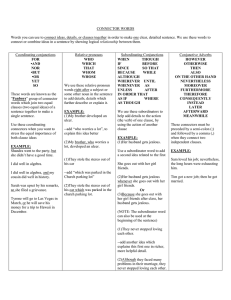
Handout

L.7.1c Intermediate / Advanced
Phrases & Clauses within a sentence
Clause
A clause is a subject + verb .
Example:
The girl is going to the park , and she is going to play there .
The two different colors represent the two different Clauses.
There are two different types of clauses: Dependent and Subordinate.
Dependent clauses – can
stand alone.
The girl is going to the park.
Subordinate clauses – cannot stand alone.
And she is going to play there…
You can’t put two complete sentences together.
The girl is going to the park, the girl is going to play at the park.
This is incorrect.
Two complete sentences cannot be separated by a comma.
Your Turn!
Underline the dependent clause in one color and the subordinate clause in a different color.
Although all animals are cute, some animals are cuter than others.
1
The verb of a sentence…
Phrase
A group of two or more linked words that DO NOT have a subject and predicate
Example: The girl is at home today, and tomorrow she is going to the theme park .
“to the theme park” is a phrase in the second clause of the complete sentence – it is a prepositional phrase.
Remember: The phrase cannot contain a subject or predicate
Your Turn!
Underline the phrase in the sentence.
I like to go to the mall, though only on the weekends.
2
Misplaced & Dangling Modifiers
A modifier modifies a sentence; it can usually be removed and not affect the sentence.
Example of a misplaced:
Susie has nearly annoyed every teacher.
You don’t want to put the modifier in the wrong place.
We almost ate all of the Thanksgiving turkey.
We didn’t “almost eat” the turkey. We ate the turkey – almost all of it.
Example of a dangling modifier:
Raised in Florida, it is natural I hate the cold weather
Raised in Florida, it is natural to hate the cold weather.
It is referring to Florida
Your Turn!
Is the modifier correct in the sentence?
The pretty girl had her hair curled. YES or NO
3