04 - Waves at Boundaries Key
advertisement
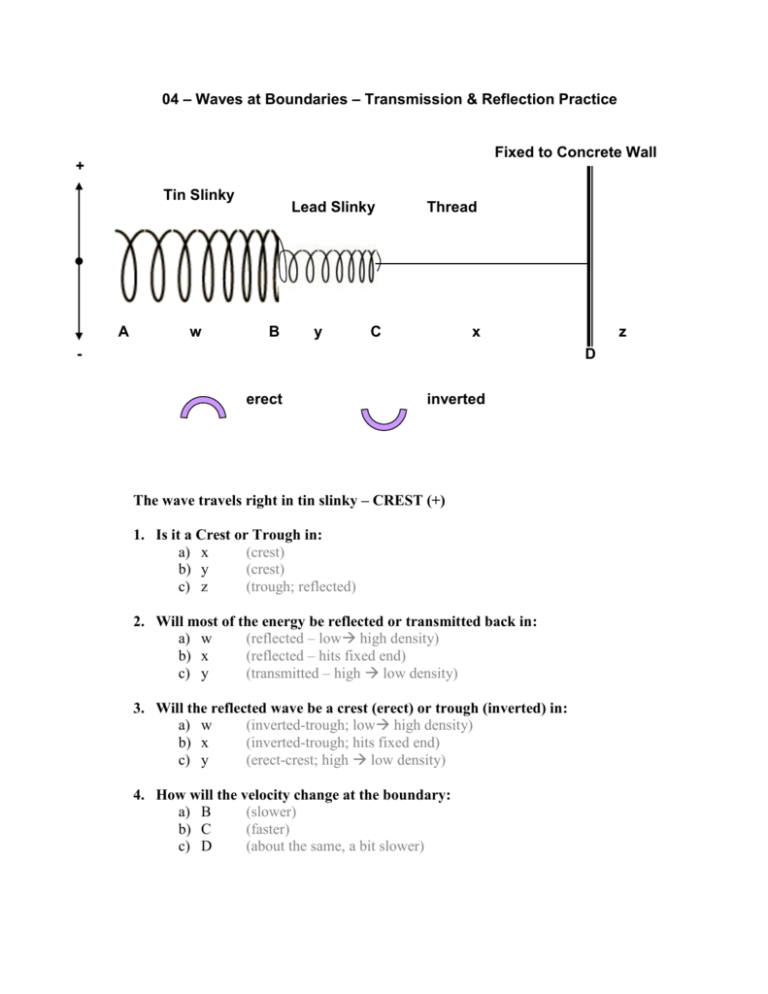
04 – Waves at Boundaries – Transmission & Reflection Practice Fixed to Concrete Wall + Tin Slinky A w Lead Slinky B y Thread C x - z D erect inverted The wave travels right in tin slinky – CREST (+) 1. Is it a Crest or Trough in: a) x (crest) b) y (crest) c) z (trough; reflected) 2. Will most of the energy be reflected or transmitted back in: a) w (reflected – low high density) b) x (reflected – hits fixed end) c) y (transmitted – high low density) 3. Will the reflected wave be a crest (erect) or trough (inverted) in: a) w (inverted-trough; low high density) b) x (inverted-trough; hits fixed end) c) y (erect-crest; high low density) 4. How will the velocity change at the boundary: a) B (slower) b) C (faster) c) D (about the same, a bit slower) 5. A wave has a length of 30.0 cm and a velocity of 2.5 cm/s. If it has a velocity of 3.70 cm/s when it enters a new medium, what is the wavelength? 44cm 6. A wave is 2.30 m long before transmission. After transmission, it is travelling at 5.26 m/s with a wavelength of 1.75 m. What is the velocity of the wave before transmission? 6.91m/s 7. A wave has a velocity of 4.00 m/s before transmission. How fast will it be going in the new medium if its new wavelength is tripled? 12.0m/s 8. The frequency and wavelength of a transmitted wave is 25 Hz and 2.00 cm, respectively. If the initial wave had a wavelength of 1.75 cm, what is the initial velocity? 44cm/s 9. A transmitted wave with a length of 2.00 m can travel 75.0 m in 30.0 s. If the wave was travelling at 3.00 m/s in the initial medium, what was the wavelength? 2.40m