Plotline
advertisement
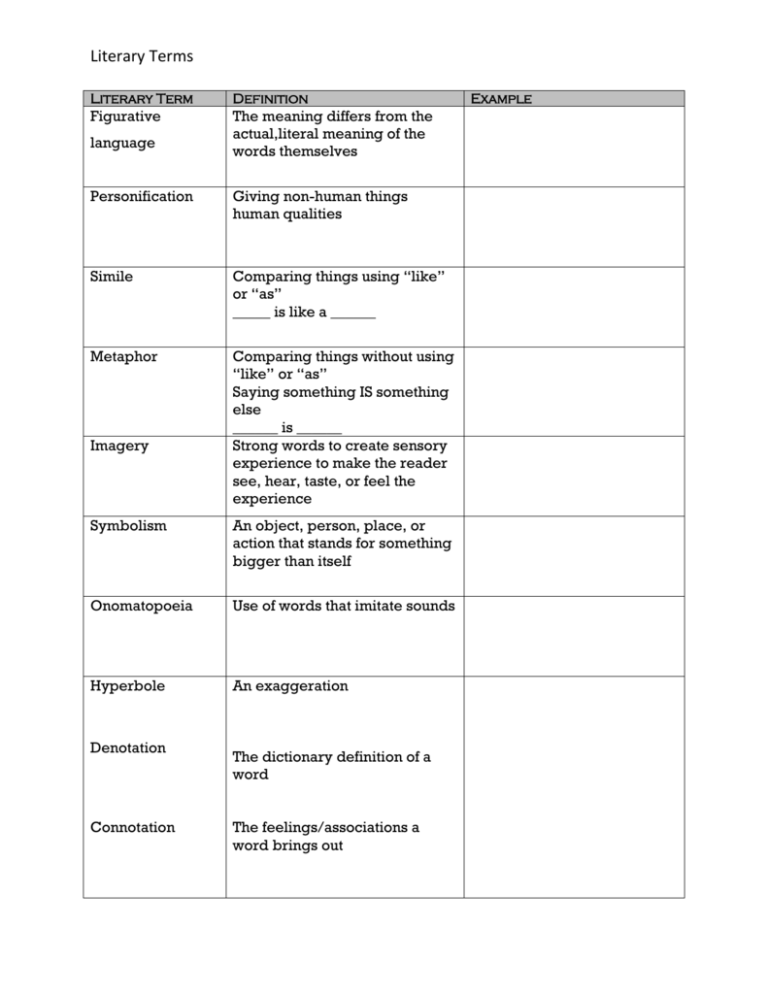
Literary Terms Literary Term Definition Figurative The meaning differs from the actual,literal meaning of the words themselves language Personification Giving non-human things human qualities Simile Comparing things using “like” or “as” _____ is like a ______ Metaphor Comparing things without using “like” or “as” Saying something IS something else ______ is ______ Strong words to create sensory experience to make the reader see, hear, taste, or feel the experience Imagery Symbolism An object, person, place, or action that stands for something bigger than itself Onomatopoeia Use of words that imitate sounds Hyperbole An exaggeration Denotation Connotation The dictionary definition of a word The feelings/associations a word brings out Example Literary Terms Literary Term Literal language Definition Factual meaning of a word or words Motif A character, event, image, or theme that appears in the literature of many cultures Allusion A reference to another literary work or situation Theme A message about life or human nature that the writer shares with the reader. The overall feeling of a work of literature Mood Dialect A representation of speech patterns of a particular region Flashback Interruption in the present action of a plot to show events that happened at an earlier time Setting The time and place of the action of a story Suspense A feeling of growing tension and excitement felt by the reader Expresses the writer’s attitude toward his or her subject Tone Irony A contrast between appearance and reality Foreshadowing Providing the reader with hints or clues about the future action of the story or play Dialogue Conversation between two or more characters Example Literary Terms Literary Term Definition Alliteration Usually, the repetition of beginning consonant sounds in neighboring words Stanza/verse A paragraph in a poem Rhyme The repetition of accented vowel sounds and all sounds following them in words close together in a poem A rhyme within a line Internal rhyme Slant rhyme or Near rhyme Rhymes involving sounds that are similar but not exactly the same Rhythm A pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables in a line of poetry Musical quality of poetry A pattern of end rhymes in a poem abab, aabb A regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables in a poem A three line poem in which the first and third lines contain five syllables and the second line contains seven A five line humorous poem with aabba rhyme scheme and a defined rhythm A kind or type of literature Rhyme scheme Meter Haiku Limerick Genre Biography The story of a person's life written by someone other than the subject of the work Example Literary Terms Literary Term Definition Narrative A story or account of events, experiences, or the like, which can be fiction or nonfiction The type of literature that consists of novels, short stories, and other prose writings that tell about imaginary people and happenings Writing that is not fiction; Prose literature that deals With real people and events rather than imaginary ones A composition in prose or verse written to be acted on a stage or before motionpicture or television cameras in which a story is told by means of dialogue and action; a play The narrator uses “I” and is in the story Fiction Non-fiction Drama First person Third person (limited or objective) Third person omniscient Audience A “nonparticipant” serves as the narrator and uses the pronouns he, it, and they Narrator knows one character’s thoughts A narrator who knows everything about all the characters is all knowing or omniscient. Narrator is a “nonparticipant” The person or group for whom a piece of literature is written Narrator/speaker The voice that tells the story Voice A writer’s unique style of language Example Literary Terms Literary Term Definition Dynamic A character whose personality changes Character Static character A character whose personality stays the same Protagonist The main character in a work of literature Antagonist The character in a work of literature opposing the protagonist Hero/heroine A character admired for bravery, great deeds, or noble qualities Conflict A struggle between two opposing forces Internal Person vs. self—a conflict within a person (like a decision) External Person vs. person—a conflict with one or more people Person vs. society—a conflict with the norms/ideals of society Person vs. nature—a conflict with something in nature Example Literary Terms Literary Term Definition Exposition The beginning of a story which introduces important background information Rising Action The stage of the plot that develops the conflict Climax The stage of the plot which is of greatest interest and can be the turning point of the story Falling Action The stage of the plot in which the story begins to draw to a close Resolution The end of the story Plotline Label the parts of the plot on the diagram. Example










