase the temperature of the surroundings and attention must be paid to what the surroundings are. Reactions that absorb heat are called endothermic and lower the surrounding temperature. Because a calorimeter is a poor conductor of heat, it minimizes heat exchange with the environment. Since energy cannot be created or destroyed, and when a reaction is completed in a calorimeter the overall energy is “trapped,” the heat change of the reaction must be equal and opposite to that of the water. The equation is as follows: energy lost = energy gained q=-q qwater = - qsubstance (msΔT)w = - (msΔT)sub In this activity, you will dissolve two different ionic solids in water and determine whether their reactions are endothermic or exothermic. As an extension for a 7pt lab, the molar heats of solution (how many joules of energy are produced when 1 mole of substance reacts) must be calculated and an energy diagram included. The two chemicals you will use are both ionic compounds, when dissolved in water one will result in an endothermic reaction, the other in an exothermic reaction. The equations are: Na2S2O3•5H2O + H2O Na+ + S2O32- + H2O Na2S2O3(s) 2 Na+(aq) + S2O32-(aq) NaOH(s) + H2O(l) Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) + H2O(l) NaOH(s) Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) Introduction: What an ionic compound is, and what it does when added to water Literature values for the endo/exo – thermic properties of each compound Describe a calorimeter and it’s purpose Variables: Independent: Dependent: Control: (and how you control for each) Hypothesis and question (should include your independent, dependent, control variables) Materials: (also include an apparatus – drawing/picture of the lab set up) Sodium thiosulfate, 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 ∗ 5𝐻2 𝑂 (s) Sodium hydroxide, NaOH (s) 2 Styrofoam Cups Thermometer Graduated Cylinder Balance/Scale Go link + temperature probe Procedures: Include a step by step procedure that includes o Compounds to be used (always with the amount and state (s, l, g) in parenthesis) o Danger precautions! If NaOH is touched or spilled, rinse with copious (lots of) amounts of water!! o Explain how data should be recorded using logger pro o For a 7….The precision of the instrument (the smallest value of measurement divided by 2) Example: if you measure with a ruler 5.45 cm, the last value 0.01/2 = 0.005 and your uncertainty is ±0.005 cm. Every measured value should have an uncertainty associated with it. Science 10 Brakke/Baier/Heathcote ECA – Chemistry – Topic 01 Data/Results: Use logger pro to collect raw data, copy and paste the graph and raw data from the lab into your lab document For a 5… Produce your own data table using excel (you may copy in the values but must create an original graph) For a 6… Draw an energy diagram for each reaction using Word Draw Tools For a 7… Calculate the molar heats of solution for both ionic compounds (use information below) Conclusion: State your results (qw and qsub for each equation, along with associated endo- or exo-thermic identification) Compare your results to literature values Describe sources of error (be specific: not precise and human error are not sufficient) Give one or two improvements that can be made to improve the error For a 7… Describe, in no more than a paragraph, how a calorimeter could be used to determine the amount of calories (energy in a peanut or a single potato chip) For a 7, students must calculate the molar heat of solution for each ionic compound. Molar Mass of Na2S2O3•5H2O = 248.21 g/mol Molar Mass of NaOH = 40.00 g/mol qsub has the unit of Joules (J) if x grams of substance (msub) are reacted then you must find how many moles of substance. The molar mass has a unit of (g/mol), so if you know the number of grams and divide by this number you will find the number of moles as follows in the example below: 100.0 g Na2S2O3•5H2O x 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 ∗5𝐻2 𝑂 248.21 𝑔 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 ∗5𝐻2 𝑂 = 0.4163 mol Na2S2O3 If 15000.0 J were produced: 15000 𝐽 0.4163 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑎2 𝑆2 𝑂3 ∗5𝐻2 𝑂 = 36032 J/mol = molar heat of solution