Smithycroft Secondary Chemistry Unit 1: Section 2 – Atomic
advertisement
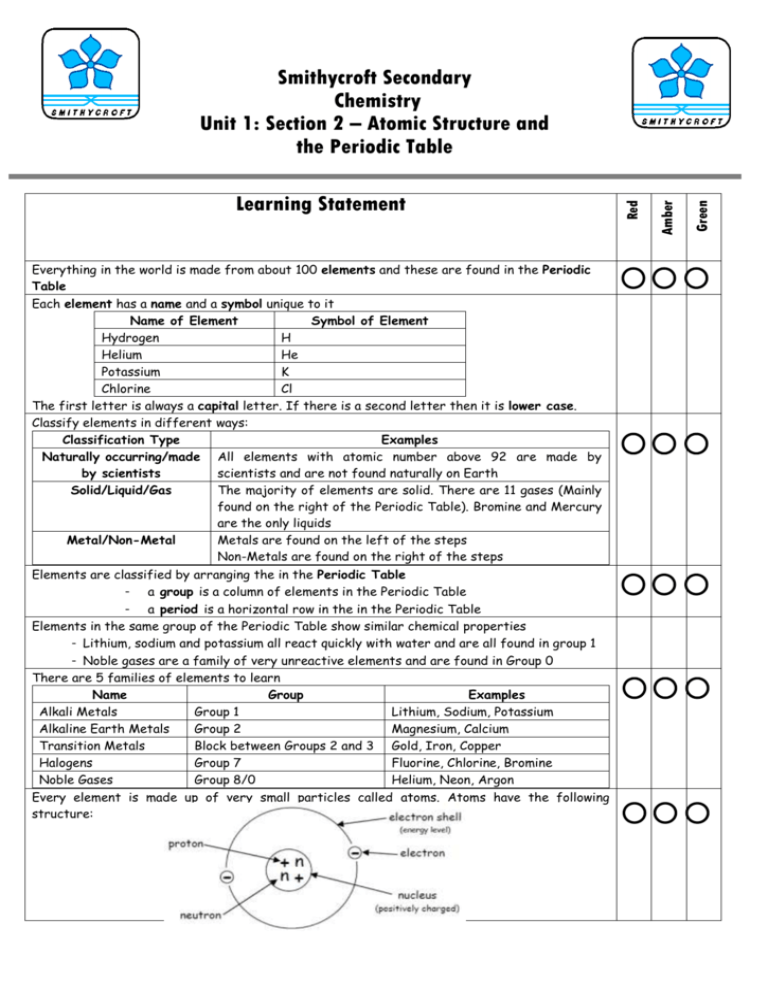
Everything in the world is made from about 100 elements and these are found in the Periodic Table Each element has a name and a symbol unique to it Name of Element Symbol of Element Hydrogen H Helium He Potassium K Chlorine Cl The first letter is always a capital letter. If there is a second letter then it is lower case. Classify elements in different ways: Classification Type Examples Naturally occurring/made All elements with atomic number above 92 are made by by scientists scientists and are not found naturally on Earth Solid/Liquid/Gas The majority of elements are solid. There are 11 gases (Mainly found on the right of the Periodic Table). Bromine and Mercury are the only liquids Metal/Non-Metal Metals are found on the left of the steps Non-Metals are found on the right of the steps Elements are classified by arranging the in the Periodic Table - a group is a column of elements in the Periodic Table - a period is a horizontal row in the in the Periodic Table Elements in the same group of the Periodic Table show similar chemical properties - Lithium, sodium and potassium all react quickly with water and are all found in group 1 - Noble gases are a family of very unreactive elements and are found in Group 0 There are 5 families of elements to learn Name Group Examples Alkali Metals Group 1 Lithium, Sodium, Potassium Alkaline Earth Metals Group 2 Magnesium, Calcium Transition Metals Block between Groups 2 and 3 Gold, Iron, Copper Halogens Group 7 Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine Noble Gases Group 8/0 Helium, Neon, Argon Every element is made up of very small particles called atoms. Atoms have the following structure: Green Amber Learning Statement Red Smithycroft Secondary Chemistry Unit 1: Section 2 – Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Atoms are made up from 3 different particles: Particle Location Charge Mass Proton Nucleus +1 1 a.m.u Neutron Nucleus Neutral 1 a.m.u Electron Outside the Nucleus -1 Almost 0 Atoms are neutral because; - The positive charge of the nucleus is equal to the sum of the negative charges of the electrons - They have the same number of protons and electrons Electrons are arranged in electron shells which are sometimes called energy levels 1st Energy Level Holds 2nd Energy Level Holds 3rd Energy Level Holds 2 Electrons 8 Electrons 8 Electrons Electrons arrangements of the 1st 20 elements are found on page 1 of the data booklet Elements with the same group have the same number of outer electrons e.g. Group 1 Alkali Metals Lithium Sodium Potassium 2,1 2,8,1 2,8,8,1 Elements with the same number of electrons in their outer shell have the same chemical properties Each element on the Periodic Table has its own atomic number - The atomic number is the number of protons The mass number of an atom is equal to the number of protons plus neutrons The number of protons, neutrons and electrons of neutral atoms can be calculated by the following: Isotopes are atoms of the same element which have: - the same atomic number but a different mass numbers - the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons Most elements have more than on isotope Relative atomic mass is the average atomic mass of all the isotopes of an element - RAM is rarely a whole number because it an average e.g. the RAM of chlorine is 35.5 - The two chlorine isotopes are 35Cl and 37Cl As RAM is closer to 35 than 37 there must be more 35Cl atoms in sample than 37Cl atoms Compounds are formed when elements react together. - 2 or more different elements chemically joined together by bonds 1 A mixture occurs when two or more substances come together without reacting Compounds can be named using the following rules: Name Ending Meaning Contains the two named elements in the compound name -ide -ate -ite Contains the two named elements in the compound plus oxygen Contains the two named elements in the compound plus oxygen Examples of the elements found in compounds: Compound Elements in Compound Sodium Chloride Sodium + Chlorine Copper Sulphate Copper + Sulphur + Oxygen Potassium Nitrite Potassium + Nitrogen + Oxygen Atoms can be held together by bonds to form molecules - atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron arrangement A covalent bond is the attraction of the shared pair of the electrons for both nuclei in nonmetal elements A molecule is a group of atoms held together by covalent bonds a diatomic molecule is made up of two atoms: 2